Often overlooked but critical to countless mechanical systems, bushings are the unsung heroes of engineering, quietly reducing friction, absorbing shocks, and prolonging the life of moving parts. Yet, selecting the right bushing can feel like navigating a maze of options, with a dizzying array of types, materials, and performance characteristics to consider. Should you opt for a simple sleeve bushing or a high-tech composite material? How do different designs adapt to the unique demands of industries like automotive, aerospace, or heavy machinery?
This guide dives deep into the world of bushings, unraveling their variations, material compositions, and the vital roles they play across diverse applications. Whether you’re fine-tuning industrial equipment or optimizing vehicle performance, understanding these mechanical components can transform efficiency and durability. Ready to discover the perfect fit for your needs? Let’s explore.
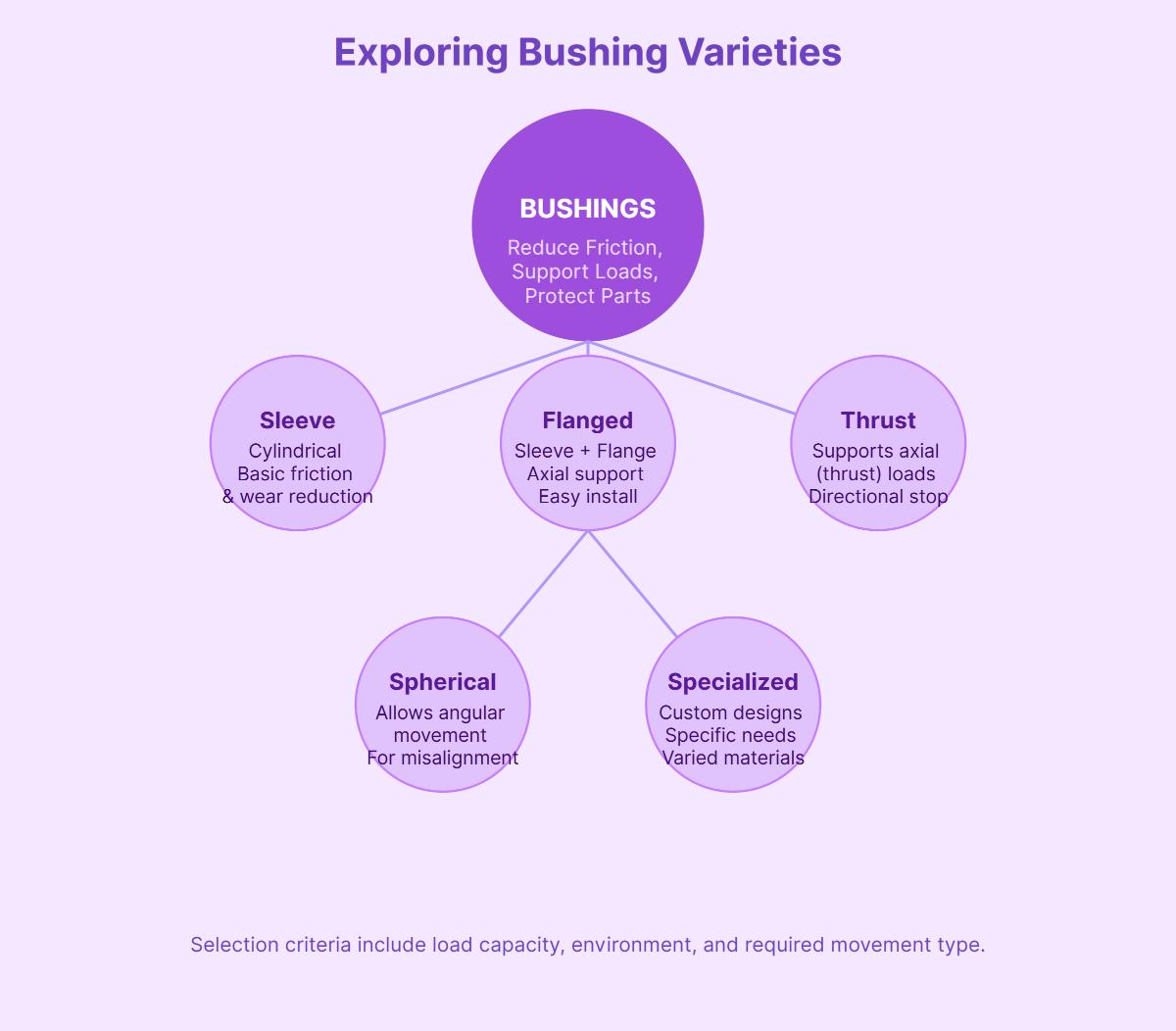
Bushings are essential mechanical components that reduce friction and wear between moving parts in various systems. They serve as a lining for holes, guiding and supporting moving parts, such as shafts or pins, within machinery. They ensure smooth operation and longevity of mechanical systems by preventing direct metal-to-metal contact, which otherwise increases wear and risk of failure.
Bushings primarily reduce friction between moving parts. By providing a smooth, low-friction surface, they help to minimize wear and tear, enhancing the durability and performance of mechanical systems. This is particularly important in high-load or high-speed applications where excessive friction can lead to significant wear and potential component failure.
Bushings also support both radial and axial loads, depending on their design and application. Radial loads act perpendicular to the axis of rotation, while axial loads act along the axis. Correctly chosen and installed bushings manage these loads, keeping moving parts aligned and functioning smoothly.
Bushings are utilized in a wide range of industries and applications due to their versatility and effectiveness.
In the automotive industry, bushings in suspension systems, steering linkages, and transmission components absorb shocks and vibrations, ensuring a smoother ride. Additionally, they reduce noise and enhance the longevity of the vehicle’s moving parts.
Aerospace applications demand lightweight and durable materials, making bushings essential components in landing gear, control systems, and engine mounts. These bushings must withstand extreme conditions, including high temperatures, pressures, and vibrations, ensuring the safety and reliability of aerospace vehicles.
In industrial machinery, bushings are found in gear assemblies, conveyor systems, and hydraulic cylinders. They facilitate the efficient operation of equipment by reducing friction and wear,
Marine environments require bushings that are resistant to corrosion and can operate reliably in wet and saline conditions. Bushings in marine applications are used in propeller shafts, rudder systems, and deck machinery, ensuring the smooth and efficient operation of vessels.
Various types of bushings are designed to meet specific requirements and applications. Some of the most common types include:
Each type of bushing is engineered to address specific challenges, offering unique benefits and performance characteristics.
The material chosen for bushings greatly affects their performance and suitability for different applications. Common materials used in bushings include:
Selecting the appropriate material involves considering factors such as load, speed, environmental conditions, and maintenance requirements.
Sleeve bushings, also called plain or cylindrical bushings, reduce friction between rotating shafts and stationary supports. Typically made from materials such as bronze, brass, steel, or polymers, these bushings provide low-friction support for linear or rotational motion. Sleeve bushings are widely used in industrial machinery, automotive systems, and aerospace applications due to their simple design and ease of installation.
Flanged bushings are similar to sleeve bushings but include a flange on one end. This flange provides axial support and prevents the bushing from moving along the shaft. The flange simplifies mounting and ensures precise alignment in housings. Flanged bushings are commonly used in applications requiring additional retention, such as conveyor rollers and automotive suspension systems.
Thrust bushings are designed to handle axial loads, or forces along the rotational axis. These bushings are commonly used in rotating machinery, such as turbines, pumps, and gear systems, where managing axial forces is crucial to maintaining system stability and performance. Materials like bronze or specialized polymers are often used for thrust bushings to ensure durability and wear resistance under high-pressure conditions.
Spherical bushings are engineered to allow angular movement and accommodate misalignment between mechanical components. These bushings are often used in applications such as automotive suspension systems, industrial linkages, and aerospace control mechanisms. Their ability to pivot and rotate ensures smooth operation in systems subject to dynamic forces or variable alignment.
Split bushings feature a longitudinal cut along their length, allowing them to be easily installed and removed without disassembling adjacent components. This design is particularly beneficial for maintenance-intensive environments, such as heavy industrial machinery, where frequent replacement or inspection is required. Split bushings are typically made from materials such as bronze, steel, or cast iron for high durability.
Self-lubricating bushings, which contain solid lubricants, eliminate the need for external lubrication, making them ideal for remote or harsh environments. These bushings are perfect for applications where regular maintenance is impractical. Common materials for self-lubricating bushings include carbon graphite, bronze impregnated with lubricants, and advanced composites.
Composite bushings are made from a combination of materials, such as polymers, fibers, and fillers, to achieve specific performance characteristics. These bushings excel in applications requiring corrosion resistance, vibration damping, or reduced weight. Composite bushings are increasingly used in industries like automotive and aerospace, where lightweight and durable components are highly valued.
Specialty bushings are customized for specific applications or environments. Examples include:
Specialty bushings are designed to address specific challenges, offering optimized solutions for demanding applications.
Choosing the right bushing material is essential for achieving durability and efficient performance. Different materials offer various characteristics, making them suitable for specific applications and operating conditions.
Characteristics: Bronze bushings are known for their high wear resistance and good thermal conductivity. They have excellent load-bearing capacity and can operate under high loads and speeds. Bronze is also self-lubricating, which reduces maintenance requirements.
Applications: These bushings are widely used in industrial machinery, automotive components, and heavy-duty applications where durability and frequent movement are required.
Characteristics: Steel bushings are celebrated for their strength, durability, and high load-bearing capacity. However, they tend to have limited corrosion resistance and a higher friction coefficient compared to other materials.
Applications: Suitable for applications demanding high strength and load capacity, such as heavy machinery and high-stress environments.
Characteristics: Polymer bushings, including PTFE, PEEK, PPS, and Nylon, offer self-lubricating properties, high-temperature resistance, and chemical resistance. These materials are ideal for environments requiring low friction and where lubrication is challenging.
Applications: Polymer bushings are used in environments requiring low friction, chemical resistance, and where lubrication is challenging.
Characteristics: Carbon-Graphite bushings are ideal for high heat and corrosive environments. They are self-lubricating and resistant to chemicals and solvents.
Applications: Ideal for chemical and pharmaceutical industries, as well as applications with high temperatures and corrosive conditions.
Characteristics: Metal-polymer bushings blend the durability of metals with the smooth, flexible properties of polymers. These bushings are versatile and can be tailored to meet specific performance requirements.
Applications: Used in a wide range of industries, including automotive, industrial machinery, and aerospace, offering a balance of durability and low maintenance.
Characteristics: Bimetallic bushings are made by combining different metals, enhancing their wear resistance and load capacity. This construction allows for the advantages of each metal to be utilized effectively.
Applications: These bushings are versatile and can be customized for specific applications, including automotive engines and heavy-duty industrial equipment.
Strengths: High load-bearing capacity, durability, and thermal conductivity. Suitable for high-stress applications.
Limitations: Often require lubrication, higher friction coefficients, and may have limited corrosion resistance.
Strengths: Low friction, self-lubricating, resistant to chemicals and corrosion. Suitable for environments where lubrication is impractical.
Limitations: Generally lower load capacity compared to metals, can have issues with UV and moisture resistance.
Composite bushings combine materials to deliver improved durability and performance:
Composite bushings are increasingly favored in industries where performance, durability, and low maintenance are critical.
The strength of bushing materials plays a key role in determining their suitability for different applications.
Sustainability is a growing priority, focusing on reducing environmental impact.
Recent advances in bushing materials aim to improve sustainability while maintaining performance.
Biodegradable polymers are gaining traction as eco-friendly alternatives. These materials decompose naturally, reducing environmental impact. Advances in polymer science have led to biodegradable bushings that offer competitive performance for specific applications.
The use of recycled and recyclable composites is another significant advancement. By integrating recycled materials into composite bushings, manufacturers can reduce waste and resource consumption. These composites maintain high performance while promoting a circular economy.
Innovations in manufacturing processes aim to reduce the environmental footprint of bushing production. Techniques such as additive manufacturing (3D printing) allow for precise material usage, minimizing waste. Additionally, new methods for producing metal bushings with lower energy consumption and emissions are being developed.
Considering strength, cost, and sustainability helps engineers choose the right bushing materials, balancing performance with environmental impact.
Bushings are essential components in various industries, performing crucial functions like reducing friction, supporting loads, and extending machinery lifespan. Their adaptability allows them to serve a wide range of applications, from heavy-duty construction equipment to precision medical devices.
In the automotive industry, bushings are vital in suspension systems to absorb shocks, reduce vibrations, and minimize wear on other components, contributing to a smoother ride and improved handling. They also play a critical role in steering systems, where they reduce friction in linkages, ensuring precise and reliable control. Additionally, bushings in transmission systems support rotating shafts and gears, enhancing efficiency and extending component longevity.
The aerospace industry demands materials capable of withstanding extreme conditions, and bushings are integral to several key systems. In landing gear assemblies, they provide essential support and reduce friction, enabling smooth operation during takeoff and landing. In control surfaces such as ailerons and rudders, bushings ensure precise movement by minimizing friction. Bushings in jet engines reduce wear and friction, enhancing the engine’s reliability and performance.
Agricultural machinery operates under harsh conditions and heavy loads, requiring durable components like bushings that reduce friction and wear. In tractors and harvesters, bushings support moving parts, ensuring reliable operation in demanding environments. Similarly, in plows and seeders, they enhance efficiency and durability by supporting rotating and sliding components.
Construction equipment functions in rugged environments where durability is paramount. Bushings in excavators support pivot points and reduce wear on moving parts, ensuring smooth operation and extending the equipment’s lifespan. In bulldozers, bushings reduce friction in tracks and blades, contributing to improved performance and reliability.
In industrial machinery, bushings are essential for maintaining smooth and efficient operation. Pumps and motors rely on bushings to reduce friction on rotating shafts, improving performance and longevity. In conveyor systems, bushings support rollers and moving parts, ensuring consistent operation. Gear assemblies also benefit from bushings, which provide low-friction support for rotating components.
In the medical field, bushings are used in surgical instruments and medical devices to reduce friction and wear, ensuring precision and durability. Stainless steel bushings in surgical tools offer corrosion resistance and biocompatibility, critical for patient safety. In imaging equipment and diagnostic tools, bushings enhance performance by improving the precision of moving parts.
The marine industry requires components that resist corrosion and function reliably in wet and saline environments. Bushings in propeller shafts, often made of bronze or stainless steel, provide durability and ensure smooth operation. In rudder systems, bushings reduce friction, enabling precise and reliable steering for ships and boats.
Selecting the appropriate bushing for a specific application involves considering several critical factors to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Material choice significantly impacts bushing performance, affecting wear resistance, load capacity, and suitability for different environments. Common materials include:
Understanding the load and speed conditions is crucial, especially since high-speed applications need materials with low friction and good thermal conductivity. Considerations include:
The operating environment affects material choice:
Proper installation of bushings is essential to ensure their effectiveness and longevity. The following practices should be followed:
Ensure precise measurements to avoid issues such as misalignment or improper fit:
Maintain a clean installation environment to prevent contamination:
Use the right tools to prevent damage to the bushing or nearby parts:
Regular maintenance can significantly extend the life of bushings and ensure they operate efficiently.
Periodically inspect bushings for signs of wear or damage:
Regular lubrication with appropriate lubricants reduces friction and wear, maintaining optimal performance:
Timely replacement of worn bushings prevents damage to other components:
Different applications may have unique requirements that influence bushing selection and maintenance practices:
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
Bushings are essential components in mechanical systems, designed to reduce friction, support loads, and protect mating parts. They come in various types, each suited to specific applications. The primary types of bushings include:
Each type of bushing is chosen based on the specific requirements of the application, such as load capacity, environmental conditions, and movement type.
Choosing the right material for a bushing is crucial for ensuring the efficiency, durability, and reliability of a mechanical system. When selecting a bushing material, consider the following factors:
By considering these factors, you can select the most suitable bushing material to enhance the performance and longevity of your mechanical system.
Bushings are commonly used in a variety of applications across different industries due to their ability to reduce friction, absorb vibration, and support moving parts, thus enhancing the longevity and performance of equipment. In the automotive industry, bushings are integral to suspension systems, engine mounts, and control arms, where they help reduce vibration and improve handling. In industrial machinery, bushings serve as vibration dampers and support components in conveyor systems, ensuring smooth operation and reducing maintenance needs. HVAC systems utilize bushings in fan motors and blower components to minimize friction and noise, increasing system efficiency. In the aerospace sector, bushings are essential for landing gear and engine mounts, providing impact absorption and vibration isolation. Maritime applications benefit from corrosion-resistant bushings in propeller shafts and rudder systems, ensuring reliable performance in harsh environments. Additionally, bushings are crucial in power transformers for insulation and support of high-voltage conductors, and in medical equipment and renewable energy systems, they help reduce vibration and enhance operational stability.
To ensure the longevity of your bushings, regular maintenance and proper installation are crucial. Start by conducting periodic inspections to identify any signs of wear, such as cracks, deformities, or excessive wear. For rubber bushings, keep them clean and use silicone-based lubricants to prevent debris accumulation. For metallic bushings, like bronze, use high-quality lubricants and follow manufacturer recommendations. Ensure proper alignment and clearances during assembly to minimize stress.
Oilless bushings require regular cleaning to maintain their self-lubricating properties. For linear bushings, adhere to recommended load capacities and lubrication schedules. Following these practices will help maintain the performance and extend the lifespan of your bushings, reducing maintenance costs and system downtime.
Common challenges in bushing installation include ensuring proper cleanliness and surface preparation, which are critical for preventing contamination that could hinder performance. Misuse of lubricants, such as using inappropriate types or amounts, can lead to improper seating and premature wear. Selecting the right installation tools and techniques is vital to avoid damaging the bushing during the process. Correct alignment and minimizing dimensional errors are necessary to prevent system vibrations and uneven loads, which can reduce bushing lifespan. Additionally, understanding the material properties and design considerations for the specific application ensures durability and effective performance. Addressing these challenges can significantly enhance the longevity and efficiency of bushings.
Yes, there are eco-friendly bushing options available. Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on sustainable materials and designs to minimize environmental impact. For example, plastic bushings, such as those offered by Igus, are lubrication-free, lightweight, and require less energy to produce compared to metal alternatives, reducing carbon footprint. Aluminum bronze bushings, like those from SelfLube, are fully recyclable and have extended lifespans, reducing material usage and waste. Lead-free bronze bushings eliminate toxic metals, ensuring safety and compliance with environmental regulations, while also being durable and recyclable. Additionally, eco fluid bushings from Trench Group use biodegradable insulation and are designed for long maintenance-free periods, further reducing environmental impact. These options demonstrate that eco-friendly bushings can enhance performance and sustainability in various applications.

