Imagine a material that offers remarkable electrical conductivity, impressive corrosion resistance, and is highly sought after in industries ranging from electronics to construction. Enter the world of 1060 aluminium alloy—a prime example of versatility and efficiency. In this comprehensive guide, we will embark on a technical deep dive to uncover the secrets behind this alloy’s chemical composition and mechanical properties, explore its myriad applications, and compare it with other aluminium alloys. Whether you are curious about its role in the electrical industry or its contributions to sustainability, this guide promises to equip you with essential knowledge and practical insights. Ready to discover why 1060 aluminium alloy is a cornerstone in modern engineering? Let’s delve into the details.
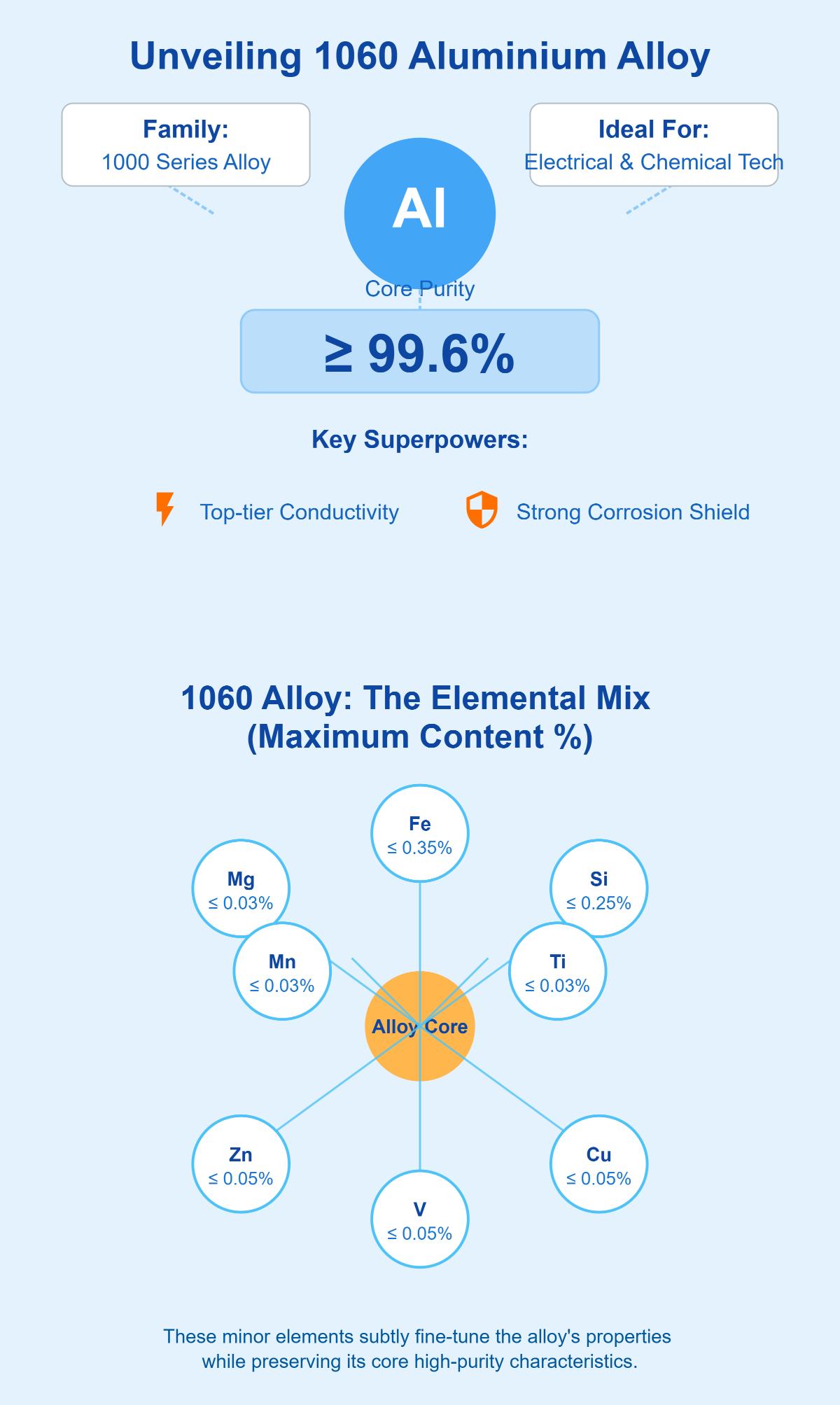
1060 aluminium alloy, part of the 1000 series, is renowned for its high purity level, containing at least 99.6% aluminium. This high purity imparts the alloy with excellent properties, making it an attractive choice for various industrial applications. The alloy’s notable attributes include superior electrical and thermal conductivity, excellent corrosion resistance, and good formability.
1060 aluminium alloy exhibits several important technical characteristics that contribute to its versatility:
1060 aluminium alloy is mostly aluminium, with trace amounts of elements like copper, iron, and silicon, which together enhance its properties:
The unique properties of 1060 aluminium alloy make it suitable for a wide range of applications:
1060 aluminium alloy conforms to several ASTM and ISO standards to ensure consistent quality and performance:
1060 aluminium is often compared with other alloys in the 1000 series:
These comparisons highlight the versatility of 1060 aluminium alloy, making it a preferred choice for many industrial applications due to its excellent combination of properties.
The 1060 aluminium alloy stands out for its high aluminium content, with at least 99.6% aluminium. This purity significantly contributes to the alloy’s excellent electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance, while trace elements enhance its mechanical performance. Here is a detailed breakdown of the typical elements found in 1060 aluminium alloy:
These trace elements are controlled to ensure that the alloy maintains its desirable properties while allowing for improved structural integrity and formability.
The mechanical properties of 1060 aluminium alloy make it versatile for many uses. The alloy cannot be strengthened by heat treatment but gains strength through cold working. Key mechanical properties include:
The 1060 aluminium alloy is highly regarded for its electrical and thermal properties, which are crucial in applications that require efficient conduction. Its high aluminium content ensures excellent electrical conductivity, making it a preferred choice for electrical applications. The alloy’s thermal conductivity is also noteworthy, supporting its use in heat dissipation applications:
One of the standout features of 1060 aluminium alloy is its excellent corrosion resistance. This property is primarily due to its high aluminium content, which forms a thin, protective oxide layer on its surface. This oxide layer acts as a barrier, protecting the underlying metal from further oxidation and corrosive elements. This characteristic makes the alloy ideal for use in environments where corrosion resistance is paramount, such as in chemical processing equipment and outdoor structures.
These chemical and mechanical properties make 1060 aluminium alloy a versatile and reliable choice for various industrial applications, offering excellent formability and strong structural benefits.
1060 aluminium alloy is highly valued in the electrical industry because its electrical conductivity is about 62% of pure copper’s. This makes it an ideal choice for manufacturing electrical conductors, such as busbars and transformer windings. The high conductivity ensures efficient transmission of electrical current with minimal energy loss. Additionally, 1060 aluminium is used in enclosures for electrical components, capacitors, and lamp holders, where its formability and corrosion resistance enhance the durability and performance of these components.
The chemical industry benefits significantly from 1060 aluminium alloy, primarily due to its exceptional corrosion resistance. This property is crucial for equipment exposed to harsh chemicals and environments. 1060 aluminium is commonly used in the construction of tanks, pipes, and railroad tank cars. Its ability to withstand corrosive substances ensures long-term reliability and safety, while its non-toxic nature makes it suitable for storing and handling various chemicals.
In the construction industry, 1060 aluminium alloy is prized for its lightweight, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal. It is frequently used in roofing and cladding applications, providing durable protection against the elements.
The versatility of 1060 aluminium alloy extends to emerging industries, where its unique properties are leveraged for advanced applications. In the renewable energy sector, 1060 aluminium is used in solar reflectors and photovoltaic panel frames. Its high reflectivity maximizes light capture, improving solar energy system efficiency. In the electronics industry, the alloy’s thermal conductivity makes it an excellent choice for heat sinks, essential for managing heat in electronic components and ensuring optimal performance.
Notable case studies highlight its use in lightweight, corrosion-resistant containers for transporting perishable goods. These containers leverage the alloy’s formability and strength, ensuring they withstand transportation rigors while maintaining content integrity. Another example is its implementation in large-scale solar farms, where its use in reflector panels has significantly boosted solar energy generation efficiency.
1060 aluminium alloy is preferred for food packaging because of its non-toxic and barrier properties. Aluminium foil containers and lids made from this alloy provide excellent protection against moisture, light, and contaminants, ensuring the freshness and safety of food products. The alloy’s formability allows for various packaging shapes and sizes, catering to different needs in the food industry.
In the automotive and transportation sectors, 1060 aluminium alloy is used for non-structural components where weight savings are critical. The alloy’s lightweight nature helps improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. Its corrosion resistance ensures the longevity of components exposed to environmental conditions, such as trim and decorative elements.
1060 aluminium alloy is ideal for heat management applications because of its thermal conductivity. It is widely used in the production of heat exchangers, essential for transferring heat in various systems, including HVAC units and industrial machinery. The alloy’s ability to efficiently dissipate heat helps maintain optimal operating temperatures, enhancing the performance and lifespan of equipment.
The 1060 aluminium alloy is governed by several ASTM standards, ensuring its quality and performance across various applications.
ASTM B209 sets requirements for dimensions, tolerances, mechanical properties, and temper designations for aluminium and aluminium-alloy sheets and plates, ensuring they meet industry standards for construction and electrical applications. This standard guarantees consistent thickness, flatness, and strength, which are essential for uses like roofing and electrical enclosures.
ASTM B210 covers seamless aluminium tubes, defining their chemical composition, mechanical properties, and dimensions. These seamless tubes are crucial for leak-proof performance in the chemical industry, where they transport corrosive substances.
ASTM B211 specifies the requirements for bar, rod, and wire products made from aluminium and aluminium alloys. For 1060 alloy, this standard ensures appropriate diameter, length, and mechanical properties, making these products suitable for industrial components that require high formability and corrosion resistance.
ASTM B221 deals with extruded bars, rods, wire, profiles, and tubes. It specifies the requirements for the extrusion process, dimensions, and mechanical properties of 1060 aluminium alloy products. These extruded items are used in a wide range of applications, from automotive parts to architectural structures, due to their custom-shaped profiles and good mechanical performance.
ASTM B483 relates to drawn tube and pipe made from aluminium and aluminium alloys. It ensures that the drawn tubes and pipes have the correct wall thickness, diameter, and mechanical properties. These products are often used in the electrical and chemical industries, where they need to withstand specific operating conditions.
In addition to ASTM standards, ISO standards also play a crucial role in regulating the 1060 aluminium alloy.
ISO 6361 is an international standard that governs wrought aluminium and aluminium alloy sheets, strips, and plates. For 1060 aluminium alloy, this standard provides a unified set of requirements for quality, dimensions, and properties. Compliance with ISO 6361 allows manufacturers to confidently export their 1060 alloy products, knowing they meet international quality standards.
Welding 1060 aluminium alloy demands specific techniques due to its high aluminium content and relatively low melting point. These methods ensure strong, reliable joints:
Precautions:
1060 aluminium alloy is highly formable, making it suitable for various fabrication processes.
Machining 1060 aluminium alloy is straightforward due to its softness and ductility.
Although 1060 aluminium alloy is not typically heat treatable for strength, it can undergo processes like annealing to adjust its mechanical properties:
The main difference between 1060 and 1050 aluminium alloys is their aluminium content and trace impurities. 1060 has a minimum aluminium content of 99.6%, while 1050 contains slightly less, at 99.5%. This marginal difference affects their properties, making 1060 slightly purer and contributing to its distinct characteristics. As a result, the mechanical properties of both alloys are similar due to their high aluminium content.
1060 aluminium alloy has about 62% IACS electrical conductivity, making it slightly better than 1050 because of its higher aluminium content. This makes 1060 a preferred choice for electrical conductors where maximum efficiency is required.
Both 1060 and 1050 alloys offer excellent corrosion resistance due to their high aluminium content, which forms a protective oxide layer. This resistance makes them suitable for environments where corrosion could be an issue. The minor differences in impurity levels do not significantly affect their corrosion resistance.
1100 aluminium alloy contains more impurities, including copper and iron, compared to the 1060 alloy. This results in a lower aluminium purity, which affects its mechanical properties and applications.
1060 aluminium alloy outperforms 1100 in electrical conductivity, again due to its higher aluminium content. This makes 1060 more suitable for electrical applications where conductivity is paramount. However, both alloys offer good thermal conductivity, making them effective in heat dissipation applications.
When selecting these alloys, consider the specific application requirements:
1060 aluminium alloy, distinguished by its high purity (99.6%), is renowned for its exceptional properties, making it a material of choice for various applications. Its high corrosion resistance, good workability, and excellent electrical conductivity play a significant role in promoting sustainability and material efficiency across industries.
The high aluminium content in 1060 alloy significantly enhances its corrosion resistance. This property is particularly beneficial in environments prone to harsh conditions, as it reduces the need for additional protective coatings or treatments. By minimizing maintenance and replacement costs, it supports long-term sustainability and resource efficiency.
1060 aluminium is highly efficient for electrical applications due to its ability to conduct electricity with minimal energy loss. This efficient conductivity ensures that electrical components such as conductors and busbars require less material to perform effectively.
The alloy’s thermal conductivity, around 230 W/m·K, makes it suitable for heat exchangers and heat sinks. This property enhances the efficiency of heat transfer systems, contributing to energy savings and reducing the risk of overheating in electronic components.
Aluminium is known for its recyclability, and the high purity of 1060 alloy further enhances its value in recycling processes. Recycling aluminium requires only about 5% of the energy needed to produce primary aluminium, significantly lowering energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. This closed-loop recycling process supports a circular economy and reduces the environmental footprint.
The excellent formability of 1060 aluminium allows it to be efficiently processed and shaped into various forms, such as sheets, plates, and coils. This versatility minimizes waste during manufacturing and optimizes material usage, making it ideal for applications requiring precise dimensions and complex shapes.
In automotive and transportation sectors, the lightweight nature of 1060 aluminium helps reduce fuel consumption and emissions. The alloy’s use in non-structural components, such as trim and decorative elements, contributes to overall vehicle weight reduction, which in turn enhances fuel efficiency and lowers greenhouse gas emissions.
Both 1060 and 1050 alloys exhibit low mechanical strength compared to other aluminium alloys but offer superior corrosion resistance and formability. This makes them suitable for applications where high strength is not necessary, but durability and workability are essential.
The use of 1060 aluminium in electrical conductors and heat exchangers enhances system efficiency, leading to reduced energy consumption and lower emissions over time. These applications benefit from the alloy’s excellent electrical and thermal properties, contributing to more sustainable and cost-effective energy solutions.
By optimizing material usage and implementing efficient processing techniques, manufacturers can significantly reduce waste. The formability and recyclability of 1060 aluminium support waste minimization strategies, promoting sustainable manufacturing practices.
The corrosion resistance of 1060 aluminium extends the lifespan of products made from this alloy. This durability reduces the need for frequent replacements, thereby conserving resources and reducing the environmental impact associated with manufacturing new products.
As industries increasingly focus on sustainability and material efficiency, the demand for materials like 1060 aluminium alloy is expected to grow. Its high recyclability, efficient use in electrical and thermal applications, and contribution to reducing energy consumption make it a valuable component in sustainable manufacturing processes.
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
The 1060 aluminium alloy is part of the 1000 series, recognized for its high purity and advantageous properties. Its chemical composition is dominated by aluminium, which constitutes at least 99.6% of the alloy. This high aluminium content is crucial for its outstanding electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance. The remaining composition includes small amounts of other elements: Copper (Cu) up to 0.05%, Iron (Fe) up to 0.35%, Magnesium (Mg) up to 0.03%, Manganese (Mn) up to 0.03%, Silicon (Si) up to 0.25%, Titanium (Ti) up to 0.03%, Vanadium (V) up to 0.05%, and Zinc (Zn) up to 0.05%. These minor elements contribute to specific properties but do not significantly alter the alloy’s primary characteristics. This composition ensures the alloy’s suitability for applications requiring high conductivity and resistance to corrosion, particularly in electrical and chemical industries.
1060 aluminium alloy, with high purity (99.6% aluminium), is widely used due to its excellent electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, formability, and weldability. In the electrical industry, it’s used for transformer windings, electrical component enclosures, and wiring. In the chemical and food sectors, it makes tanks, railroad tank cars, and food packaging. For construction, it serves as roofing and decorative elements. It’s also used in thermal applications like heat exchangers, and in lighting fixtures and solar reflectors. Additionally, it’s found in household items such as kitchen utensils.
1060 aluminium alloy, part of the 1000 series, is known for its high purity with a minimum of 99.6% aluminium content. This gives it exceptional electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for electrical and chemical applications. Compared to other aluminium alloys, 1060 has lower mechanical strength, which can be an advantage or disadvantage depending on the application. For instance, 1050 alloy, with a slightly lower aluminium content (99.5%), has marginally higher tensile strength but slightly reduced conductivity. In contrast, 6063 alloy, which includes silicon and magnesium, offers higher strength and better heat-treatability, making it suitable for structural and architectural uses. Thus, the choice between 1060 and other aluminium alloys depends on the specific needs of conductivity, formability, and strength for each application.
Yes, there are practical tutorials for working with 1060 aluminium alloy. These tutorials focus on both welding and forming techniques due to the alloy’s excellent formability and weldability. For welding, methods such as gas welding, arc welding, and resistance welding are recommended. It’s crucial to use filler rods made from the same 1060 alloy to maintain weld joint integrity. When forming, both cold working (e.g., bending, deep drawing) and hot working (processing between 900°F to 500°F) can be effectively utilized. Practical tutorials often emphasize the importance of surface preparation, temperature control during processing, and applying protective coatings in corrosive environments. Additionally, using appropriate tools and lubricants during machining can optimize tool life and surface finish. These tutorials help ensure high-quality results while maintaining the alloy’s mechanical properties and performance.
1060 aluminium alloy, known for its high purity, excellent corrosion resistance, and superior thermal and electrical conductivity, finds advanced applications in several emerging industries. In the electrical and renewable energy sectors, it is used for transformer windings and electrical components due to its high electrical conductivity, enhancing efficiency and reducing energy loss. Additionally, its high reflectivity makes it ideal for solar reflectors and lighting fixtures, improving energy efficiency and light capture.
In the chemical and food processing industries, the alloy’s strong corrosion resistance makes it suitable for chemical storage tanks, containers, and processing equipment, ensuring durability in harsh environments. It is also used in food handling and packaging, benefiting from its corrosion resistance and formability.
In construction and transportation, 1060 aluminium is used for roofing materials and siding panels due to its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties, providing aesthetic appeal and durability. It is also employed in non-structural applications in railroad tank cars, enhancing safety and efficiency in chemical transport.
For heat management applications, the alloy’s high thermal conductivity is advantageous for heat exchangers and refrigeration systems, facilitating efficient heat transfer. It is also used in insulation jackets and heat sinks to maintain temperature control and effectively dissipate heat. These advanced applications highlight the alloy’s versatility and its critical role in emerging industries.
The 1060 aluminium alloy significantly contributes to sustainability due to its high purity, excellent recyclability, and energy efficiency. Composed of at least 99.6% aluminium, it offers superior corrosion resistance, reducing the need for protective coatings and extending the lifespan of products, thus minimizing waste. Its recyclability is a key environmental advantage, as aluminium can be recycled repeatedly without losing its properties, conserving raw materials and reducing landfill waste. Moreover, recycling aluminium consumes substantially less energy compared to producing new aluminium, leading to lower greenhouse gas emissions.
In terms of energy efficiency, 1060 aluminium alloy’s high thermal and electrical conductivity makes it ideal for applications such as heat exchangers and electrical components, which helps in reducing energy consumption. Additionally, its high reflectivity is utilized in lighting fixtures and solar reflectors, enhancing light capture and further contributing to energy savings.
Lastly, the lightweight and formable nature of 1060 aluminium facilitates easier transportation and installation, reducing logistical costs and environmental impact in construction projects. Its use in sustainable construction practices supports green building certifications, promoting energy-efficient and environmentally friendly designs. These attributes collectively make 1060 aluminium alloy a valuable material for sustainable and environmentally conscious applications.

