Washers, though small and often overlooked, play a crucial role in the integrity and functionality of countless mechanical assemblies. Among these, crush washers and flat washers stand out for their unique characteristics and specialized applications. But what exactly sets these two types apart? Is there a clear-cut scenario when one should be favored over the other? In this article, we’ll delve into the distinct differences between crush washers and flat washers, exploring their definitions, functions, and material standards. We’ll also provide practical examples to help you determine the best washer for your specific needs. Ready to become a washer expert? Let’s dive in.
Washers are essential in mechanical assemblies, enhancing the performance and longevity of fasteners. They are widely used in numerous industries, including automotive, aerospace, construction, and manufacturing, to ensure the reliability and integrity of joints and connections. Understanding the differences between washer types is crucial for selecting the right one, as this can significantly impact the assembly’s functionality and safety.
Washers work alongside bolts, screws, and nuts to meet specific mechanical needs. Their primary roles include distributing the load of fasteners, preventing damage to surfaces, reducing the risk of loosening due to vibration, and in some cases, creating a seal to prevent leaks. The choice of washer type depends on the particular requirements of the application, such as the need for sealing, load distribution, or resistance to environmental conditions.
A detailed comparison between crush washers and flat washers is essential for engineers, mechanics, and DIY enthusiasts to make informed decisions. Each type of washer has unique characteristics that make it suitable for particular applications. Knowing these differences helps users choose the right washer for optimal mechanical performance and reliability.
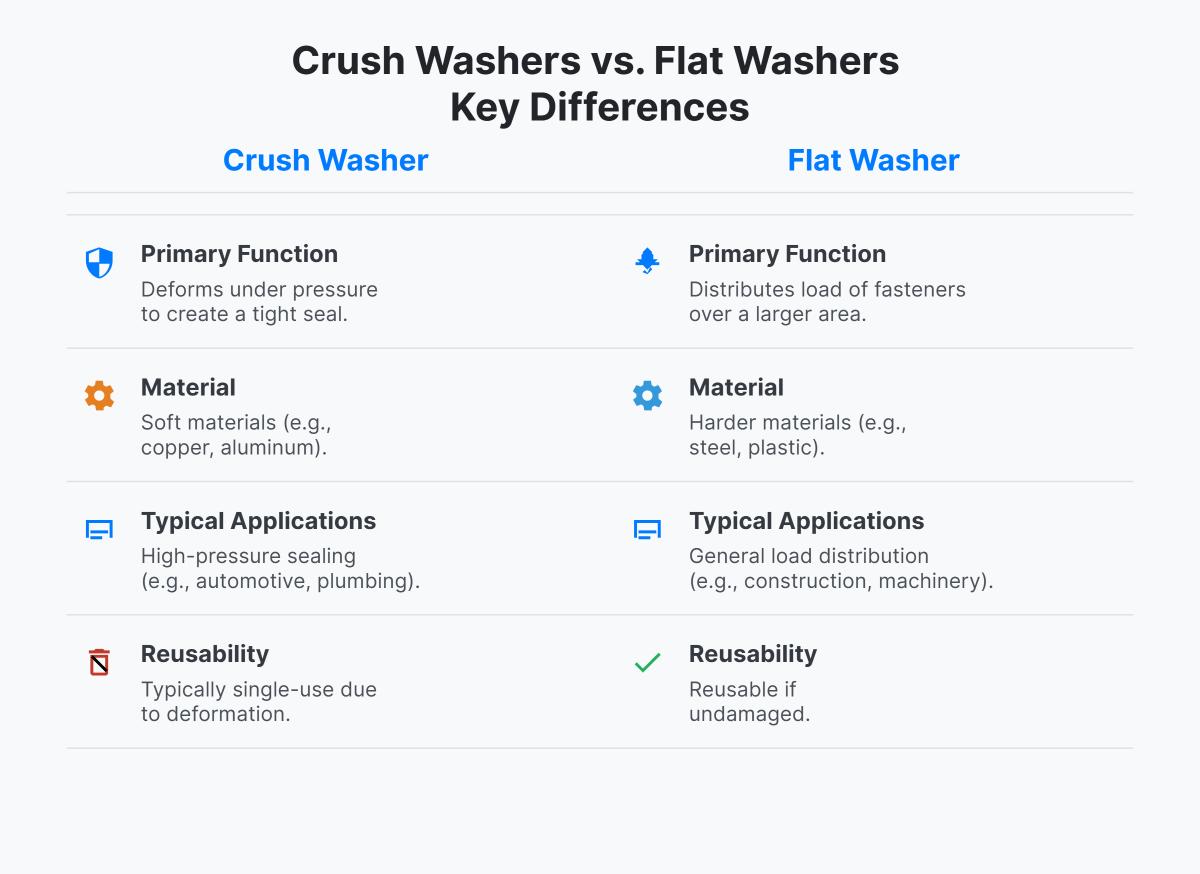
Crush washers, also known as sealing washers, are designed to create a leak – proof seal in fluid or gas systems. Made from softer materials like copper, aluminum, or rubber, crush washers deform under pressure to fill any irregularities between the mating surfaces. This deformation ensures a tight seal that prevents leaks, making them ideal for high – pressure environments. However, due to their deformable nature, crush washers are generally single – use and must be replaced if removed.
Flat washers, on the other hand, are used primarily to distribute the load of a fastener over a larger surface area. This helps prevent damage to the material being fastened and reduces the risk of the fastener loosening due to vibration. Made from harder materials such as steel or plastic, flat washers can be reused multiple times, provided they remain structurally sound. They are versatile components used in a wide range of applications, from construction to machinery assembly.
Comparing these washers clarifies their differences and guides users to the most suitable choice for their needs. By understanding the distinct roles and advantages of each type, users can make more informed choices, ensuring the efficiency and reliability of their mechanical assemblies.
Crush washers, also known as sealing washers, are designed to create a tight seal in assemblies involving fluids or gases. These washers are typically made from softer materials like copper, aluminum, or rubber. The softness allows the washer to deform under pressure, filling any gaps between the surfaces. This ensures a tight seal, preventing leaks and maintaining system integrity.
Flat washers are simple, circular discs used to distribute the load of a threaded fastener such as a bolt or screw. They are usually made from materials like steel, stainless steel, nylon, or rubber. These washers spread the load over a larger surface area, preventing damage to the assembly material and reducing the risk of loosening due to vibration.
Crush washers and flat washers have distinct designs tailored to their specific functions. Crush washers are designed to deform under pressure, creating a tight seal between surfaces. This deformation is crucial for preventing leaks in high-pressure environments. In contrast, flat washers are designed to provide a uniform bearing surface for fasteners. They distribute the load over a larger area, preventing damage to the material and reducing the risk of fastener loosening due to vibration.
The materials used for crush washers and flat washers are chosen based on their specific functions. Crush washers are usually made from softer materials like copper, aluminum, or rubber. These materials are selected because they can deform under pressure, ensuring a secure seal. However, flat washers are made from harder materials such as steel, stainless steel, or plastic. These materials provide the strength and durability needed to distribute loads effectively without deforming under normal conditions.
The performance characteristics and installation requirements of crush washers and flat washers are tailored to their specific applications. Crush washers excel in situations where a leak-proof seal is essential. Their ability to deform and fill surface irregularities makes them ideal for sealing applications in automotive oil pans, hydraulic systems, and gas fittings. However, because they deform during use, crush washers are generally not reusable. They must be installed correctly to ensure a proper seal; incorrect installation can lead to leaks and system failures.
In contrast, flat washers perform best where load distribution is critical. They protect surfaces from damage by spreading the load of the fastener over a larger area and help prevent loosening due to vibration. Flat washers can often be reused multiple times, provided they remain structurally sound, making them a cost-effective choice for many applications. They do not have specific orientation requirements and can be installed in any direction, simplifying the assembly process.
One of the key practical differences between crush washers and flat washers is their reusability. Crush washers are designed for single-use applications. Once they have deformed to create a seal, they cannot be reused, as their sealing ability is compromised. In contrast, flat washers can be reused multiple times if they remain intact and undamaged. This reusability makes flat washers a more economical option for applications where sealing is not a primary concern.
Crush washers are typically crafted from soft metals such as copper and aluminum, or rubber. Soft metals are preferred due to their ability to deform and create a tight seal. Copper is particularly favored for its excellent malleability and high resistance to corrosion, making it suitable for environments with moisture or chemicals.
The primary function of a crush washer is to deform under pressure and create a tight seal. The material must deform permanently without cracking to ensure a tight seal. This deformation fills any gaps between the mating surfaces, preventing leaks in high-pressure environments.
In high-pressure applications like automotive oil pans, hydraulic systems, and gas fittings, crush washers need to meet strict material standards. These washers must withstand specific pressure and temperature conditions, such as those in hydraulic systems. The material should maintain its sealing integrity under high fluid pressures and potential temperature fluctuations.
Flat washers are typically made from harder materials like steel, nylon, or rubber. Harder materials are essential for load distribution and surface protection. Steel offers high strength and durability, making it suitable for applications requiring heavy load distribution. Nylon is often used for its self-lubricating properties and corrosion resistance in certain environments.
Unlike crush washers, flat washers are designed not to deform under normal pressure. The material must maintain its shape and structure to effectively distribute the load of threaded fasteners over a larger surface area. This non-deformation characteristic ensures that the washer can be reused multiple times if it remains structurally intact.
Flat washers are expected to be versatile, available in various sizes and thicknesses to suit different applications. Cost-effectiveness and reusability are key considerations in material standards for flat washers. In construction and machinery assembly, where large numbers of washers are used, a cost-effective and reusable material like steel is a popular choice.
| Characteristics | Crush Washers | Flat Washers |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Soft metals (copper, aluminum) or rubber | Harder materials (steel, nylon) |
| Function-Based Material Requirement | Ability to deform permanently for sealing | Resistance to deformation for load distribution |
| Reusability Impact on Material | Single-use due to deformation, so material must be replaceable | Reusable if intact, so material must maintain long-term integrity |
| Application-Specific Material Considerations | Withstand high pressure and temperature variations in sealing applications | Suit different load levels and environmental conditions in load-distributing applications |
Crush washers are mainly used to create seals that prevent leaks, ensuring the seal’s integrity. This makes them ideal for use in automotive systems like oil pans and brake systems, where preventing leaks is crucial for safety. They are also beneficial in hydraulic systems, as they seal under high pressure to keep hydraulic fluid contained and maintain performance.
Flat washers usually aren’t used for sealing, but they can help distribute the load in applications where a sealing fastener is used. This can be seen in certain gasket applications where the flat washer ensures even pressure distribution, aiding the gasket in forming a seal.
Crush washers are especially effective in high – pressure environments due to their ability to deform and fill surface irregularities, ensuring a leak – proof seal. This makes them ideal for systems with high – pressure fluids or gases, like gas fittings and hydraulic systems.
Flat washers are generally not used as primary sealing components in high – pressure environments. However, they can be used in conjunction with other sealing elements to distribute the load and protect the sealing components from damage.
Although crush washers are not typically designed for load distribution, their ability to deform can provide some load – bearing benefits in specific applications. However, their primary function remains sealing, and they are not the optimal choice for load distribution tasks.
Flat washers are great at spreading the load of a fastener over a larger area, preventing damage. This makes them ideal for use in construction, machinery assembly, and furniture manufacturing, where material integrity is important.
Crush washers are particularly suited for applications where a secure, leak-proof seal is required. Their ability to deform under pressure makes them ideal for sealing fluid and gas connections. Here are some scenarios where crush washers are the optimal choice:
In systems where high-pressure fluids or gases are involved, such as hydraulic systems or gas fittings, crush washers provide a reliable seal. Their deformation under pressure ensures that any gaps between mating surfaces are filled, effectively preventing leaks.
Crush washers are commonly used in automotive applications, particularly in oil pans and brake systems. They ensure that connections remain leak-free, ensuring the vehicle operates safely and efficiently.
Given that crush washers deform permanently, they are best used in applications where components are not frequently disassembled. Once used, they need to be replaced to maintain their sealing integrity.
Flat washers are versatile components used primarily for load distribution. They are suitable for a wide range of applications where it is essential to protect surfaces from damage and ensure the stability of fasteners. Here are some situations where flat washers are the best choice:
Flat washers are excellent for distributing the load of a fastener over a larger surface area. This prevents damage to the material being fastened and reduces the risk of the fastener loosening due to vibration. They are particularly useful in construction, machinery assembly, and furniture manufacturing.
Flat washers can be reused multiple times if they remain intact and undamaged, making them a cost-effective option.
For applications where sealing is not a primary concern, flat washers are the go-to choice. They offer stability and load distribution without deforming, making them ideal for general mechanical assemblies.
To decide between a crush washer and a flat washer, consider the following factors:
| Criterion | Crush Washer | Flat Washer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Sealing | Distributes load evenly |
| Material | Softer metals (e.g., copper, aluminum) or rubber | Harder materials (e.g., steel, nylon) |
| Deformation | Deforms under pressure to create a seal | Maintains shape to distribute load |
| Reusability | Single-use | Reusable if undamaged |
| Ideal Applications | High-pressure fluid/gas systems, automotive | Construction, machinery assembly, furniture |
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
Crush washers and flat washers differ in multiple aspects. Crush washers are designed to deform under pressure, made from soft materials like copper or aluminum, and are used to create a tight seal in high – pressure applications such as automotive and plumbing. They are typically single – use due to their deformation during installation. On the other hand, flat washers are circular plates made of harder materials like steel or plastic. Their main function is to distribute the load of threaded fasteners over a larger area in applications like construction and machinery. They can be reused if undamaged.
You should use a crush washer instead of a regular (flat) washer when the application requires a reliable seal under high-pressure conditions. Crush washers are specifically designed to deform upon tightening, which creates a tight seal by filling gaps or imperfections between two surfaces. This makes them ideal for situations where preventing leaks is critical, such as in automotive oil drain plugs, hydraulic systems, and gas fittings. Unlike flat washers, which primarily distribute load and protect surfaces without significant deformation or sealing properties, crush washers ensure a leak-proof connection but are typically intended for single use due to their deformation during installation.
When selecting a crush washer, you should look for material standards that ensure optimal performance and reliability. Crush washers are typically made from soft metals like copper and aluminum, or sometimes rubber, due to their high ductility. This allows them to deform under pressure and create a tight, leak-proof seal. Key material properties to consider include:
To determine if a washer is suitable for high-pressure environments, consider the material properties, design, and functionality of the washer. Crush washers, typically made from soft metals like copper or aluminum, are designed to deform under pressure, creating a tight seal that is ideal for preventing leaks in high-pressure and high-temperature applications. Their ability to conform to surface irregularities ensures system integrity and operational safety.
In contrast, flat washers are made from harder materials like stainless steel and are used primarily for load distribution and surface protection rather than sealing. They do not deform under pressure, making them less suitable for sealing in high-pressure environments but excellent for high-load applications where durability and resistance to deformation are essential.
Crush washers, typically made from softer metals like copper or aluminum, are primarily designed for sealing applications. However, they can also contribute to load distribution, particularly in scenarios where maintaining an even pressure across mating surfaces is crucial during the sealing process. A practical example of this is in automotive applications, such as sealing oil drain plugs. When the plug is tightened, the crush washer deforms to create a tight seal while simultaneously distributing the load to ensure that the surfaces are pressed together evenly. This helps prevent leaks and maintains the integrity of the connection, showcasing the dual role of crush washers in both sealing and load distribution.
Yes, specific industries have preferences for either crush or flat washers. Crush washers are favored in automotive, plumbing, and aerospace industries due to their excellent sealing under pressure. For example, in automotive, they’re used in oil drain plugs; in plumbing, they prevent leaks in fluid or gas systems. Flat washers, however, are preferred in construction, machinery, and furniture assembly. They distribute load and protect surfaces, like preventing damage to wooden frameworks in construction and guarding sensitive components in machinery.

