When it comes to selecting the right stainless steel for your project, understanding the nuances between different ASTM standards is crucial. ASTM A240 and ASTM A276 are two widely recognized specifications, each serving distinct roles in engineering and manufacturing. If you’ve ever wondered how these materials differ in terms of mechanical properties, applications, and cost-efficiency, you’re not alone. This article delves into the key differences between ASTM A240 and A276, providing you with the insights needed to make an informed choice. So, which material is best suited for your specific needs? Let’s explore the comparative details that set these standards apart.
ASTM standards are essential in engineering and manufacturing, offering guidelines and specifications that ensure material quality, safety, and performance. Developed by ASTM International, these standards cover a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and textiles, and are used globally to maintain consistency in material properties and testing methods.
ASTM standards play a vital role in various industries by ensuring that materials meet specific criteria for mechanical properties, chemical composition, and other essential characteristics. This uniformity helps engineers and manufacturers achieve reliable and predictable results, enhancing the safety and efficiency of their projects.
ASTM standards are categorized based on the type of material and its application. For example, standards for metals include specifications for steel, aluminum, and titanium, among others. Each category addresses different aspects of the material, such as its strength, hardness, and resistance to corrosion.
Mechanical properties and chemical composition are primary focuses of ASTM standards. Mechanical properties include tensile strength, yield strength, and elongation, which determine how a material behaves under different types of stress and strain. Chemical composition standards specify the exact elements and compounds that must be present in a material, ensuring it has the desired characteristics like corrosion resistance or thermal stability. For instance, stainless steel standards detail the required percentages of chromium and nickel to achieve optimal corrosion resistance. Accurate measurement and adherence to these properties ensure that materials can withstand the demands of their intended applications.
ASTM standards also define the testing methods used to evaluate materials. These methods include procedures for measuring mechanical properties, conducting chemical analyses, and assessing other critical features. Standardized testing methods enable precise comparisons across various materials and batches.
ASTM standards address the unique material requirements of various industries, ensuring each sector’s specific needs are met. For example, the aerospace industry demands materials with high strength-to-weight ratios, while the medical field requires biocompatible materials. ASTM standards help ensure that materials used in these industries meet the necessary requirements.
ASTM standards are widely adopted around the world, making them a cornerstone of international trade and manufacturing. Their global acceptance ensures that materials sourced from different countries meet the same rigorous standards, facilitating smoother collaboration and integration in international projects.
While ASTM International is a leading standards organization, there are other entities like ISO (International Organization for Standardization) and DIN (German Institute for Standardization) that also develop standards. Comparing these organizations, ASTM standards are often more specific and detailed, particularly in the context of material properties and testing methods. This specificity makes ASTM standards highly valuable in industries where precision and reliability are paramount.
The benefits of adhering to ASTM standards are numerous. They provide a clear framework for material selection, ensuring that engineers and manufacturers can choose the best materials for their projects. Additionally, ASTM standards help reduce the risk of material failure, enhance product quality, and improve overall safety and reliability.
ASTM A240 is a standard from ASTM International detailing requirements for various types of stainless steel plates, sheets, and strips. These materials are designed for use in pressure vessels and for general applications, including architectural, construction, and aesthetic purposes.
ASTM A240 specifies the chemical composition and mechanical properties for various stainless steel grades. These properties are critical in determining the suitability of the materials for specific applications.
The standard includes detailed requirements for the chemical composition of stainless steel grades. For instance, it specifies the minimum and maximum percentages of elements such as chromium, nickel, manganese, silicon, and carbon. These specifications ensure the material has the required corrosion resistance and mechanical strength.
ASTM A240 outlines the necessary mechanical properties for stainless steel, such as:
These properties are crucial for ensuring that the material performs reliably under various conditions.
Due to their excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical properties, ASTM A240 stainless steels are used in various applications such as:
ASTM A240 covers various grades of stainless steel, each suited for specific needs. Notable grades include:
ASTM A276 is a standard that specifies the requirements for hot-finished or cold-finished stainless steel bars used in various shapes and applications. These bars are available in rounds, squares, hexagons, and other shapes like angles, tees, and channels. They are essential in industries requiring high mechanical strength and corrosion resistance, such as marine, food processing, and surgical instruments.
The chemical composition includes elements like chromium, nickel, and molybdenum, which enhance the material’s corrosion resistance and strength. Each grade of stainless steel under ASTM A276 has specific requirements for these elements to ensure consistent performance.
ASTM A276 specifies different conditions like annealed (Condition A), hardened and tempered (Conditions H and T), and cold worked (Conditions S and B). Each condition enhances specific mechanical properties such as strength and toughness:
These bars are perfect for marine environments due to their high corrosion resistance. They are widely used in food processing equipment, surgical instruments, and structural components, offering both reliability and durability in demanding conditions.
Tensile strength measures how well a material can resist being pulled apart. For ASTM A240 stainless steel, the tensile strength typically reaches around 150 ksi (1,000 psi per ksi), making it suitable for applications that require durability under stress. ASTM A276 stainless steel, especially in its hardened and tempered conditions, can achieve a higher tensile strength of approximately 185 ksi, offering enhanced performance in high-stress environments.
Yield strength is the stress level at which a material starts to deform permanently. ASTM A240 generally exhibits a yield strength of 115 ksi, which is sufficient for many structural and pressure vessel applications. In contrast, ASTM A276, with its higher yield strength of about 155 ksi, is better suited for applications that demand superior strength and minimal deformation under load.
Hardness indicates how well a material resists indentation. ASTM A240 stainless steels balance hardness and ductility to avoid brittleness and ensure good wear resistance. ASTM A276 stainless steels, particularly those in hardened conditions, offer higher hardness, making them ideal for cutting tools and applications requiring high wear resistance.
Corrosion resistance is a critical factor in selecting stainless steels for various environments. ASTM A240 stainless steels, such as grades 304 and 316, include high chromium and nickel content, providing excellent resistance to corrosion, especially in harsh environments like marine and chemical processing. ASTM A276 stainless steels also resist corrosion well, though their performance can vary based on the grade and heat treatment.
ASTM A240 stainless steels are well-suited for extreme conditions due to their high resistance to corrosion and ability to maintain mechanical properties at both high and low temperatures. This makes them ideal for applications like pressure vessels and heat exchangers in chemical processing plants.
ASTM A276, while also durable, may not perform as well in extreme environments compared to ASTM A240. However, its higher strength and hardness make it suitable for applications requiring high mechanical performance, such as structural components in marine and automotive industries.
Machinability refers to how easily a material can be cut into desired shapes. ASTM A276 stainless steels are generally easier to machine due to their specific composition and heat treatment processes. Adding elements like sulfur and phosphorus to some grades improves machinability. In contrast, ASTM A240 stainless steels, particularly those with higher alloy content, can be more challenging to machine, requiring specialized tooling and techniques.
Forming involves shaping materials into desired configurations through processes like bending, rolling, and forging. ASTM A240 stainless steels are typically more ductile and easier to form due to their balanced mechanical properties. ASTM A276 stainless steels, especially those in hardened conditions, can be more difficult to form without cracking or breaking.
Welding is a critical fabrication process for many stainless steel applications. ASTM A240 materials, with their higher nickel and chromium content, can be more challenging to weld, often requiring specific techniques and post-weld treatments to avoid issues like cracking and reduced corrosion resistance. ASTM A276 materials, especially those not heavily alloyed, can generally be welded using conventional methods with fewer complications.
The cost of stainless steel materials can vary significantly based on their composition, processing, and market demand. Generally, ASTM A276 stainless steels tend to be less expensive than ASTM A240 steels. This cost difference is primarily due to the simpler manufacturing processes and the lower alloy content in ASTM A276 steels.
When considering cost efficiency, it is essential to evaluate both the initial material cost and the total lifecycle cost. ASTM A240 stainless steels, with their superior corrosion resistance and durability, may offer better long-term value in applications where maintenance and replacement costs are high, such as in chemical processing and marine environments. ASTM A276 steels, being more affordable and easier to machine, are cost-efficient for applications requiring high strength and toughness, like automotive and structural components.
ASTM A240 stainless steel is ideal for pressure vessels due to its excellent mechanical strength and resistance to corrosion. These vessels are crucial in industries such as chemical processing and power generation, where they must withstand high pressures and corrosive environments. The high chromium and nickel content in ASTM A240 grades ensures longevity and reliability under extreme conditions.
The food processing industry demands materials that are both hygienic and durable, and ASTM A240 stainless steel grades like 304 and 316 offer exceptional corrosion resistance, making them ideal for equipment handling food products. Their ability to resist contamination and maintain cleanliness is crucial in preventing foodborne illnesses.
In the shipbuilding industry, materials must endure harsh marine environments. These plates and sheets provide the necessary corrosion resistance to saltwater, ensuring the structural integrity of ships. ASTM A240 stainless steel is particularly beneficial for constructing hulls, decks, and other critical components.
ASTM A276 stainless steel bars are commonly used in structural components due to their high tensile and yield strength. These properties make them ideal for constructing frameworks, supports, and reinforcements in various engineering projects. The availability of different shapes, such as rounds, squares, and hexagons, allows for versatile use in complex structures.
The automotive industry relies on materials that can withstand mechanical stress and corrosive environments. ASTM A276 stainless steel grades, such as 410 and 420, offer the necessary hardness and strength for components like drive shafts, exhaust systems, and engine parts. Their ability to resist wear and tear ensures the longevity and performance of automotive parts.
In general engineering applications, ASTM A276 stainless steel bars are favored for their durability and machinability. These bars are used in the fabrication of tools, fasteners, and machine parts that require precise dimensions and high strength. The variety of conditions (annealed, hardened, and tempered) available under this standard allows engineers to select the appropriate material for specific requirements.
When comparing corrosion resistance, ASTM A240 generally outperforms ASTM A276 due to its higher chromium and nickel content. This makes it more suitable for applications exposed to aggressive chemicals and extreme environments, such as chemical processing and marine applications.
ASTM A276 stainless steel bars generally exhibit higher tensile and yield strengths compared to ASTM A240 sheets and plates. This makes ASTM A276 more appropriate for structural and high-stress applications where mechanical performance is critical.
ASTM A240 stainless steels are easier to form and weld, making them preferable for applications requiring complex shapes and assembly processes. On the other hand, ASTM A276 stainless steels are more machinable, which is advantageous in producing precise components and intricate designs.
While ASTM A276 stainless steels are typically less expensive than ASTM A240, the latter’s superior corrosion resistance and durability can offer better long-term value in certain applications. For industries where maintenance and replacement costs are significant, ASTM A240 may be a more cost-effective choice despite the higher initial material cost.
In the aerospace industry, materials must combine strength, lightweight properties, and corrosion resistance. ASTM A240 stainless steels are used for components like aircraft skins and internal structures due to their ability to withstand high temperatures and resist corrosion. ASTM A276 bars are used in landing gear and other critical mechanical parts requiring high strength.
Medical equipment demands biocompatible and sterile materials. ASTM A240 stainless steel grades are used for surgical instruments and implants due to their excellent corrosion resistance and ability to be sterilized. ASTM A276 bars are utilized in the fabrication of medical tools and devices that require precise machining and high strength.
For chemical processing, materials must resist aggressive chemicals and high temperatures. ASTM A240 stainless steels are perfect for constructing tanks, pipes, and reactors in chemical plants, ensuring safe handling of hazardous substances. Their high resistance to corrosion makes them ideal for these applications. ASTM A276 stainless steels are used in fittings and supports that require high mechanical strength and durability.
The oil and gas industry requires materials that can withstand harsh environments and mechanical stress. ASTM A240 stainless steels are used for pipelines and pressure vessels due to their corrosion resistance and ability to maintain structural integrity under extreme conditions. ASTM A276 bars are employed in drilling equipment and structural components that demand high strength and toughness.
The aerospace industry demands materials that can endure extreme conditions such as high temperatures, mechanical stress, and corrosive environments.
ASTM A240 stainless steel is commonly used for components like aircraft skins, internal structures, and other critical parts due to its high resistance to oxidation and corrosion, ensuring longevity and reliability even in harsh aerospace environments. The material’s ability to maintain mechanical properties at elevated temperatures is crucial for aerospace applications, where performance and safety are paramount.
ASTM A276 stainless steel bars are utilized in aerospace for parts that demand high strength and toughness, such as landing gear, fasteners, and structural supports. The superior tensile and yield strengths of ASTM A276 make it ideal for these high-stress applications. Additionally, the machinability of ASTM A276 allows for the precise manufacturing of complex components required in aerospace engineering.
Medical equipment must meet strict standards for biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and sterilization.
ASTM A240 stainless steel is often used in the manufacture of surgical instruments, implants, and other medical devices. Its excellent corrosion resistance ensures that these devices can be sterilized repeatedly without degrading. The material’s biocompatibility is also essential for implants and other devices that come into direct contact with the human body.
ASTM A276 stainless steel bars are used for tools and devices that require high strength and precision, such as orthopedic instruments and dental tools. Its high machinability enables the creation of intricate designs and fine details needed for medical applications. Moreover, its strength ensures the durability and reliability of medical instruments.
The chemical processing industry deals with aggressive chemicals and extreme operating conditions, requiring materials with exceptional corrosion resistance and mechanical properties.
ASTM A240 stainless steel is ideal for constructing tanks, pipes, and reactors used in chemical plants. Its high chromium and nickel content provide excellent resistance to corrosive chemicals, ensuring safe and long-term operation. The material’s ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures makes it suitable for critical applications in chemical processing.
ASTM A276 stainless steel bars are used in fittings, supports, and other structural components within chemical plants. The high strength and toughness of ASTM A276 make it suitable for applications where mechanical performance is crucial. Additionally, the corrosion resistance of ASTM A276 ensures that these components can withstand exposure to harsh chemicals.
The oil and gas sector operates in highly challenging environments, necessitating materials that can withstand high pressures, temperatures, and corrosive conditions.
ASTM A240 stainless steel is used for pipelines, pressure vessels, and other critical infrastructure in the oil and gas sector. Its excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical properties ensure the integrity and safety of these components, even under extreme conditions. The material’s ability to handle both high and low temperatures makes it suitable for various oil and gas applications.
ASTM A276 stainless steel bars are employed in the construction of drilling equipment, support structures, and other mechanical components. The high strength and hardness of ASTM A276 are essential for withstanding the mechanical stress encountered during drilling operations. The material’s resistance to corrosion also ensures long-term durability in the harsh environments typical of oil and gas exploration and production.
In the shipbuilding industry, selecting the right material is crucial for withstanding the harsh marine environment. ASTM A240 stainless steel is frequently chosen for its excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical properties. For instance, in constructing a new fleet of cargo ships, engineers opted for Type 316 stainless steel, which falls under the ASTM A240 standard. The high chromium and molybdenum content in this grade ensures resistance to saltwater corrosion, enhancing the ship’s durability and structural integrity. The material’s ability to withstand high pressures and fluctuating temperatures made it ideal for this demanding application.
In the automotive industry, components must withstand heavy mechanical stress and exposure to corrosive substances like road salts and engine fluids. ASTM A276 stainless steel is commonly used for its superior mechanical properties and machinability. A leading car manufacturer selected ASTM A276 Grade 410 for the production of drive shafts and engine parts. This grade’s high tensile strength and hardness allowed the components to endure the rigorous demands of high-performance vehicles. Additionally, the material’s excellent machinability facilitated the precise manufacturing of complex parts, ensuring optimal performance and durability.
Cost efficiency plays a vital role in large-scale manufacturing projects. A company specializing in the production of industrial equipment faced a decision between using ASTM A240 and ASTM A276 stainless steels for different components. For parts exposed to highly corrosive environments, such as chemical processing tanks, ASTM A240 was selected despite its higher initial cost. The superior corrosion resistance and longevity of ASTM A240 materials justified the investment by reducing maintenance and replacement costs over time. Conversely, for structural components that required high strength but operated in less severe conditions, ASTM A276 stainless steel was chosen. The lower cost and ease of machining made ASTM A276 a cost-effective choice, balancing performance with budget constraints.
The main difference between ASTM A240 and ASTM A276 is their material forms and compositions.
ASTM A240 is ideal for high-temperature and high-pressure environments. Common applications include:
ASTM A276 is better suited for applications where strength and machinability are essential, such as:
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
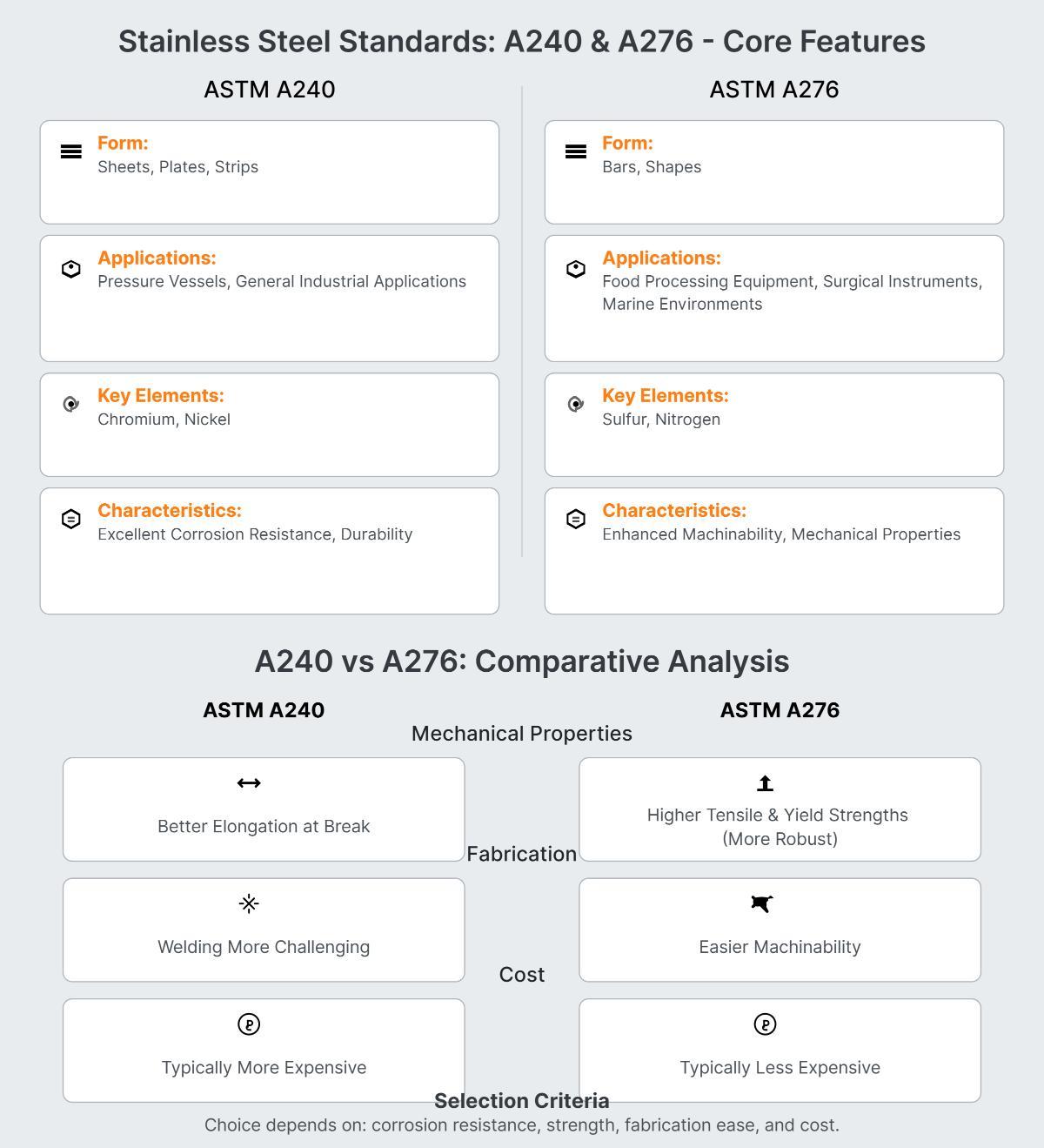
ASTM A240 and ASTM A276 are both standards for stainless steel, but they serve different purposes and have distinct characteristics. ASTM A240 is designed for stainless steel sheets, plates, and strips, commonly used in pressure vessels and general industrial applications due to its excellent corrosion resistance and durability. It includes key alloying elements such as chromium and nickel.
In contrast, ASTM A276 covers stainless steel bars and shapes, including elements like sulfur and nitrogen that enhance machinability and mechanical properties. This standard is suitable for applications like food processing equipment, surgical instruments, and marine environments where superior strength and corrosion resistance are required.
Mechanically, ASTM A276 has higher tensile and yield strengths compared to ASTM A240, making it more robust. However, ASTM A240 offers better elongation at break, which can be advantageous in certain applications. Machinability is easier with ASTM A276, while welding is more challenging with ASTM A240 due to its higher alloy content.
Cost-wise, ASTM A276 is typically less expensive than ASTM A240, reflecting differences in manufacturing processes and material composition. Thus, selecting between these standards depends on the specific requirements of the application, such as corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, fabrication ease, and cost considerations.
ASTM A240 and ASTM A276 are each suited for specific applications due to their unique properties and forms.
ASTM A240 is ideal for high-temperature and high-pressure environments, making it suitable for pressure vessels, heat exchangers, and chemical processing plants. It is also widely used in the aerospace, medical, energy, and automotive sectors due to its excellent corrosion resistance and ability to withstand extreme conditions.
On the other hand, ASTM A276 is preferred for applications requiring high strength and machinability. It is commonly used in marine and shipbuilding, food processing equipment, and surgical instruments. ASTM A276 is generally easier to machine and more cost-effective, although it is less suited for extreme conditions compared to ASTM A240.
The mechanical properties of ASTM A240 and ASTM A276 stainless steels differ primarily in tensile strength, yield strength, and operating temperature range. ASTM A240, which is commonly used for sheets, plates, and strips, typically exhibits a tensile strength of around 150 ksi (1,000 MPa) and a yield strength of approximately 115 ksi (790 MPa). Conversely, ASTM A276, used for bars and shapes, has higher tensile strength at about 185 ksi (1,275 MPa) and yield strength around 155 ksi (1,070 MPa).
In terms of elongation at break, ASTM A240 offers better ductility at 40% compared to ASTM A276’s 30%. Furthermore, ASTM A240 can withstand a broader operating temperature range from -425°F to 815°F (-253°C to 439°C), which makes it suitable for extreme environments such as cryogenic applications and high-temperature processes. ASTM A276 operates effectively within a narrower range of -50°F to 700°F (-46°C to 371°C).
The higher strength and corrosion resistance of ASTM A276 make it more suitable for applications requiring superior mechanical properties, such as in marine environments and food processing equipment. In contrast, ASTM A240’s broad temperature range and robust properties are ideal for demanding environments like chemical processing plants, pressure vessels, and heat exchangers.
ASTM A240 and ASTM A276 standards cover different forms and types of stainless steel, each serving specific applications.
ASTM A240 includes stainless steel sheets, plates, and strips. The types of stainless steel in this standard include:
ASTM A276 covers stainless steel bars and shapes, such as rounds, squares, and hexagons. It includes:
When comparing the costs of ASTM A240 and ASTM A276 stainless steel, several factors must be considered, including material form, manufacturing processes, and application requirements. ASTM A240 covers stainless steel sheets, plates, and strips, primarily used in high-stress applications like pressure vessels and heat exchangers. The cost of ASTM A240 materials is influenced by the presence of expensive alloying elements like chromium and nickel, which enhance corrosion resistance and strength, and by the complex manufacturing processes required to achieve desired properties.
On the other hand, ASTM A276 covers stainless steel bars and shapes, making it suitable for structural applications, fasteners, and equipment in food processing and pharmaceutical environments. Although ASTM A276 materials are generally more expensive due to the complex manufacturing processes for shaping, they offer cost savings in applications not requiring extreme temperature performance. The ease of machining and welding also contributes to lower production costs in some contexts.
ASTM A240 and ASTM A276 stainless steels serve distinct industry-specific applications based on their forms and properties. ASTM A240 covers flat products like plates, sheets, and strips, making it ideal for high-temperature and corrosive environments. Industries such as chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and power generation utilize ASTM A240 for pressure vessels, heat exchangers, and architectural cladding due to its high corrosion resistance and mechanical strength.
Conversely, ASTM A276 pertains to stainless steel bars and shapes, including rounds, squares, and hexagons. This standard is particularly suited for structural and precision applications. Industries like food processing, marine, and general engineering favor ASTM A276 for its excellent machinability and ease of forming into structural components, shafts, and fasteners. The choice between these standards depends on the specific requirements of the application and the desired form of the stainless steel.

