Imagine you’re piecing together a complex puzzle, where each piece needs to fit seamlessly for the entire picture to make sense. In the world of mechanical and piping systems, couplers, couplings, and adapters are those critical pieces that ensure everything connects perfectly. But what exactly sets them apart, and why are they so vital? This comprehensive guide will demystify these essential components, breaking down their definitions, differences, and applications.
You’ll discover how couplers and couplings serve distinct roles, with couplers primarily linking similar components and couplings providing flexibility and alignment in mechanical systems. We’ll also delve into the various materials used to manufacture these connectors, and why the choice of material matters. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of how these elements work together to maintain the integrity and efficiency of intricate systems.
Ready to unlock the secrets of these vital connectors? Let’s dive in and explore the fascinating world of couplers, couplings, and adapters.
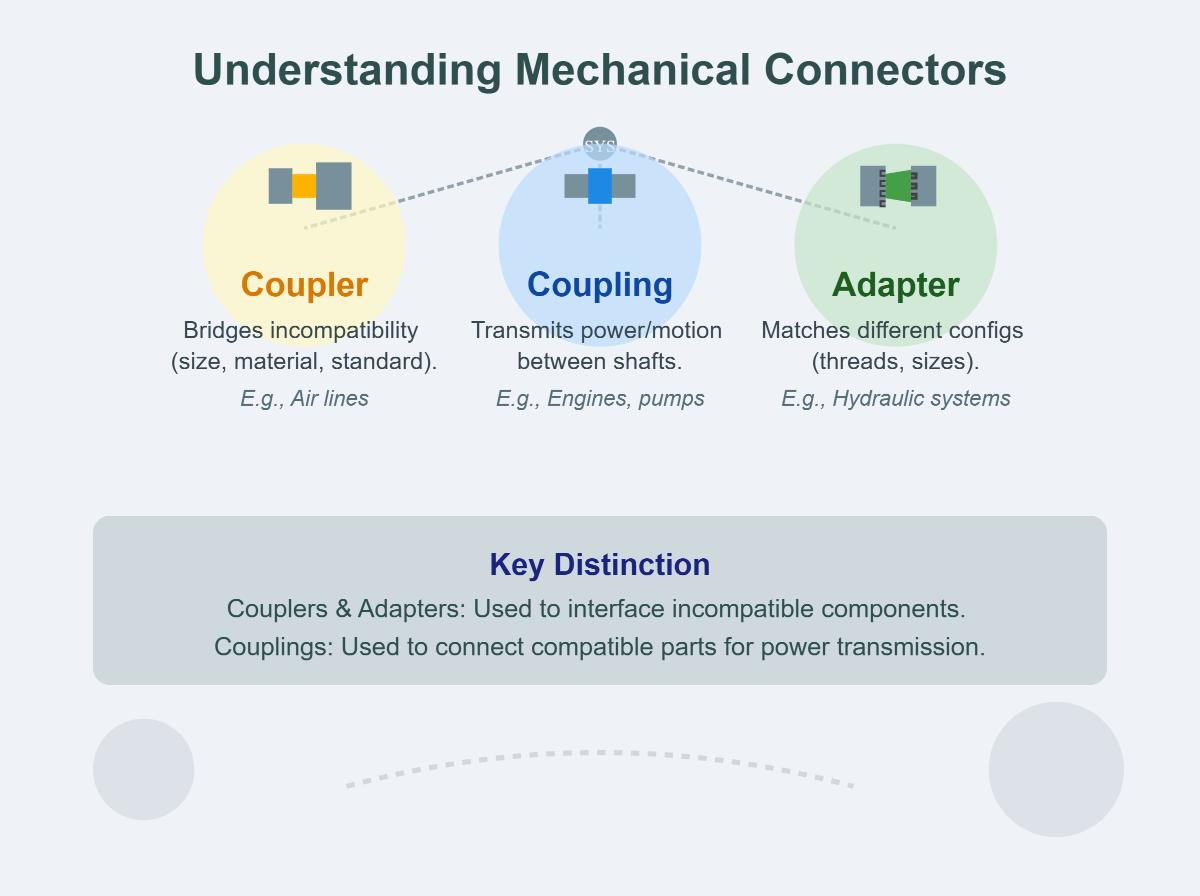
A coupler is a device that connects two parts, such as in a plumbing or electronic system, to transfer signals, fluids, or power. Couplers are designed to enable quick and efficient connections and disconnections, which is especially useful in systems that require frequent assembly and disassembly. In various applications, couplers can be found in hydraulic, microwave, and fiber optic systems.
A coupling is a mechanical device used to connect two shafts together at their ends for the purpose of transmitting power. Couplings are primarily used in mechanical systems to join two pieces of rotating equipment, allowing them to operate as a single unit. Unlike couplers, couplings are typically intended for more permanent connections and are designed to handle the stresses and misalignments, which can happen when the shafts are not perfectly in line, that can occur during operation.
An adapter is a component used to connect parts with different sizes, threads, or types. They ensure compatibility and a leak – free, secure connection, which helps maintain the system’s integrity.
Couplers, couplings, and adapters are vital in mechanical and piping systems for reasons like efficiency, reliability, flexibility, and safety. First, they facilitate quick and easy connections and disconnections, saving time during maintenance and repairs. Second, they ensure secure and stable connections, which is critical for the safe and effective operation of systems. Third, they provide the flexibility to connect components with different specifications, making systems more versatile. Fourth, they reduce the risk of leaks, misalignments, and other issues that can lead to system failures.
Visual diagrams can greatly enhance understanding by showing the physical appearance of couplers, couplings, and adapters, and their application in various systems. For instance, a hydraulic system diagram could illustrate how a coupler connects two hoses, a coupling transfers power between pumps, and an adapter links a hose to a valve. These visual representations make it easier to grasp the differences between these components and their roles in different systems.
Couplers, couplings, and adapters are essential components for maintaining the integrity and functionality of piping networks, including water supply systems, industrial pipelines, and HVAC systems.
In water supply systems, couplers are often used to connect pipes of varying materials and sizes. For instance, ductile iron couplings are highly valued for their durability and compatibility with various pipe materials, such as steel, cast iron, and PVC, ensuring a leak-free connection essential for maintaining water pressure and preventing contamination.
Industrial pipelines, which transport fluids and gases, rely on flexible couplings for their ability to accommodate thermal expansion, contraction, and slight misalignments. These couplings are especially useful in industries where piping systems undergo frequent modifications and repairs. Their flexibility helps reduce stress on the pipes and prevents potential damage.
In HVAC systems, adapters are often used to connect components with different thread types or sizes. For example, an adapter may be required to link a copper pipe to a steel valve, ensuring a secure and efficient connection. This adaptability is essential for maintaining the system’s integrity and performance. Properly selected and installed adapters help prevent leaks, ensure optimal flow rates, and accommodate thermal expansion and contraction.
Mechanical systems, such as engines, machinery, and testing equipment, utilize couplers, couplings, and adapters to ensure the smooth transmission of power, motion, and signals between various components.
In mechanical power transmission systems, couplings are essential for connecting rotating shafts. Rigid couplings are used when precise alignment is necessary, such as in high-speed machinery where even a slight misalignment can cause significant issues. Flexible couplings, on the other hand, can absorb minor misalignments and vibrations, making them ideal for applications where alignment precision is challenging to maintain.
Machinery and equipment often require quick and reliable connections between hoses, pipes, and other components. Couplers facilitate these connections, allowing for easy assembly and disassembly during maintenance or replacement. For example, quick-connect couplers in hydraulic systems allow for fast changes of hydraulic lines, reducing downtime and enhancing operational efficiency.
In testing equipment, such as electromechanical testing machines, adapters are used to connect grips and fixtures with different thread types or sizes. This versatility allows for a wide range of testing configurations, accommodating various sample sizes and testing conditions. Adapters ensure that the testing setup is secure and reliable, which is crucial for obtaining accurate and repeatable results.
In residential and commercial plumbing systems, flexible couplings are frequently used to repair damaged pipes. These couplings can connect pipes of different materials and sizes, providing a quick and effective solution to leaks or breaks. Their ability to accommodate slight misalignments makes them particularly useful in older buildings where pipe alignments may not be perfect.
Hydraulic systems in construction and manufacturing equipment often use adapters to connect hoses and fittings with different thread types. This adaptability ensures that hydraulic components from various manufacturers can be integrated seamlessly, enhancing the system’s versatility and functionality.
In industrial machinery, magnetic couplings are employed to transfer power without physical contact. This is especially beneficial in applications where isolation of the driving and driven components is required, such as in pump systems handling hazardous or sensitive fluids. Magnetic couplings prevent leaks and reduce wear and tear on the components, extending the machinery’s lifespan.
Stainless steel is widely used to make couplers, couplings, and adapters because it resists corrosion and is very strong. It is particularly suitable for harsh environments where exposure to chemicals, moisture, or extreme temperatures is common. Stainless steel components are frequently used in water supply systems, chemical processing, and food and beverage industries.
Brass, known for its malleability and resistance to corrosion, is ideal for water and gas systems as it can withstand high temperatures and pressures without degrading. Brass couplers and adapters are often found in plumbing and HVAC systems due to their durability and ease of installation.
Carbon steel is strong and affordable, making it common in industrial piping. It is strong enough to handle high – pressure applications and is often used in the construction of couplings that require robust performance. However, carbon steel is prone to corrosion, so it is typically coated or treated to enhance its longevity.
Aluminum is lightweight and corrosion – resistant, making it a suitable material for applications that require less strength but more flexibility. It is often used in industries where weight reduction is crucial, such as aerospace and automotive sectors. Aluminum couplers and adapters are easy to handle and install, providing reliable connections without adding significant weight to the system.
Ductile iron is extensively used in water supply systems due to its strength and durability. It can withstand high pressures and resist wear and tear, making it ideal for long – term applications. Ductile iron couplings are often used to connect large – diameter pipes in municipal water and wastewater systems, ensuring a secure and leak – free connection.
Casting is a common manufacturing process for producing couplers, couplings, and adapters. This method involves pouring molten metal into a mold to create the desired shape. Casting is suitable for producing complex geometries and large quantities of components. Materials like ductile iron and brass are often cast to form durable and precise fittings.
Machining is a process that involves cutting, drilling, and shaping materials to achieve the final dimensions and specifications. This method is commonly used for manufacturing stainless steel and carbon steel components. Machining ensures high precision and tight tolerances, which are essential for creating reliable and leak – free connections.
Forging shapes metal with compressive forces, like a hammer or press, enhancing its strength and durability, making it perfect for high – stress components like couplings.
Extrusion is a process where a material is forced through a die to create a continuous shape. This method is often used for manufacturing aluminum components, as it allows for the production of long, uniform parts with consistent cross – sections. Extruded aluminum adapters and couplers are lightweight and offer excellent corrosion resistance.
In water supply systems, materials like stainless steel, brass, and ductile iron are preferred for their corrosion resistance and durability. These materials ensure that the couplers and couplings can withstand continuous exposure to water without degrading, maintaining a secure and leak – free connection.
For industrial piping systems, carbon steel and stainless steel are commonly used due to their strength and ability to handle high pressures. These materials are suitable for applications involving the transport of gases, chemicals, and other fluids that require robust and reliable connections.
In HVAC systems, brass and aluminum are often used for their ease of installation and resistance to corrosion. Brass adapters ensure secure connections between different components, while aluminum couplers provide flexibility and reduce the overall weight of the system.
Machinery and power transmission systems benefit from stainless steel and forged aluminum components, which provide the strength and durability to handle dynamic loads and stresses, ensuring reliable operation and a long service life.
The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) establishes standards for designing and manufacturing mechanical components like couplers, couplings, and adapters. These standards ensure that products are safe, reliable, and compatible with other system components.
ASME B31.3 outlines the requirements for piping systems in chemical, petroleum, and other process industries, covering materials, design, fabrication, assembly, and testing to ensure all components, including couplers and couplings, meet safety and performance criteria.
ASME B16.5 specifies the dimensions, tolerances, materials, and pressure – temperature ratings for pipe flanges and flanged fittings. This standard ensures that couplings and adapters in flanged connections are compatible and can handle the system’s operational pressures and temperatures.
ANSI (American National Standards Institute) oversees the creation and use of norms and guidelines that directly impact businesses in nearly every sector. ANSI standards for couplers, couplings, and adapters ensure consistency, safety, and interoperability across different manufacturers and industries.
ANSI B1.20.1 specifies the requirements for the design and performance of pipe threads. This standard ensures that threaded couplers and adapters offer secure, leak – free connections, crucial for maintaining piping system integrity.
ANSI/ISA 75.02 outlines the testing procedures for determining the flow capacity of control valves. Couplings used in control valve assemblies must comply with this standard to ensure accurate flow control and system performance.
Components such as couplers and adapters must be listed and labeled by recognized testing agencies to confirm they meet industry standards. This ensures that these components have been tested for safety and performance, providing confidence in their use.
Regularly inspecting and maintaining couplers, couplings, and adapters is crucial for ensuring they continue to meet industry standards. This involves checking for wear, corrosion, and other issues that could affect system integrity.
Choosing the right materials and construction methods is critical for ensuring that couplers, couplings, and adapters meet the required standards. For example, materials must be able to withstand the specific environmental conditions they will be exposed to, such as high pressures, temperatures, or corrosive substances.
Understanding and adhering to these standards and compliance requirements is crucial for selecting the right couplers, couplings, and adapters, ensuring efficient, safe, and reliable operations in various applications.
In the manufacturing and engineering industries, sustainability is becoming an increasingly hot-button issue. The selection of materials for couplers, couplings, and adapters plays a significant role in promoting sustainable practices.
Innovation continues to drive improvements in the functionality and versatility of couplers, couplings, and adapters.
Adherence to industry standards is essential for ensuring compatibility and safety across different systems.
Understanding these trends and implementing best practices in material selection, design efficiency, and innovation can significantly enhance the sustainability and efficiency of systems that rely on couplers, couplings, and adapters.
Couplers, couplings, and adapters play crucial roles in various industries. Their applications range from plumbing systems to complex machinery, ensuring efficient and reliable operations.
In agricultural and construction machinery, hydraulic coupler adapters are vital for connecting different implements to machines like tractors or skid-steer loaders. For example, a hydraulic adapter can connect hoses with different profiles to a pump, ensuring the equipment works smoothly. This adaptability is essential for quick changes in the field, reducing downtime and enhancing productivity.
Airline couplers are extensively used in industrial pneumatic systems to connect tools and hoses. For example, in an automotive assembly line, quick-connect airline couplers enable workers to swiftly change pneumatic tools, ensuring continuous operation and minimizing delays. Universal couplers can connect different plug styles, offering flexibility and convenience in fast-paced environments.
Flexible couplings are frequently used in residential and commercial plumbing to repair leaks or replace damaged pipes. For example, a flexible coupling can connect a PVC pipe to a cast iron pipe, accommodating slight misalignments and ensuring a leak-free seal. This flexibility is especially useful in older buildings where pipes may be misaligned.
A farm in the Midwest faced challenges with frequent hydraulic hose replacements on their tractors. Using hydraulic coupler adapters, they quickly connected hoses with different threads and profiles, significantly reducing maintenance time. This adaptation led to increased efficiency during planting and harvesting seasons, as the machinery could be quickly repaired and put back to work.
In a manufacturing plant, the use of universal airline couplers allowed for a more flexible pneumatic system. Workers could switch between pneumatic tools without needing multiple couplers, streamlining the process and cutting inventory costs. This improvement led to a 20% increase in production efficiency, as tool changes were faster and more straightforward.
A municipal water supply system faced issues with pipe joint failures due to thermal expansion and contraction. By implementing flexible couplings, they were able to accommodate the thermal movements and prevent pipe stress. This solution not only extended the lifespan of the piping system but also ensured a consistent water supply without interruptions.
In a materials testing laboratory, adapters were used to connect grips and fixtures with different thread sizes to the testing machine. This flexibility allowed the lab to conduct a wide range of tests on various materials without needing multiple machines. The use of adapters significantly reduced setup time and increased the lab’s testing capabilities.
Understanding the practical applications and benefits of these components through real-world examples helps illustrate their importance in maintaining efficient and reliable systems across various industries.
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
A coupler, coupling, and adapter are all components used to connect different parts within mechanical and piping systems, but they serve distinct purposes:
The main difference lies in their purpose and application: couplers and adapters are used to interface incompatible components, while couplings are used to connect compatible parts for power transmission.
Couplers, couplings, and adapters are crucial in plumbing and mechanical systems. Couplers connect two or more pipes in plumbing, useful for repairs, new builds, and stress relief. They come in various materials like brass and PVC. In plumbing, they maintain water flow, connecting backflow preventers. Couplings are used in both plumbing and mechanical systems. In plumbing, they connect pipes of the same or different materials. In mechanical systems, they link machinery components like pumps and motors, ensuring smooth power – transmission. Adapters are used to connect components with different thread sizes or types. In plumbing, they bridge gaps between mismatched fittings. In mechanical systems, especially hydraulic ones, they integrate components from different manufacturers.
Couplers, couplings, and adapters are made from various materials based on application requirements. Steel and carbon steel are popular for their strength and durability, suitable for high – pressure scenarios like in hydraulic systems. Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance, ideal for marine or chemical industries. Brass is strong, durable, corrosion – resistant, and easy to machine, often used with water or mild chemicals. Aluminum is lightweight and corrosion – resistant, used when weight is a concern. Other materials include cast iron for wear – resistant components, copper for piping due to its corrosion resistance, and plastics like polypropylene for chemical – resistant and lightweight applications. The material choice depends on pressure, corrosion resistance, and cost.
Industry standards like ASME and ANSI are crucial in the application of couplers and couplings, ensuring reliability, safety, and compatibility in various systems. The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) sets comprehensive standards, such as ASME B16.11, which specify the requirements for forged fittings, including threaded full couplings. These standards ensure uniformity in design, material selection, and manufacturing processes, thus enhancing performance and safety in high-pressure and high-temperature environments.
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) also plays a significant role, primarily in ensuring compatibility and interchangeability of fittings within broader systems. While ANSI is more commonly associated with flanges, its standards help ensure that couplings integrate seamlessly with ANSI-compliant equipment and pipes, which is vital in industries like oil and gas, petrochemical, and power generation.
Adhering to ASME and ANSI standards ensures that couplers and couplings meet necessary specifications, reducing installation complexities and enhancing operational efficiency in industrial applications.
Recent innovations in coupler and coupling design focus on enhancing adaptability, efficiency, and user convenience. For couplers, advancements include versatile designs that bridge compatibility gaps between different components, such as quick-disconnect couplers that enable fast, tool-free connections in hydraulic systems while resisting environmental factors. Frame couplers for bicycles have also improved, allowing easier disassembly and reassembly for travel.
In coupling design, notable developments include Schmidt offset couplings, which maintain constant angular velocity despite parallel misalignment, and flexible couplings that absorb shocks and dampen vibrations, improving machine stability. Dry disconnect couplings (DDC) have been upgraded to enhance flow capacity and reduce coupling force, making them more efficient for handling liquids, chemicals, and gases. These innovations aim to improve performance and reliability in various applications, from mechanical systems to transportation and industrial settings.
Sustainability trends in the manufacturing of couplers and couplings are increasingly focused on using eco-friendly materials and adopting energy-efficient production methods. Manufacturers are turning to recyclable and biodegradable materials like advanced polymers and composites, which provide durability and reduce environmental impact. Additionally, energy-efficient processes are being implemented to lower the carbon footprint and comply with environmental regulations.
Technological innovations, such as IoT sensors and AI-driven predictive maintenance, are improving manufacturing efficiency and sustainability by enabling real-time monitoring and optimizing resource use. The adoption of circular economy practices, including product designs that allow for disassembly and remanufacturing, extends product lifespans and reduces waste.
Furthermore, data-driven decision-making facilitated by digital transformation helps manufacturers track sustainability metrics and optimize production processes. Sustainable supply chain management, including responsible sourcing and optimized logistics, also plays a crucial role in reducing emissions.
Overall, these trends highlight a move towards more sustainable practices in the coupler and coupling industry, emphasizing environmental responsibility and resource efficiency.

