When it comes to the backbone of industrial manufacturing, 40Cr steel stands out as a versatile and reliable material. Whether you’re an engineer, a manufacturer, or a metalworking enthusiast, understanding the properties and equivalents of 40Cr steel can significantly impact your projects. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate details of 40Cr steel, from its chemical composition to its mechanical properties, and explores how various heat treatment processes enhance its performance. We’ll also compare 40Cr steel to other similar steels, examining cost-effectiveness, availability, and sustainability. Discover why 40Cr steel is a preferred choice in industries such as automotive and agriculture, and how its robust properties and regional equivalents can optimize your applications. Ready to uncover the full potential of 40Cr steel? Let’s dive in!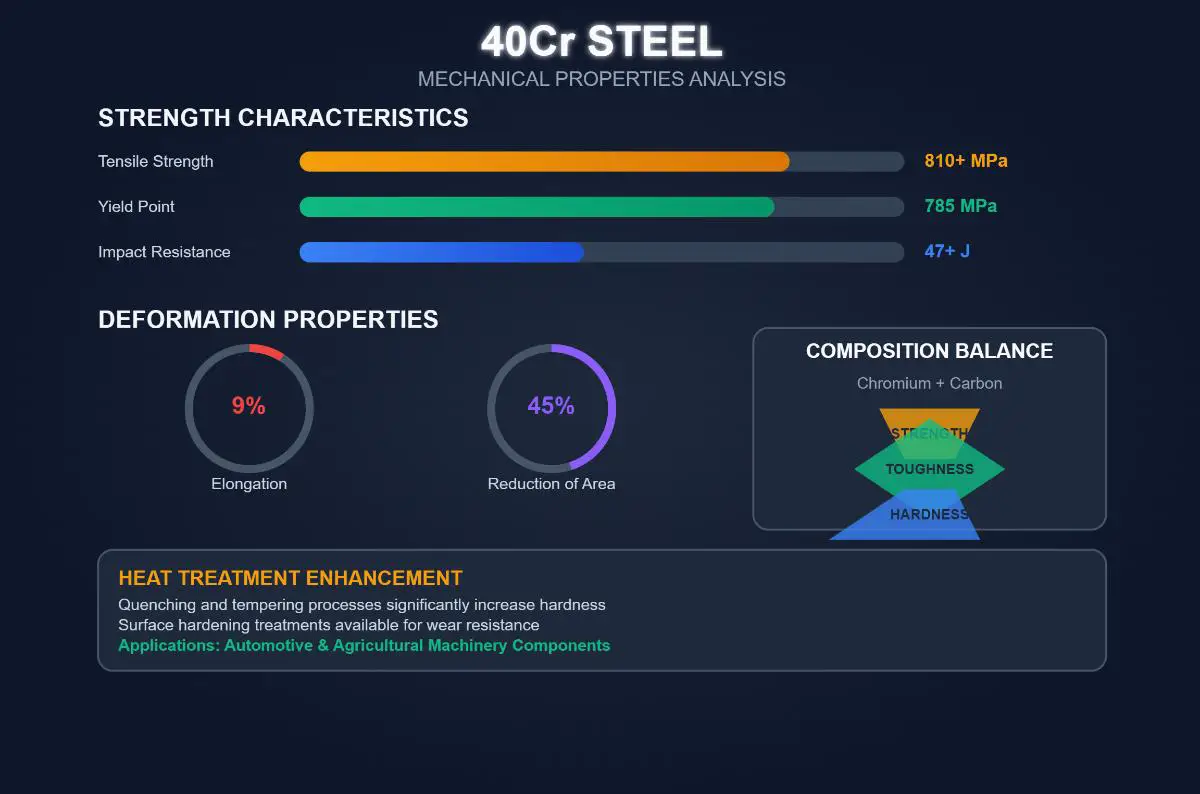
40Cr steel is a high-quality alloy structural steel that meets Chinese GB standards. It is recognized for its excellent mechanical properties and cost-effectiveness, making it a popular choice in various industries for components requiring high tensile strength and wear resistance.
40Cr steel’s high strength and durability are primary reasons for its widespread use in manufacturing and metalworking. The steel’s composition, which includes carbon and chromium, contributes to these properties, making it suitable for components that experience significant stress and wear.
The versatility of 40Cr steel is another significant factor in its widespread use. It can be applied in various sectors such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and machinery manufacturing. This adaptability stems from the steel’s ability to undergo various heat treatment processes, enhancing its mechanical properties to meet specific requirements.
40Cr steel contains around 1% chromium and controlled amounts of carbon and other elements, ensuring a balance between hardness, strength, and toughness. The precise control of these elements is essential in achieving the desired mechanical properties.
The mechanical properties of 40Cr steel are a result of its chemical composition and heat treatment processes. These properties include:
Heat treatment processes like quenching and tempering are crucial for optimizing 40Cr steel’s performance. These treatments alter the microstructure of the steel, enhancing its hardness, strength, and impact resistance. Typical heat treatment parameters for 40Cr steel include quenching at temperatures between 800-880°C and tempering at around 520°C.
In the automotive industry, 40Cr steel is used for gears, drive shafts, axles, and engine components due to its high strength and wear resistance. These characteristics make it ideal for parts that experience constant stress and friction.
The aerospace industry utilizes 40Cr steel for landing gear components, engine parts, and structural frames. The steel’s reliability and ability to withstand high stress and impacts are critical for aerospace applications.
40Cr steel is employed in the construction and machinery manufacturing sectors for cranes, hoisting machinery, industrial gears, and machine tool spindles. Its durability and strength ensure the longevity and efficiency of these components.
In agriculture, 40Cr steel is used for tractor components, plow parts, and mechanical arms. The steel’s robustness and wear resistance are essential for the demanding conditions in agricultural applications.
Understanding the equivalents and alternatives to 40Cr steel is important for selecting the appropriate material for specific applications. Comparative analysis with other alloy steels, such as 42CrMo and AISI 4140, can help determine the best choice based on mechanical properties, cost-effectiveness, and availability.
The chemical makeup of 40Cr steel is crucial to its strength and functionality. The alloying elements in 40Cr steel are meticulously balanced to achieve specific characteristics, making it a versatile material in various engineering applications. The standardized chemical composition of 40Cr steel according to the Chinese GB/T 3077 standard is as follows:
| Element | Composition Range (%) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | 0.37 – 0.44 | Provides strength and hardness |
| Silicon (Si) | 0.17 – 0.37 | Improves strength, hardness, and acts as a deoxidizer |
| Manganese (Mn) | 0.50 – 0.80 | Enhances hardenability and tensile strength |
| Chromium (Cr) | 0.80 – 1.10 | Increases wear resistance, hardenability, and corrosion resistance |
| Phosphorus (P) | ≤ 0.035 | Impurity, kept low to avoid brittleness |
| Sulfur (S) | ≤ 0.035 | Impurity, kept low to improve machinability |
| Copper (Cu) | ≤ 0.30 (optional) | May be added to improve corrosion resistance |
| Nickel (Ni) | ≤ 0.30 (optional) | Can enhance toughness |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | ≤ 0.15 (optional) | Sometimes added to increase strength and hardenability |
Carbon is the primary element influencing the strength and hardness of 40Cr steel. The carbon content, ranging from 0.37% to 0.44%, ensures that the steel has enough strength and hardness for various mechanical applications while maintaining sufficient ductility for forming and machining.
Silicon serves as a deoxidizer in steel manufacturing. It removes oxygen, preventing gas bubbles and impurities. Additionally, silicon improves the overall strength and hardness of the steel, contributing to its robustness.
Manganese boosts hardenability and tensile strength, refines grain size for a uniform microstructure, and reduces brittleness, enhancing durability under stress.
Chromium, present at 0.80% to 1.10%, is crucial for improving hardenability, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance. It helps the steel maintain its strength at elevated temperatures, making it suitable for high-stress applications.
Both phosphorus and sulfur are considered impurities in steel. They are kept at low levels (≤ 0.035%) to avoid adverse effects on the steel’s toughness and machinability. Excessive phosphorus can lead to brittleness, while sulfur can cause hot shortness during hot working processes.
The specific balance of elements in 40Cr steel provides a combination of properties that make it highly effective in various industrial applications:
Understanding the chemical composition of 40Cr steel and the role of each element is crucial for selecting the appropriate material for specific engineering applications, ensuring optimal performance and durability.
Tensile strength is a crucial property of 40Cr steel, indicating its ability to resist forces that try to pull it apart. Typically, 40Cr steel exhibits a tensile strength ranging from 810 MPa to over 1000 MPa, and when subjected to appropriate heat treatment, such as quenching and tempering, its tensile strength can reach up to 1300 MPa. This high tensile strength makes 40Cr steel suitable for applications requiring materials that can endure significant stress without failure.
The yield point of 40Cr steel shows the stress level at which it starts to deform plastically. For 40Cr steel, the yield strength is approximately 785 MPa. This property is crucial in engineering applications where the steel is subjected to loads that should not cause permanent deformation. The high yield strength ensures that 40Cr steel components maintain their shape and structural integrity under operational loads.
Hardness is a measure of a material’s resistance to deformation, particularly permanent indentation. For 40Cr steel, hardness values can vary depending on the heat treatment process applied. After quenching and tempering, 40Cr steel can achieve a hardness level suitable for applications where wear resistance is essential. This property is particularly beneficial in manufacturing parts like gears and shafts, which are subjected to friction and wear.
Impact resistance measures how well a material can absorb energy from sudden impacts without breaking. For 40Cr steel, the impact absorbing energy is typically greater than or equal to 47 J. This property ensures that 40Cr steel can withstand dynamic and impact loads, making it suitable for components in high-stress environments such as automotive and machinery applications.
Elongation after break is a measure of ductility, indicating how much a material can stretch before breaking. For 40Cr steel, the elongation after break is at least 9%. This level of ductility allows 40Cr steel to undergo significant deformation before breaking, which is essential for shaping processes like forging and machining.
Reduction of area is another measure of ductility, representing the reduction in cross-sectional area of a material specimen after fracture. For 40Cr steel, this value is typically at least 45%. A high reduction of area value indicates good ductility and toughness, ensuring that the steel can withstand high stress and deformation without fracturing.
Quenching is a process designed to increase the hardness and strength of 40Cr steel. This involves rapid cooling to transform the steel’s microstructure into martensite, a hard and brittle phase.
Quenching results in a hard but brittle microstructure. It significantly increases the steel’s hardness and strength but also introduces internal stresses and reduces toughness, necessitating further treatment like tempering.
Tempering aims to reduce the brittleness caused by quenching while retaining sufficient strength and hardness.
Tempering improves toughness and ductility by decomposing some of the martensite into tempered martensite or bainite. This process balances the hardness and toughness of the steel, making it more suitable for practical applications.
Annealing helps relieve internal stresses, improve machinability, and prepare the steel for subsequent heat treatment.
Annealing refines the grain structure, softens the steel, and improves its ductility and toughness. This process makes the steel easier to machine and form.
Normalizing aims to refine grain size and homogenize the microstructure, thereby enhancing mechanical properties and cutting performance.
Normalizing results in a more uniform and finer grain structure than annealing. This leads to improved strength and toughness without excessive hardness.
For example, a heat treatment cycle for a camshaft application may involve:
This cycle achieves a balance of hardness, strength, and toughness suitable for components subjected to heavy loads and wear.
40Cr steel is a medium carbon chromium alloy structural steel known for its excellent strength, toughness, and wear resistance. It typically contains about 0.40% carbon and roughly 1% chromium, with some variations including small amounts of molybdenum to enhance performance. This composition imparts good hardenability and mechanical properties suitable for a wide range of engineering applications, especially in machinery manufacturing.
| Property / Steel Type | 40Cr Steel | 4140 Steel | 45 Steel | 40MnB & Similar Alloys |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Content | ~0.40% | ~0.40% | ~0.45% | Varies (Mn, B additions) |
| Chromium Content | ~1.0% | ~1.0% | Lower (less Cr) | Usually lower Cr, more Mn/B |
| Hardenability | Medium, water/oil quenchable | Comparable, slightly different hardenability profiles | Lower than 40Cr | Varies; alternatives to 40Cr with similar hardenability |
| Tensile & Yield Strength | High | Similar to 40Cr | Slightly lower | Comparable depending on alloying |
| Wear Resistance | High, due to Cr | High | Lower | Usually good, depending on alloy |
| Toughness | Excellent | Good | Moderate | Good, sometimes superior for toughness |
| Machinability | Moderate (~60%) | Comparable | Better machinability | Varies |
| Weldability | Limited, prone to cracking | Better weldability than 40Cr | Better weldability | Often better weldability |
| Typical Applications | Gears, shafts, engine parts, heavy-duty components | Similar to 40Cr; also used in tooling | General machine parts | Used as cost-effective alternatives in some cases |
Both 4140 and 40Cr are chromium-molybdenum alloy steels with similar carbon content and mechanical properties. However, 4140 may have slightly better toughness and weldability, making it popular in tooling and structural applications. 40Cr is often preferred for its higher wear resistance and surface hardness, essential for components requiring durability.
45 steel has higher carbon content but generally lower chromium, resulting in lower hardenability and wear resistance. 40Cr surpasses 45 steel in these aspects, making it more suitable for components requiring surface hardening and durability.
These steels may be used as substitutes for 40Cr in some applications to reduce chromium costs. They typically maintain similar mechanical properties but may differ in hardenability, toughness, and weldability. Selection depends on specific performance requirements and manufacturing considerations.
40Cr steel’s balance of strength, toughness, wear resistance, and machinability makes it ideal for:
Its versatility is enhanced by surface hardening treatments (quenching, tempering, nitriding) that allow the steel to meet diverse operational demands.
40Cr steel is recognized globally, with several international standards providing equivalent grades that share similar chemical compositions and mechanical properties. These equivalents ensure compatibility and performance across different regions and industries, allowing for interchangeability in engineering applications.
| Country/Standard | Equivalent Grade | Standard Code | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| China | 40Cr | GB/T 3077 | Original Chinese standard |
| USA | 5140 | ASTM A29/A29M | Common alloy steel grade |
| Germany | 41Cr4 (1.7035) | DIN EN 10083-3 | Widely accepted European grade |
| Japan | SCr440 | JIS G4104 | Japanese industrial standard |
| France | 41Cr4 (1.7035) | NF EN 10083-3 | French equivalent |
| UK | 41Cr4 (1.7035) | BS EN 10083-3 | British standard equivalent |
| ISO | 41Cr4 | ISO 683-1 | International standard |
When 40Cr steel is unavailable or specific mechanical requirements need to be met, several alternatives offer similar or enhanced properties. These alternatives include steels with different alloy compositions and performance characteristics.
| Steel Type | Notes |
|---|---|
| 4140 Steel | Often chosen for components needing increased ductility, such as heavy-duty machinery parts. |
| Manganese-Boron and Silicon-Manganese Steels | Examples include 40MnB, 45MnB, 35SiMn, 42SiMn, 40MnVB, and 42MnV. They provide good hardenability and toughness, making them suitable for mold manufacturing and medium-load mechanical parts. |
| 4340 Steel | Ideal for parts exposed to extreme stress and requiring high fatigue resistance, such as aerospace components and high-performance machinery. |
Here’s a comparison of the mechanical properties between 40Cr steel and 4140 steel:
| Property | 40Cr Steel | 4140 Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Yield Strength | ~800 MPa | Comparable (~800 MPa) |
| Tensile Strength | ≥810 MPa | Similar or slightly higher |
| Elongation | ~15% | ~25% (higher ductility) |
| Impact Toughness | Good, low temp. | Slightly better impact toughness |
| Hardenability | Good | Good |
| Fatigue Strength | High | High |
40Cr steel and its equivalents are used in machine parts, medium-load components, mold manufacturing, and automotive parts, balancing strength and toughness.
40Cr steel is widely used in the automotive industry because it combines strength, hardness, and wear resistance. The steel’s mechanical properties are enhanced through heat treatment processes such as quenching and tempering, making it ideal for high-performance and durable automotive components.
Gear shafts and sleeves are essential parts that need high strength and fatigue resistance to manage power transmission stresses. 40Cr steel’s excellent hardenability and wear resistance ensure that these parts can endure long-term operation without significant wear or failure.
Connecting rods and crankshafts are subjected to cyclic loading and must maintain structural integrity under dynamic stresses. The toughness and durability of 40Cr steel make it an excellent choice for these components, ensuring reliable performance and longevity.
Axles and screws in automotive applications benefit from the wear resistance and machinability of 40Cr steel. These properties ensure precision fitting and a long service life, even under demanding conditions.
In the machinery and equipment manufacturing sector, 40Cr steel is favored for its balance of mechanical strength and machinability, making it suitable for medium-strength components.
40Cr steel shafts are crucial for efficient power transmission in various machines. The steel’s wear resistance and strength reduce maintenance requirements and extend the operational life of these components.
Cutting tools such as drill bits and milling cutters benefit from the hardness and toughness of 40Cr steel. These properties help maintain tool sharpness and precision, even under high stress, ensuring consistent performance in manufacturing processes.
Hydraulic components, which operate under high pressures, require materials with durability and resistance to wear. 40Cr steel’s mechanical properties make it suitable for these applications, ensuring reliable and long-lasting performance.
The construction industry uses 40Cr steel for its high strength, toughness, and load-bearing capacity. These properties are critical for ensuring the safety and longevity of structures and components.
40Cr steel is used in structural beams and columns in buildings and bridges, where high strength and toughness are essential. The steel’s ability to resist deformation and wear under dynamic forces ensures the stability and durability of these structures.
Fasteners such as bolts and nuts made from 40Cr steel provide secure and stable connections capable of withstanding heavy loads and environmental stress. The steel’s mechanical properties ensure reliable performance in construction applications.
Components like gears and shafts in construction machinery, such as cranes and earth-moving equipment, utilize 40Cr steel for its durability and strength. These properties are essential for the efficient and safe operation of heavy machinery.
40Cr steel is employed in the energy and power sector for applications that demand toughness and wear resistance under high stress.
Wind turbine components, including shafts and gears, require high strength and fatigue resistance to operate reliably under fluctuating loads and environmental conditions. 40Cr steel’s mechanical properties make it suitable for these demanding applications.
Drilling tools in the oil and gas industry face extreme mechanical stress and abrasive conditions. 40Cr steel’s toughness and wear resistance extend the life of these tools, ensuring efficient and reliable operation.
Structural and mechanical parts in turbines and generators benefit from 40Cr steel’s mechanical stability. The steel’s properties ensure that these components can withstand the high stress and wear conditions typical in power generation environments.
The defense sector uses 40Cr steel for its strength, toughness, and wear resistance, which are vital for reliable performance in harsh conditions.
Components in armored vehicles must endure impact and mechanical stress. 40Cr steel’s mechanical properties ensure that these parts can withstand the rigors of military use.
Protective gear and equipment made from 40Cr steel provide reliable performance in harsh conditions. The steel’s toughness and durability are essential for ensuring the safety of military personnel.
Military tools and machinery components require durable materials that maintain functionality under extreme use. 40Cr steel’s strength and impact resistance make it suitable for these applications, ensuring long-term reliability and performance.
40Cr steel is a versatile and widely used alloy structural steel that combines high strength, wear resistance, and durability with cost-effectiveness. Its well-balanced chemical makeup, especially the inclusion of carbon and chromium, greatly enhances its mechanical properties, making it suitable for various industries such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and machinery manufacturing.
The mechanical properties of 40Cr steel, such as high tensile strength, yield strength, and impact toughness, make it suitable for medium to high-strength applications, while its efficient hardenability allows effective quenching and tempering, enhancing its performance in demanding conditions. Additionally, the steel exhibits good machinability, which simplifies processing and reduces manufacturing costs.
Heat treatment processes like quenching, tempering, annealing, and normalizing play a critical role in optimizing the mechanical properties of 40Cr steel. These treatments alter the steel’s microstructure, improving its hardness, strength, and toughness. Understanding these processes is essential for choosing the right heat treatment parameters to achieve desired performance characteristics.
When compared to steels like 4140 and various manganese-boron and silicon-manganese alloys, 40Cr steel shows superior wear resistance, hardenability, and overall mechanical performance. While 40Cr steel has limited weldability, its advantages in other areas make it a preferred choice for components subjected to high stress and wear.
Several international standards provide equivalent grades to 40Cr steel, ensuring compatibility and performance across different regions and industries. Alternatives like 4140 steel and other alloyed steels can be chosen to meet specific mechanical requirements or for cost considerations.
40Cr steel’s balanced properties make it ideal for a wide range of applications, including automotive components, machinery manufacturing, construction, energy and power sector, and defense and military applications. Its ability to undergo various surface treatments further enhances its suitability for parts requiring high durability and wear resistance.
The demand for high-performance materials like 40Cr steel is expected to grow as industries continue to seek reliable and cost-effective solutions for their engineering needs. Advances in heat treatment technologies and surface enhancement processes will further expand the applications of 40Cr steel, ensuring its continued relevance in the manufacturing and metalworking sectors.
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
40Cr steel is a widely utilized alloy steel known for its excellent mechanical properties, making it suitable for engineering and machinery applications. The main properties of 40Cr steel include:
40Cr steel exhibits a balance of hardness, strength, and toughness due to its chromium and carbon composition. It is also known for its good wear resistance and ability to undergo surface hardening treatments. These properties make it ideal for high-strength components in the automotive and agricultural machinery industries.
The equivalents of 40Cr steel vary by country and standard, and they include several similar alloy steels that offer comparable mechanical properties. For instance, in the United States, the equivalents are ASTM/AISI 5140 and G51400. In Germany, the equivalent grades are 41Cr4 and 1.7035 according to DIN standards. France uses 42C4 and 41Cr4 under NF standards, while in Japan, the equivalents are SCr440 and SCr440H as per JIS standards. The UK also recognizes 41Cr4 and 1.7035 under BS standards. Additionally, ISO standard lists 41Cr4 as an equivalent. These equivalents share similar characteristics such as high tensile strength, good hardenability, and excellent wear resistance, making them suitable for similar applications in the automotive and machinery sectors.
40Cr steel is widely used in various industries due to its excellent combination of strength, toughness, wear resistance, and machinability. In the machinery and equipment manufacturing sector, it is commonly used for gears, shafts, precision tools, and hydraulic components, benefiting from its high tensile strength and durability. In the automotive industry, 40Cr steel is employed in making crankshafts, gears, axles, and engine components, where its fatigue resistance and machinability are crucial. The construction industry uses 40Cr steel for structural elements such as beams, columns, and fasteners, owing to its high strength and toughness. Additionally, the energy sector utilizes 40Cr steel in drilling equipment, wind turbine components, and pipeline systems due to its wear resistance and reliability under harsh conditions. Lastly, the defense and military sectors also use 40Cr steel for various components requiring robust performance and durability.
Heat treatment processes such as quenching, tempering, annealing, and normalizing significantly enhance the mechanical properties of 40Cr steel. Quenching involves heating the steel to 800-880°C and rapidly cooling it, resulting in increased hardness but brittleness, which is mitigated by subsequent tempering at around 520°C. Tempering relieves internal stresses and balances hardness with toughness, improving wear resistance and overall strength. Annealing is used to relieve stresses and improve ductility by heating and slowly cooling the steel. Normalizing refines the microstructure and improves cutting performance by heating and cooling the steel in air. These treatments collectively improve hardness, strength, toughness, and wear resistance, making 40Cr steel suitable for high-performance applications in industries such as automotive and agriculture.
40Cr steel is a medium carbon, chromium-alloyed structural steel known for its balanced mechanical properties, including high tensile strength, yield strength, and good toughness. When compared to other similar steels, such as 4140, 45#, and 35CrMo, 40Cr stands out in several ways.
40Cr has a tensile strength of 810-1000+ MPa and a yield strength of around 785-800 MPa, which are higher than those of 4140 steel (~650 MPa yield strength). This makes 40Cr suitable for applications requiring high strength and toughness. Compared to 45# steel, which has higher carbon content and thus higher hardness, 40Cr offers better ductility and toughness, making it more versatile for dynamic loading conditions.
Additionally, 40Cr is more cost-effective compared to 35CrMo steel, while still providing similar mechanical properties, making it an economical choice for many applications. Heat treatment processes such as quenching and tempering significantly enhance the hardness and wear resistance of 40Cr, making it suitable for high-stress components.
40Cr steel offers several advantages and disadvantages, making it a versatile yet occasionally challenging material for industrial applications.
Advantages of 40Cr steel include its high strength and wear resistance, especially after heat treatments like quenching and tempering, which enhance its mechanical properties significantly. This makes it ideal for components requiring durability and longevity. Additionally, it provides a good balance of hardness and toughness, suitable for parts under heavy loads and impacts. Its versatility and cost-effectiveness also contribute to its widespread use in industries such as automotive and agriculture, where reliability and affordability are crucial. Furthermore, 40Cr steel is relatively easy to process and solder, facilitating the manufacturing of gears, shafts, and other mechanical components.
On the downside, the high carbon content in 40Cr steel can make it difficult to machine, complicating fabrication and potentially increasing production costs and time. It is also more susceptible to corrosion compared to steels with lower carbon content, necessitating additional protective measures in corrosive environments. The high carbon content further results in lower ductility, making the steel more prone to breaking or cracking under stress rather than deforming. Moreover, achieving the optimal properties of 40Cr steel requires heat treatment, which adds to the production cost and complexity.

