Imagine a sudden leak in your underground plumbing system – the water is gushing, and you have no idea how to stop it. The solution lies in a simple but often overlooked component: the underground water shut-off valve. These crucial devices come in various types, each with unique features and applications tailored to different needs. Whether you’re a homeowner looking to safeguard your property or a plumber seeking reliable solutions, understanding the different types of underground water shut-off valves can make all the difference. But how do you choose the right one, and what are the key considerations for installation and maintenance? Dive into the world of underground valves and uncover the essentials that keep your water systems running smoothly and securely.
Underground water shut-off valves are vital components of water systems, enabling efficient control of water flow while remaining protected beneath the surface. These valves are installed below ground level, commonly housed in valve boxes or meter pits, to protect them from external environmental factors such as extreme weather and accidental damage. They serve as a critical interface between the main water supply line and the distribution network, ensuring efficient and reliable water management.
Underground shut-off valves are indispensable for controlling water flow and regulating pressure, ensuring safe and efficient operation during emergencies, repairs, or routine maintenance. By isolating sections of the plumbing network, these valves help minimize disruptions and ensure efficient operation. Maintaining proper water pressure is crucial to prevent damage to pipes and fixtures, and these valves assist in regulating pressure within the plumbing system, providing a consistent and safe water supply for residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
Built from durable materials, underground shut-off valves resist corrosion and wear, staying protected from harsh weather conditions to ensure long-term reliability. Their installation below ground shields them from extreme environmental conditions, reducing the risk of damage and extending their lifespan.
In addition to residential and commercial plumbing, underground water shut-off valves are widely used in irrigation systems. They help manage water distribution efficiently, ensuring optimal performance for agricultural, landscaping, and outdoor watering needs.
Installing shut-off valves underground keeps your space uncluttered, safeguards the valves from tampering, and protects them from damage caused by freezing or UV exposure. This underground placement eliminates the need for additional surface-level hardware, keeping the area tidy and unobstructed while enhancing the safety and durability of the valves.
When selecting and installing an underground water shut-off valve, it is important to consider factors such as compatibility with the existing piping material, the required flow rate, and the specific application. Proper selection ensures optimal performance and reliability, whether the valve is used for residential plumbing, irrigation systems, or industrial water management.
By combining durability, efficiency, and protection, underground water shut-off valves are a cornerstone of modern water management systems.
Ball valves are popular in underground water systems because they are durable, reliable, and easy to use. These valves feature a spherical disc with a hole through the center, controlling the flow of water. When the handle is turned 90 degrees, the ball rotates to either allow or block water flow.
Gate valves, traditional shut-off valves, control water flow by raising or lowering a gate, but they are only effective in fully open or closed positions.
Angled fixture valves, or angle stop valves, are designed to control water flow at a 90-degree angle. These valves are compact and ideal for tight spaces.
Electric diaphragm valves use electricity to automate water flow control, making them ideal for modern underground systems. The valve’s operation is controlled by a diaphragm that opens or closes based on electrical signals.
Butterfly valves are lightweight, compact, and operate quickly using a rotating disc controlled by a lever or gear.
The choice of an underground water shut-off valve depends on several factors, including the specific application, water pressure requirements, ease of access, and long-term maintenance needs. Ball valves are favored for their reliability and ease of use, while electric diaphragm valves are ideal for advanced, automated systems. Gate valves and angled fixture valves are suited for specific use cases where traditional or localized control is required.
Underground water shut-off valves benefit significantly from their placement below the surface, where they are shielded from harsh weather conditions such as freezing temperatures, heavy rainfall, and UV radiation. This protection prevents damage and ensures the valve remains reliable over the long term. Additionally, underground placement reduces the risk of corrosion and wear, which are common issues for valves exposed to external elements.
By being installed underground, these valves reduce the risk of accidental tampering or damage. In emergency situations, such as a burst pipe or water leakage, they allow quick and effective isolation of the affected area, minimizing water damage to nearby structures. Their concealed location also prevents unauthorized access, adding an extra layer of security to water management systems.
Underground water shut-off valves offer a streamlined solution for properties where space is limited. Since the valves are installed below ground, they eliminate the need for bulky hardware above the surface, keeping the area uncluttered. This design is especially advantageous for urban environments, residential properties, and commercial spaces where maximizing available space is a priority.
These valves play a crucial role in managing water flow effectively, helping to prevent flooding and erosion in vulnerable areas. By controlling water distribution, they prevent excess water buildup, which is crucial for irrigation and uneven terrain.
Underground shut-off valves contribute to water conservation efforts by allowing precise regulation of water flow. This ensures water is used only when needed, reducing waste and improving efficiency. For applications such as irrigation systems, this precise control is essential for maintaining optimal water usage without over-saturating the soil.
Constructed from robust materials designed to withstand underground conditions, these valves are highly durable and require minimal maintenance. Their resistance to soil pressure and moisture gives them a longer lifespan than surface-mounted valves, making them a cost-effective choice for long-term water management.
In the event of a water system failure, such as a burst pipe, underground shut-off valves enable rapid isolation of the problem area. This quick action minimizes damage to infrastructure and property, reducing repair costs and downtime. Their reliability during emergencies makes them an indispensable component in modern plumbing systems.
Modern underground valves, such as electric diaphragm valves, offer enhanced functionality by integrating automation and remote control capabilities. These features allow precise water flow management without manual intervention, making them ideal for smart water systems and large-scale applications.
Proper planning and preparation are essential for the successful installation of underground water shut-off valves. Start by identifying the main water line and locating the appropriate spot for the valve installation. Ensure you have all necessary tools and materials on hand to avoid interruptions during the process.
After the valve is installed, it’s time to reconnect the supply lines and test for leaks.
Proper planning, careful execution, and regular testing are key to successfully installing underground water shut-off valves. By following these steps and addressing common challenges, you can ensure a reliable and efficient water management system.
Regular inspections are essential to keep underground water shut-off valves working efficiently and lasting longer. Conduct visual checks for signs of damage, corrosion, or mineral buildup. Test the valves by turning them off and on to ensure they function properly. Exercising the valves periodically helps prevent seizing and ensures they can be operated effectively during emergencies.
Corrosion and mineral deposits can prevent the valve from working properly. Clean the valves using a small brush and soapy water to remove dirt and corrosion. Dry the valves thoroughly and apply lubricant to reduce friction and prevent future buildup.
Valves that are not used frequently can seize due to mineral buildup or corrosion. When operating older valves, especially gate valves, turn handles slowly and avoid excessive force. Regularly exercising these valves can prevent seizing and ensure they remain functional.
Regularly inspect components such as seals and gaskets for wear and tear. Promptly replace any worn-out parts to prevent leaks and ensure the valve operates correctly. Keeping spare components on hand can expedite repairs.
Ensure that all shut-off valves are easily accessible. Clear any obstructions that might hinder access in case of an emergency. Maintaining a clear space around the valves facilitates quicker maintenance and repairs.
For complex maintenance tasks or if you encounter persistent issues, consider hiring professional maintenance services. Professionals can thoroughly inspect, repair, and ensure your valves meet industry standards, giving you peace of mind. Professional services are particularly valuable for large-scale or commercial systems where reliability is paramount.
Follow the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule to make your valves last longer and avoid expensive repairs. Regular maintenance according to the manufacturer’s schedule ensures optimal performance and reliability.
By following these maintenance tips, you can ensure that your underground water shut-off valves function effectively, reducing the risk of leaks and water damage during emergencies.
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
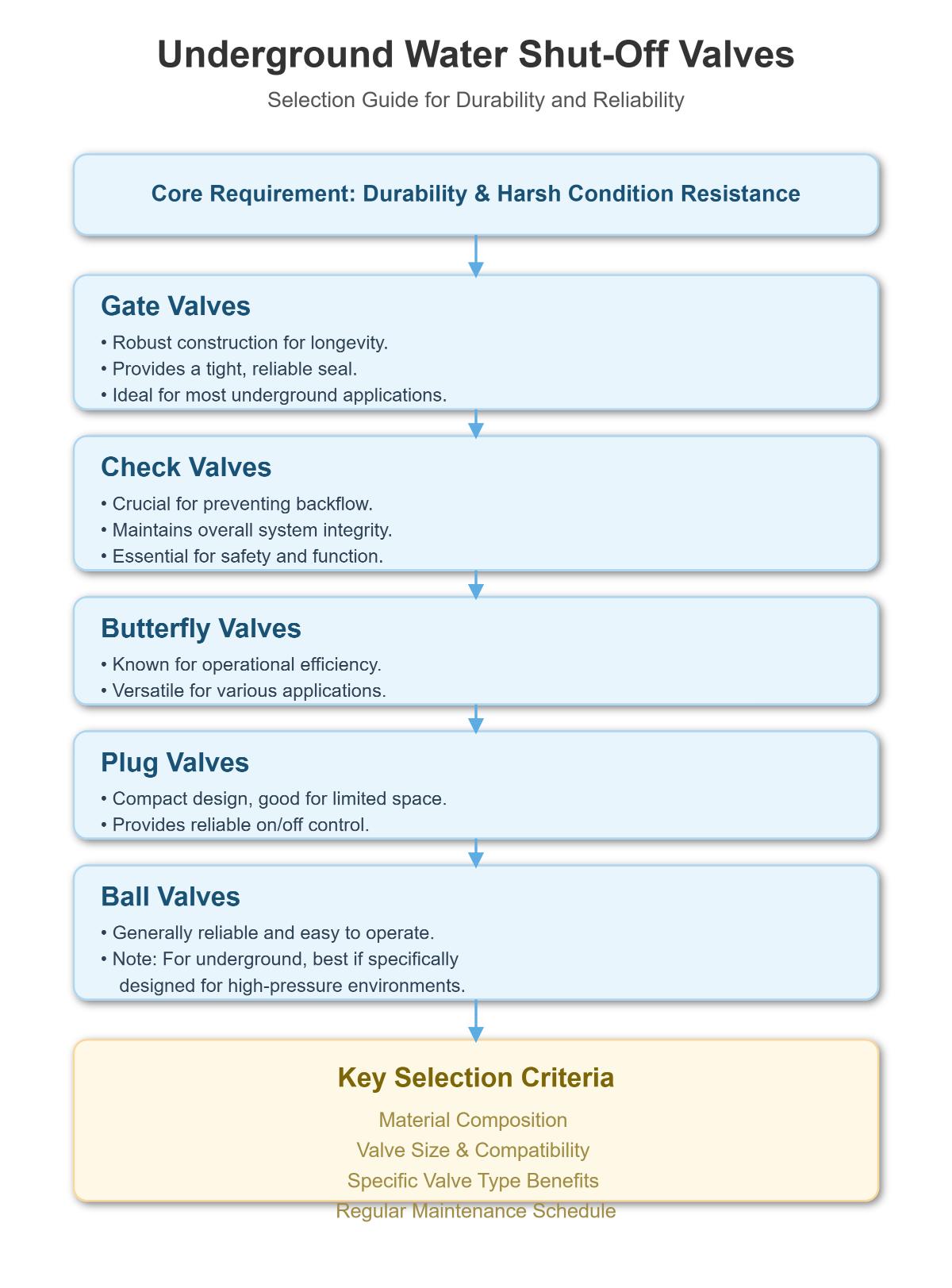
Several types of water shut-off valves are suitable for underground installations due to their durability and ability to withstand harsh conditions. Gate valves are robust and provide a tight seal, making them ideal for underground applications. Check valves are crucial for preventing backflow and maintaining system integrity. Butterfly valves offer efficiency and versatility, while plug valves are compact and provide reliable on/off control. Ball valves are reliable and easy to operate, though they may not be the first choice for all underground systems unless designed for high-pressure environments. Material, size, type, and regular maintenance are key considerations for selecting the appropriate valve.
To correctly install an underground water shut-off valve, begin by selecting a reliable valve type, such as a ball valve or gate valve, made from durable materials like brass or stainless steel. Shut off the main water supply and drain the system by opening faucets. Excavate a hole for the valve box, ensuring it is deep enough for insulation and protection from elements. Connect the valve securely to the piping using appropriate fittings. Reconnect the water supply and check for leaks. Regular inspection and maintenance are essential to ensure the valve’s longevity and functionality.
To install underground water shut-off valves, you will need tools such as an adjustable wrench, pipe wrench, pipe cutters, deburring tool, crimping tool, and Teflon tape or pipe dope. Essential materials include a new shut-off valve, PVC or copper pipes, insulation materials, trenching equipment, and cement or concrete. Ensure the valve type and size are compatible with your plumbing system, and use corrosion-resistant materials for durability. Follow steps to shut off the water supply, drain the system, access the pipes, replace the old valve, install the new valve, reconnect supply lines, and test for leaks.
Yes, using a ball valve for underground water systems is advisable due to its quick shut-off capability, durability, and low maintenance requirements. Ball valves operate with a simple quarter-turn mechanism, making them ideal for emergencies or routine maintenance. Their resistance to corrosion and wear ensures reliable performance in underground environments, provided the valve is made from appropriate materials like brass or stainless steel. Additionally, selecting a ball valve with suitable pressure ratings and considering pre-insulated options for temperature control enhances functionality. Overall, ball valves are a practical choice for underground applications, combining efficiency and resilience.
Electric diaphragm valves offer several benefits for underground usage, including precise flow control and pressure regulation, which ensure consistent water supply and prevent pipe damage. They require low maintenance, making them ideal for challenging underground access, and their corrosion-resistant materials enhance durability. These valves allow safe isolation for maintenance and are compatible with various fluids. Additionally, they can be integrated into automation systems for remote control and monitoring, and their gradual opening and closing mechanism helps reduce water hammer, protecting underground pipelines. Overall, they enhance operational efficiency and reliability in water management systems.
Underground water shut-off valves should be inspected and maintained at least annually to ensure optimal performance and prevent issues such as leaks, corrosion, and wear. Regular checks help identify potential problems early, ensuring reliable operation, especially in emergencies. Signs indicating the need for replacement include aging infrastructure, frequent leaks, regular repairs, and difficulty operating the valve. Professional inspections by a licensed plumber are advisable for thorough assessment and maintenance. This preventive approach can extend the lifespan of the valves and ensure the efficiency of the home’s plumbing system.

