Imagine a material that combines the best qualities of copper and zinc, enhanced by a touch of lead to create a versatile, high-performance alloy. Enter C3604 brass, a marvel in the world of metallurgy, celebrated for its exceptional machinability and robust mechanical properties. But what exactly makes C3604 brass so special? In this deep dive, we will unravel the chemical composition of this unique alloy, breaking down the roles of copper, zinc, and lead in its structure. We’ll also explore its impressive mechanical properties, from tensile strength to durability, and reveal why C3604 brass is a preferred choice in various industries, including automotive and electrical engineering. By the end of this article, you’ll understand not just the “what” and “how,” but also the “why” behind the widespread use of C3604 brass in modern engineering. Ready to explore the fascinating world of C3604 brass? Let’s get started.
C3604 brass, often referred to as free-cutting or leaded brass, is a copper-zinc alloy known for its exceptional machinability, durability, and resistance to corrosion. This alloy is widely utilized in various industries due to its advantageous properties, making it a subject of significant interest in material science and engineering.
The importance of C3604 brass comes from its unique combination of mechanical properties and ease of machining, which are critical in manufacturing and engineering applications. Its high copper content provides excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, while the addition of lead enhances machinability, allowing for precise and efficient manufacturing processes.
The alloy’s composition ensures strong resistance to corrosion, making it particularly beneficial in environments where exposure to moisture and chemicals is common. This durability extends the lifespan of components made from C3604 brass, reducing maintenance costs and improving overall system reliability.
C3604 brass is renowned for its superb machinability, a property largely attributed to the presence of lead. The lead acts as a lubricant, reducing friction and wear on cutting tools, thus facilitating smoother and faster machining operations. This makes C3604 brass an ideal choice for producing intricate and detailed components.
The alloy’s composition ensures a robust resistance to corrosion, which is particularly beneficial in environments where exposure to moisture and chemicals is common. This durability extends the lifespan of components made from C3604 brass, reducing maintenance costs and improving overall efficiency and reliability.
C3604 brass finds extensive use in multiple sectors, including:
Innovations in alloy processing and component manufacturing are continually improving the performance and uses of C3604 brass, making it a versatile material in modern engineering. Understanding the composition, properties, and applications of C3604 brass is essential for leveraging its benefits in various industrial applications, ensuring effective and efficient use in engineering projects.
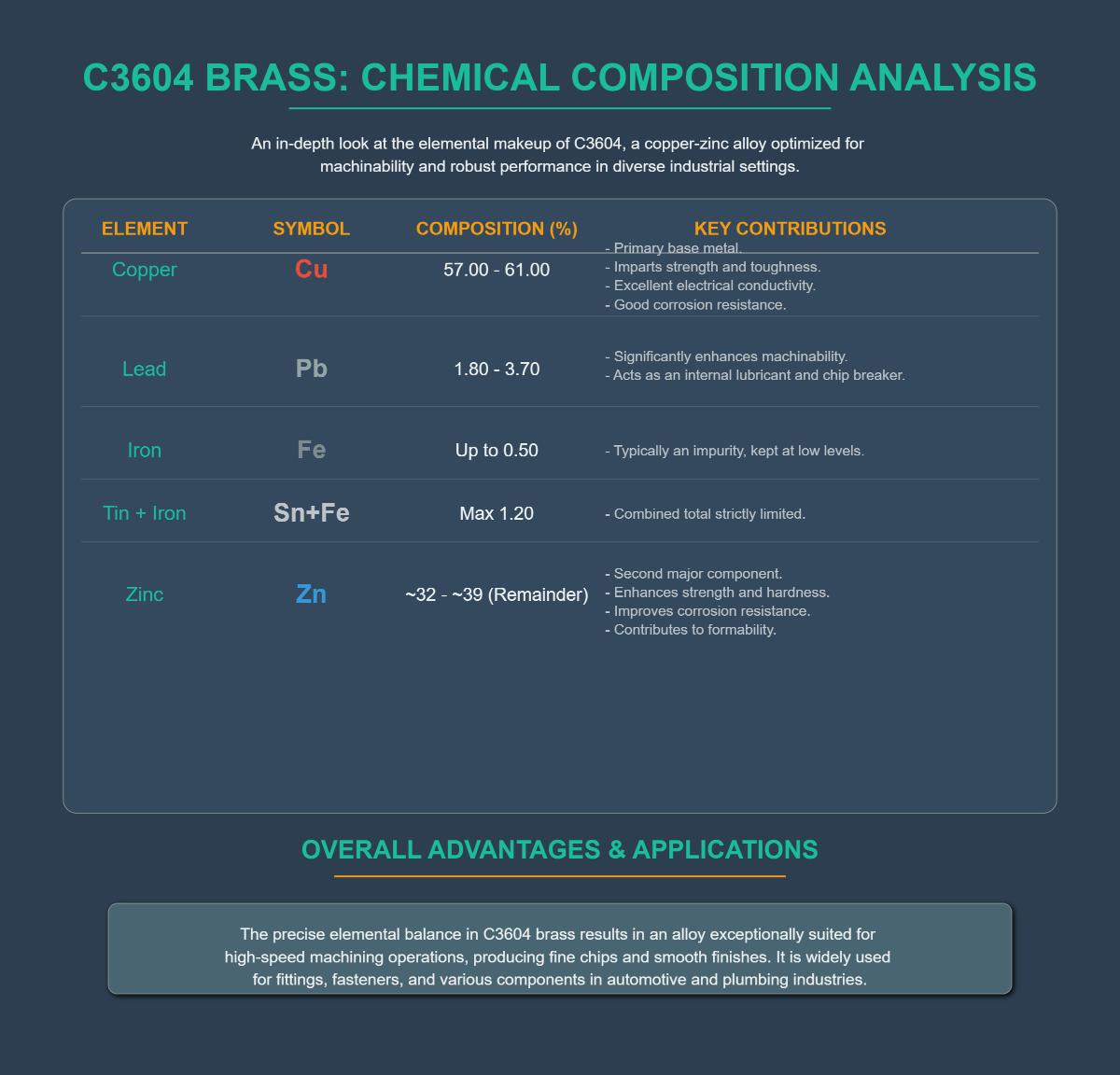
C3604 brass is a copper-zinc alloy designed for superior machinability and versatility in various industrial applications. Its chemical composition is carefully balanced to achieve a combination of desirable properties. Below is a breakdown of the primary elements that make up C3604 brass.
Copper makes up 57.00% to 61.00% of C3604 brass. This high copper content is crucial as it imparts several essential properties to the alloy:
Zinc, which constitutes approximately 32% to 39% of the alloy, plays a critical role in enhancing C3604 brass’s properties:
Lead is present in C3604 brass in the range of 1.80% to 3.70%. The inclusion of lead is primarily for improving machinability:
Iron and tin are present in trace amounts, with iron content limited to up to 0.50% and the combined content of tin and iron restricted to a maximum of 1.20%. These elements are kept low to maintain the alloy’s optimal properties:
C3604 brass is often compared with other types of brass, such as free-cutting brass, to highlight its unique advantages:
Understanding the chemical composition of C3604 brass is fundamental for selecting the right material for specific engineering tasks. The carefully balanced proportions of copper, zinc, lead, iron, and tin ensure that the alloy meets the demanding requirements of various industrial applications.
C3604 brass has a density of about 8.4 to 8.47 g/cm³, offering a balance between strength and ease of machining. This moderate density makes the alloy suitable for various applications that require robust yet workable materials.
With a minimum ultimate tensile strength of around 335 MPa (48,500 psi), C3604 brass can withstand significant stress, making it ideal for components exposed to heavy loads and mechanical stress.
C3604 brass has a minimum hardness of 80 HV (Vickers Hardness), ensuring good resistance to surface wear and deformation, which enhances the durability of parts made from this alloy.
The elastic modulus of C3604 brass is around 105 GPa, but it can reach up to 140 GPa in some cases. This high stiffness helps the material return to its original shape after deformation, crucial for applications needing resistance to bending or flexing.
C3604 brass demonstrates some ductility, allowing for a degree of deformation before rupture. This elongation at break property is beneficial in applications requiring flexibility and the ability to absorb impact without immediate failure.
The thermal conductivity of C3604 brass is about 118 W/(m·K). This high thermal conductivity makes the alloy efficient in applications involving heat transfer, such as heat exchangers and cooling systems. Effective thermal management is critical in maintaining the performance and longevity of components.
C3604 brass offers moderate electrical conductivity, ranging from 24% to 28% IACS (International Annealed Copper Standard). While not as conductive as pure copper, this level of electrical conductivity is sufficient for many electrical components, ensuring reliable performance without the necessity for pure copper.
The melting point of C3604 brass lies between 873°C and 890°C (1610°F and 1630°F). This high melting point maintains the material’s stability under heat, making it suitable for applications involving elevated temperatures and thermal stress.
Due to its mechanical and thermal properties, C3604 brass is widely used in making electrical connectors, automotive parts, aviation components, and machinery parts. Its strength, machinability, and durability make it suitable for gears, bearings, fuse holders, and other critical components.
C3604 brass is highly valued in the electrical industry due to its excellent electrical conductivity and machinability. It is commonly used to manufacture connectors, sockets, switches, and terminal blocks due to its stable electrical properties and environmental resilience. The alloy’s ability to maintain consistent performance under various conditions is crucial for ensuring the safety and efficiency of electrical networks. Its corrosion resistance further enhances longevity, making it ideal for high-reliability applications.
The mechanical properties of C3604 brass, including its strength, durability, and excellent machinability, make it a preferred material for various mechanical parts. It is extensively used in the production of gears, bushings, valve guides, and other precision components that require intricate shapes and fine details. These parts benefit from the alloy’s superior machinability, which allows for efficient production with high dimensional accuracy. The wear resistance of C3604 brass also contributes to the durability and longevity of mechanical components, reducing the need for frequent replacements and maintenance.
In the automotive industry, C3604 brass is utilized for a variety of components that demand precision and reliability. This includes parts such as fuel injectors, connectors, bushings, and valve guides, where precision and reliability are essential. The alloy’s machinability allows for the production of complex parts with high dimensional accuracy, which is crucial for the proper functioning of automotive systems. Additionally, the corrosion resistance and mechanical strength of C3604 brass ensure that these components can withstand harsh operating conditions, including exposure to fuels, lubricants, and varying temperatures.
C3604 brass is widely used in the plumbing industry for the production of fixtures and fittings such as faucets, valves, and connectors. Its corrosion resistance is a significant advantage in this application, as plumbing components are frequently exposed to water and other fluids. The ability of C3604 brass to withstand high water pressure and temperature changes ensures the reliability and safety of plumbing systems. Furthermore, the alloy’s machinability allows for the creation of precise and leak-proof fittings, which are essential for maintaining efficient and effective plumbing infrastructure.
The attractive appearance and ease of fabrication make C3604 brass a popular choice for decorative and architectural applications, such as door handles, light fixtures, and ornamental hardware. The alloy’s ability to be easily polished and finished enhances its aesthetic appeal, making it suitable for high-end decorative purposes. Additionally, the durability and corrosion resistance of C3604 brass ensure that these decorative elements maintain their appearance and functionality over time, even in outdoor or high-traffic environments.
C3604 brass is also used extensively in the production of various industrial hardware components, such as fasteners, pump shafts, and couplings. The strength and machinability of the alloy make it ideal for creating components that require precise dimensions and high durability. These properties ensure that industrial hardware made from C3604 brass can perform reliably under mechanical stress and in challenging industrial environments. The alloy’s resistance to corrosion further enhances the longevity of these components, making them a cost-effective choice for industrial applications.
Recent trends in the use of C3604 brass include advancements in sustainable manufacturing processes and the development of new applications in emerging industries. Efforts to reduce environmental impact have led to innovations in the recycling and processing of brass alloys, making C3604 brass a more sustainable material choice. Additionally, its unique combination of properties continues to drive its adoption in cutting-edge fields such as renewable energy and advanced manufacturing technologies, where high-performance materials are essential for achieving technological advancements.
Free-cutting brass, like C3604 brass, is designed for excellent machinability. However, there are differences in their chemical compositions and resultant properties. C3604 brass typically contains 57-61% copper, 32-39% zinc, and 1.8-3.7% lead, with trace amounts of iron and tin. The lead content in C3604 brass is crucial for enhancing machinability. Free-cutting brass variants might have similar or slightly different compositions, impacting their specific mechanical and corrosion resistance properties.
C3604 brass is renowned for its superior machinability due to its lead content, which acts as a chip breaker, reducing tool wear and allowing high-speed operations. Free-cutting brass alloys also contain lead, but the exact amount can vary, potentially making C3604 brass more suitable for applications requiring extremely high precision and smooth finishes.
Copper-zinc alloys are categorized by their zinc content:
C3604 brass, with its balanced zinc content, falls within the alpha-beta brass category, offering a good compromise between machinability, strength, and corrosion resistance.
The lead content in C3604 brass enhances machinability significantly. Other copper-zinc alloys might not include lead or have it in lower quantities, impacting their ease of machining. For instance, alloys without lead are less machinable but may be preferred in applications where lead-free materials are required for environmental or health reasons.
C3604 brass is preferred in the electrical industry for components like connectors and terminals due to its good electrical conductivity and excellent machinability. Other copper-zinc alloys with lower zinc content might offer better conductivity but at the cost of machinability.
For mechanical parts like gears and valve guides, the choice between C3604 brass and other copper-zinc alloys depends on the required balance of strength, machinability, and corrosion resistance. C3604 brass is often chosen for its superior machinability and adequate strength.
Alpha brasses are ideal for applications needing extensive cold working, such as producing intricate shapes and thin-walled components, due to their high ductility.
Alpha-beta brasses, including C3604, offer a mix of ductility and strength, making them versatile for both hot working and machining processes. They are used in a wide range of industrial applications.
Beta brasses are utilized in applications where high strength is paramount, such as in heavy-duty engineering components. However, their reduced ductility limits their use in applications requiring significant deformation.
These comparisons help select the right alloy for specific engineering needs, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
C3604 brass is a copper-zinc alloy with a specific chemical composition designed to enhance machinability and performance in various industrial applications. The composition includes:
Copper serves as the primary component, contributing to the alloy’s strength, corrosion resistance, and electrical conductivity. Zinc enhances these properties, particularly corrosion resistance and formability. Lead is added to improve machinability by acting as a lubricant during the machining process. This specific combination of elements makes C3604 brass particularly suitable for high-speed machining operations and a variety of industrial applications.
C3604 brass, also known as free-cutting brass, is valued for its mechanical properties that make it highly suitable for various engineering applications. The alloy primarily consists of copper and zinc with a small addition of lead to enhance machinability. Its key mechanical properties include a minimum tensile strength of 335 MPa, which enables it to withstand significant stress. The alloy has a hardness of at least 80 HV, providing resistance against surface wear and deformation. It also exhibits some ductility, allowing for deformation before rupture, and has a modulus of elasticity ranging from 105 to 140 GPa, reflecting its stiffness. The density of C3604 brass is between 8.4 and 8.47 g/cm³, striking a balance between strength and machinability. These properties make C3604 brass ideal for precision-engineered components in industries such as electrical, automotive, and aviation.
C3604 brass, also known as free-cutting or free-machining brass, is widely used across various industries due to its excellent machinability, corrosion resistance, and good electrical conductivity. Typical applications of C3604 brass include:
C3604 brass is a type of copper-zinc alloy known for its excellent machinability and is often referred to as free-cutting brass. Compared to other copper-zinc alloys, such as 360 brass, C3604 brass has a slightly different composition and properties that make it particularly suitable for certain applications.
The composition of C3604 brass includes 57% to 61% copper, a significant amount of zinc, and 1.8% to 3.7% lead, which enhances its machinability. In contrast, 360 brass typically has a 60-40 copper-zinc ratio with about 3% lead. Both alloys offer good corrosion resistance and high machinability, making them ideal for manufacturing mechanical and electrical parts.
However, C3604 brass has a broader range of lead content, providing superior machinability and mechanical properties, such as a higher tensile strength. This makes it more versatile and preferred in industries requiring precise and efficient machining, such as automotive and aviation sectors.
Emerging trends in the use of C3604 brass are focused on enhancing its environmental sustainability and expanding its applications in high-tech industries. One significant trend is the development of lead-free alternatives due to increasing regulatory pressures, such as the RoHS Directive in Europe, which aims to reduce lead in electronic and automotive components. Researchers are creating new brass alloys that maintain the machinability and strength of C3604 brass while being free from lead, making them more environmentally friendly.
Additionally, advancements in machining techniques, such as high-speed CNC operations, are improving the efficiency of working with C3604 brass. These techniques enable high-speed operations with minimal tool wear, making the production of precision components more cost-effective.
In the automotive and electrical industries, C3604 brass continues to be highly valued for its durability, corrosion resistance, and electrical conductivity. It is extensively used in auto parts and electrical connectors, benefiting from its ability to withstand high pressures and temperatures.
C3604 brass, also known as free-cutting brass, is highly beneficial in industrial applications due to its unique composition and properties. This alloy consists primarily of copper and zinc, with a small amount of lead, which enhances its machinability. The lead content reduces friction and facilitates chip formation, making C3604 brass ideal for precision machining tasks. Additionally, this alloy offers good corrosion resistance, which ensures durability in various environments, both indoor and outdoor.
Its moderate electrical conductivity makes it suitable for electrical components such as connectors and sockets. In the mechanical domain, C3604 brass is used to manufacture parts like bearings, gears, and shafts due to its high strength. In the automotive industry, it is employed in components like fuel injectors and fuse holders, benefiting from its durability and corrosion resistance. Moreover, the high machinability of C3604 brass leads to efficient CNC machining, reducing tool wear and increasing processing speed, which translates to cost savings and optimized production processes. Overall, its combination of mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, and machinability makes C3604 brass an optimal choice for a wide range of industrial applications.

