When it comes to choosing the right material for knife making, the battle between 440C and 3Cr13 stainless steel is a frequent topic of debate among enthusiasts and professionals alike. Both materials boast impressive qualities, but what sets them apart? In this comprehensive comparison, we delve into the distinct properties, strengths, and weaknesses of each type of stainless steel. Whether you’re a seasoned knife maker or a hobbyist aiming to create the perfect blade, understanding the nuances of 440C and 3Cr13 stainless steel is crucial. Are you ready to discover which material reigns supreme for your next knife-making project? Let’s dive in and explore the differences that could make or break your blade.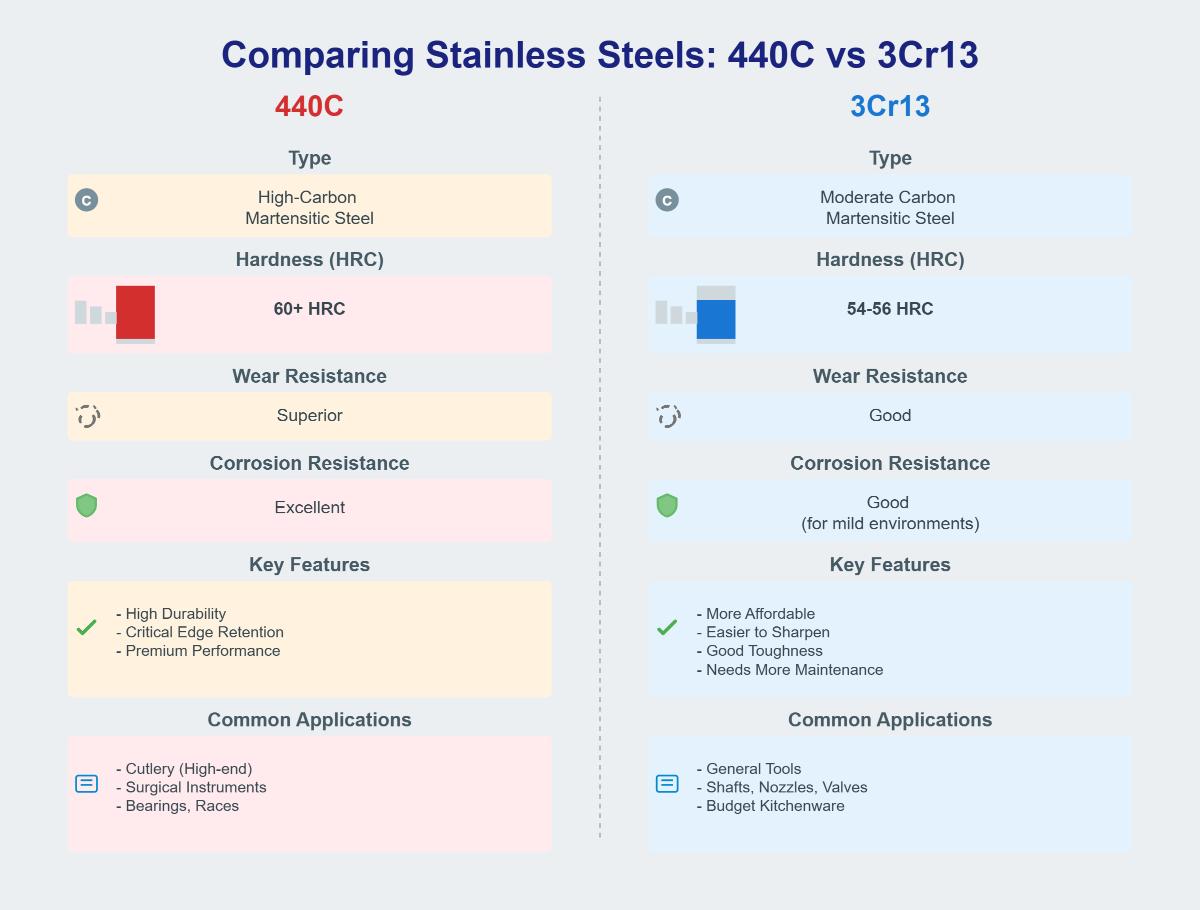
Stainless steel is highly valued in knife making due to its excellent resistance to corrosion and its ability to maintain a sharp edge. These properties are essential for knives, which often come into contact with moisture, acidic substances, and other corrosive elements. The choice of stainless steel affects the knife’s performance, longevity, and maintenance requirements.
Stainless steels used in knife making are primarily martensitic, known for their ability to be heat-treated for hardness and sharpness. Among the many stainless steels available, 440C and 3Cr13 are two commonly used grades, each with distinct characteristics.
440C stainless steel is a high-carbon, high-chromium alloy that provides an excellent balance of hardness and corrosion resistance. With a carbon content of approximately 1.0–1.2%, 440C can achieve a high level of hardness, making it ideal for applications where edge retention is critical, while its chromium content, typically around 16–18%, ensures strong resistance to rust and staining.
3Cr13 stainless steel, a Chinese grade, contains about 0.3% carbon and 13% chromium. This lower carbon content compared to 440C results in reduced hardness but offers greater ductility and ease of sharpening. While it provides decent corrosion resistance, it is generally less durable than 440C.
When selecting stainless steel for knife making, several performance factors must be considered:
Heat treatment is a critical process for optimizing the properties of stainless steel in knife making. Martensitic stainless steels like 440C and 3Cr13 undergo austenitizing, quenching, and tempering processes to achieve the desired hardness and toughness.
Comparing 440C and 3Cr13 helps determine which is best for different knife uses:
Understanding these differences allows knife makers and users to choose the right stainless steel based on the intended use and performance requirements.
440C stainless steel is a high-carbon steel known for its hardness, strength, and wear resistance. Its composition includes:
The high carbon content boosts hardness and strength, while chromium adds moderate corrosion and excellent wear resistance.
After heat treatment, 440C stainless steel typically reaches a hardness of 58 to 60 HRC, making it ideal for applications needing superior edge retention and wear resistance. Its mechanical properties vary with heat treatment and typically include:
440C stainless steel offers good corrosion resistance, moderate compared to austenitic stainless steels. The high chromium content helps resist rust and staining, making it suitable for environments where moderate corrosion resistance is necessary.
Due to its high hardness, 440C stainless steel is challenging to machine and requires precise heat treatment to reach its full potential. Key considerations for machining 440C include:
Knowing these properties helps in choosing 440C stainless steel for specific uses, especially in knife making where edge retention and durability are essential.
3Cr13 stainless steel, a martensitic grade, is known for its balance of mechanical properties and affordability. It consists of the following elements:
The moderate carbon content ensures a good balance between hardness and toughness, while the chromium provides essential corrosion resistance.
3Cr13 stainless steel, heat-treated to achieve a hardness of around 54-56 HRC, is suitable for applications requiring moderate wear resistance and strength, with mechanical properties such as:
These characteristics demonstrate 3Cr13’s reliability under stress, making it suitable for various applications.
3Cr13 stainless steel has good corrosion resistance in mild environments like dilute nitric acid and weak organic acids at room temperature. It performs better than lower chromium steels like 410 and 420J1 but does not match the superior corrosion resistance of higher-grade stainless steels such as 440C. This makes it suitable for applications where moderate corrosion resistance is sufficient.
3Cr13 is relatively easier to machine compared to higher carbon stainless steels like 440C. Its moderate hardness allows for simpler machining processes, making it a preferred choice for mass production and budget-friendly applications. Key aspects of machining 3Cr13 include:
3Cr13 stainless steel is known for its ease of sharpening and good edge retention. It is resistant to chipping and breaking, which is crucial for blade applications. This property makes 3Cr13 practical for knives that require frequent maintenance and sharpening.
While 3Cr13 provides a balanced combination of mechanical properties and cost-effectiveness, 440C stainless steel offers higher hardness and superior wear resistance due to its higher carbon content. The comparison includes:
Choose 3Cr13 for affordable, easy-to-maintain tools, and 440C for high-performance applications needing maximum hardness and wear resistance.
Knife makers favor 440C stainless steel for its outstanding hardness, wear resistance, and edge retention. These properties make 440C stainless steel ideal for high-performance applications, especially in tactical and outdoor knives where durability and sharpness are paramount. Its high hardness (58-60 HRC) ensures the knife withstands heavy use and stays sharp longer. This makes it suitable for survival situations, hunting, and military applications.
440C stainless steel is ideal for precise and clean cuts, making it a top choice for culinary and surgical tools. Its ability to achieve a razor-sharp edge and maintain it under continuous use is crucial for tasks that demand accuracy and reliability.
Knife collectors and enthusiasts often prefer 440C stainless steel for custom and collectible knives. The steel’s superior polishability and resistance to corrosion ensure that these knives not only perform well but also maintain their aesthetic appeal over time.
3Cr13 stainless steel balances affordability, ease of sharpening, and decent performance, making it suitable for applications prioritizing cost-effectiveness and moderate durability over maximum hardness.
3Cr13 stainless steel is frequently used in kitchen knives due to its moderate hardness (54-56 HRC) and ease of sharpening. These properties make it practical for everyday use in food preparation, where knives must be sharp but also easy to maintain. The steel’s good corrosion resistance ensures longevity even with frequent exposure to moisture and acidic food.
For general-purpose knives that see varied use, 3Cr13 stainless steel offers a good balance of toughness and ease of maintenance. These knives are ideal for tasks such as cutting ropes, opening packages, and other daily chores. The moderate hardness allows for quick resharpening, ensuring the knife remains functional without requiring specialized tools or techniques.
In scenarios where cost is a significant consideration, such as mass production or entry-level knives, 3Cr13 stainless steel is an excellent choice. Its lower production costs and satisfactory performance make it suitable for budget-conscious consumers and large-scale manufacturing.
Both 440C and 3Cr13 stainless steels serve distinct purposes in knife making, catering to different needs based on performance requirements, cost considerations, and ease of maintenance. The choice between these materials ultimately depends on the specific application and user preferences.
The chemical composition of stainless steel significantly affects its properties and applications.
3Cr13 stainless steel contains approximately 0.26–0.35% carbon and 12–14% chromium, providing balanced hardness, toughness, and essential corrosion resistance. With 0.95–1.20% carbon and 16–18% chromium, 440C is harder and more wear-resistant, making it ideal for applications needing superior edge retention and durability.
440C’s higher carbon content results in greater hardness (58-60 HRC) and wear resistance compared to 3Cr13 (52-56 HRC). This makes 440C more suitable for applications requiring long-lasting edge retention.
3Cr13, being softer and tougher, resists impact better and is less prone to brittleness. It is easier to sharpen and maintain, making it practical for general-purpose knives.
While 3Cr13 has moderate corrosion resistance suitable for general outdoor and kitchen applications, 440C’s higher chromium content generally provides superior protection in demanding environments.
The choice between 3Cr13 and 440C stainless steels depends on the intended application.
3Cr13 is used widely in budget-friendly knives, general-purpose cutting tools, and applications where ease of sharpening and toughness are prioritized. It is suitable for users who require reliable performance with regular maintenance and resharpening. Additionally, it is favored in manufacturing processes requiring easier machining and cost efficiency.
440C is preferred for high-performance knives, surgical instruments, and tactical or outdoor knives where edge retention and hardness are critical. It is more appropriate for demanding environments requiring superior wear resistance and corrosion protection, despite the higher cost and machining difficulty.
When comparing 440C and 3Cr13 stainless steel, it is essential to understand their composition standards, as these determine their properties and best uses.
440C stainless steel typically conforms to ASTM A276 standards. With a higher carbon content (0.95-1.2%) and chromium (16-18%), it achieves excellent hardness and wear resistance. These attributes make 440C well-suited for demanding applications such as premium cutlery and surgical instruments, where high performance and durability are required.
3Cr13 stainless steel follows Chinese standards and has a lower carbon content (about 0.3%) with approximately 13% chromium. This composition makes 3Cr13 a cost-effective option for general-purpose applications, offering a balance of affordability and performance.
The mechanical properties of 440C and 3Cr13 stainless steels, governed by different standards, reflect their suitability for various applications, with 440C known for its high hardness ranging from 58-60 HRC after heat treatment. This high hardness ensures exceptional edge retention and wear resistance, which is crucial for precision cutting tools. However, this also introduces brittleness, requiring careful handling during machining to prevent fracturing.
3Cr13 delivers better toughness and ease of sharpening, with hardness typically between 52-56 HRC. This makes 3Cr13 particularly effective for budget-friendly knives and tools that require regular maintenance, as it can be sharpened without specialized equipment while still delivering practical day-to-day performance.
Corrosion resistance is a defining characteristic for stainless steels, especially where exposure to moisture or chemicals is expected.
Even with higher chromium, 440C is less corrosion-resistant than 3Cr13 because of its higher carbon content. As a result, 440C is most suitable for environments where moderate corrosion resistance is acceptable and where the advantages of superior hardness and wear resistance are prioritized.
3Cr13 offers better resistance to corrosion, especially in moist environments. The lower carbon content helps guard against rust and staining, making it an ideal choice for consumer products and general applications that face regular exposure to moisture.
Both 440C and 3Cr13 stainless steels must meet relevant industry standards and hold appropriate certifications for their intended uses.
440C is often certified for food-grade and medical uses, where durability and edge retention are essential. Stringent certification ensures that 440C complies with the high safety and performance demands of these sensitive applications.
3Cr13 is often certified for general consumer products, highlighting its affordability and easy maintenance. These certifications guarantee 3Cr13 meets the necessary standards for everyday utility items, offering reliable performance at a lower cost.
Choosing between 440C and 3Cr13 stainless steel typically depends on the specific application and regulatory requirements.
440C is preferred for high-performance uses requiring excellent edge retention and wear resistance, such as tactical knives and surgical tools. Its certifications attest to its reliability in demanding situations where consistent quality and durability are essential.
3Cr13 is suitable for general-purpose knives and tools, where cost, ease of sharpening, and moderate performance are priorities. Certifications for 3Cr13 ensure it fulfills the requirements for day-to-day use, providing a practical solution for value-conscious users.
Knowing the standards and certifications of 440C and 3Cr13 helps manufacturers and consumers choose the right material, ensuring performance and industry compliance.
The practical applications of 440C and 3Cr13 stainless steels are heavily influenced by their distinct material compositions and properties. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate steel for specific knife-making applications.
| Property | 3Cr13 Stainless Steel | 440C Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Content | ~0.3% | 0.95-1.20% |
| Chromium Content | 12-14% | 16-18% |
| Hardness (HRC) | 52-56 | 58-60 |
| Wear Resistance | Moderate (suitable for general use) | High |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Toughness | High (more impact resistant) | Lower (more brittle) |
| Machinability | Easier | Challenging |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
High-Performance Cutting Tools and Blades: The superior hardness (58-60 HRC) and excellent edge retention of 440C make it a preferred choice for premium knives, tactical blades, and surgical instruments. Its high corrosion resistance makes it ideal for use in moist or chemically exposed environments.
Wear-Resistant Components: Due to its high wear resistance, 440C is suitable for mechanical parts such as bearings and valve components, which are subject to constant friction and wear.
Challenges in Manufacturing: 440C’s brittleness and hardness make machining difficult, requiring specialized CNC equipment. This increases production costs and complexity, necessitating careful handling to avoid cracking.
General-Purpose Knives and Tools: Its moderate hardness (52-56 HRC) and higher toughness make 3Cr13 perfect for budget-friendly knives, kitchen cutlery, and everyday tools. Its ease of sharpening and impact resistance make it practical for frequent use.
Ease of Machining and Sharpening: The lower hardness of 3Cr13 allows faster CNC machining with less tool wear, reducing manufacturing costs. This makes it attractive for mass production, where frequent resharpening is acceptable.
Better Corrosion Resistance in Mild Environments: Although less corrosion resistant than 440C, 3Cr13 performs well in typical indoor or light outdoor applications, providing adequate protection against rust and staining.
Outdoor and Tactical Knives: 440C excels in tactical knives designed for heavy-duty outdoor use. Its edge retention and corrosion resistance ensure reliability in harsh conditions like wet or abrasive environments. However, 440C’s brittleness means it must be handled carefully to avoid chipping.
Kitchen and Everyday Cutlery: 3Cr13 is commonly used in kitchen knives and budget blades where frequent sharpening is not a drawback. Its toughness helps resist chipping from typical household use, and easier sharpening suits users without professional sharpening tools.
Mass Production vs. Specialty Manufacturing: Manufacturers often select 3Cr13 for large-scale production knives due to its machinability and lower cost. Conversely, luxury or specialized knives use 440C to justify higher price points with superior performance.
Mechanical Components: The wear resistance of 440C has led to its successful use in bearings and precision parts, where 3Cr13’s lower hardness would be inadequate.
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
When comparing 440C and 3Cr13 stainless steels, several key differences emerge in their composition, properties, and applications.
440C is a high-carbon martensitic stainless steel known for its superior hardness and wear resistance, typically achieving a hardness of 60 HRC or higher. It also offers excellent corrosion resistance due to its higher chromium content. This makes 440C suitable for high-wear applications such as cutlery, surgical instruments, and bearings, where durability and edge retention are critical.
On the other hand, 3Cr13 is also a martensitic stainless steel but with moderate carbon content, leading to a lower hardness range of 54-56 HRC. While it provides good corrosion resistance, it is more suited to mild environments. 3Cr13 is commonly used in applications requiring moderate hardness and corrosion resistance, such as tools, shafts, nozzles, and valves. It is more affordable and easier to sharpen, though it may require more frequent maintenance compared to 440C.
When deciding which stainless steel is better for making knives, 440C or 3Cr13, it depends on the specific needs and preferences of the user.
440C stainless steel is superior in terms of hardness, edge retention, and wear resistance due to its higher carbon content, typically reaching Rockwell hardness values of 58–60 HRC. This makes it ideal for heavy-duty or professional applications where long-lasting sharpness is crucial, such as in tactical, outdoor, or high-end kitchen knives. However, 440C is more brittle and challenging to sharpen, requiring more careful handling and advanced sharpening tools.
On the other hand, 3Cr13 stainless steel, with a lower carbon content and hardness (around 50–55 HRC), offers better toughness and is easier to sharpen. This makes it more suitable for general-purpose, budget-friendly knives where ease of maintenance and cost-effectiveness are priorities. 3Cr13 is less prone to chipping and cracking, making it a practical choice for everyday carry knives or for users who prefer frequent, simple maintenance.
440C stainless steel exhibits higher corrosion resistance compared to 3Cr13 stainless steel. This is primarily due to its higher chromium content, typically between 16% to 18%, which forms a more robust protective chromium oxide layer on the surface. This layer is more effective in preventing rust and withstands exposure to moisture, mild chemicals, and humid environments better than 3Cr13. In contrast, 3Cr13 contains approximately 12% to 14% chromium, resulting in a less stable oxide layer that provides moderate corrosion resistance, suitable for less aggressive environments. Consequently, 440C is preferable for applications requiring superior corrosion resistance, such as premium cutlery and outdoor tools, whereas 3Cr13 is more commonly used in budget knives and general-purpose tools where ease of maintenance is prioritized.
Machining challenges associated with 440C and 3Cr13 stainless steels mainly stem from their differing hardness and toughness. 440C stainless steel has a high hardness range of 58–60 HRC due to its higher carbon and chromium content, which results in significant tool wear and requires the use of robust, expensive cutting tools such as carbide or ceramic. This material’s brittleness also increases the risk of cracking or chipping during machining, necessitating careful control of machining parameters like feed rate and cutting speed to prevent damage. Consequently, machining 440C is slower and more costly, but it yields parts with excellent wear resistance and durability.
On the other hand, 3Cr13 stainless steel has a lower hardness range of 52–56 HRC and higher toughness, making it easier to machine. Its softer nature reduces tool wear and allows for faster machining speeds without compromising tool life. The material’s better ductility and toughness minimize the risk of cracking or chipping, making it more forgiving during aggressive machining processes. This translates into lower tooling costs and shorter production times, making 3Cr13 suitable for general-purpose tools and budget-friendly knives where extreme hardness is not critical.
In the context of knife making, there are no specific standards or certifications for the materials 440C and 3Cr13 stainless steel themselves. However, the American Bladesmith Society (ABS) provides certifications such as Journeyman Smith and Master Smith that focus on the overall craftsmanship, performance, and quality of knives, indirectly reflecting the quality of the materials used. These certifications ensure that the knives meet high standards of fit, finish, and durability, which can be influenced by the choice of steel. While 440C is known for its high hardness and excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for high-performance knives, 3Cr13 is more affordable and commonly used in budget-friendly options. The selection between these materials should be based on the intended use and budget considerations.
Although 440C and 3Cr13 stainless steels can technically be used to make knives, they are not interchangeable due to their distinct properties and performance characteristics.
440C stainless steel has a higher carbon content (around 1.0–1.2%), resulting in greater hardness (58-60 HRC), superior wear resistance, and excellent edge retention. These attributes make it ideal for high-performance, tactical, or outdoor knives that require long-lasting sharpness and durability. However, it is more challenging to machine and less corrosion-resistant compared to 3Cr13.
On the other hand, 3Cr13 stainless steel, with lower carbon content (approximately 0.3%), achieves a softer hardness (54-56 HRC). It offers better corrosion resistance and is easier to machine, making it cost-effective for manufacturing. 3Cr13 is suitable for budget-friendly, everyday knives where ease of maintenance and frequent resharpening are acceptable.

