Copper tubing may seem like a one-size-fits-all material, but in reality, the type of copper you choose can make or break the success of your project. Whether you’re working on an HVAC system or a residential plumbing installation, understanding the differences between refrigeration copper and plumbing copper is critical. From their material composition to their ability to handle varying pressures and temperatures, these two types of tubing are designed for very different applications. But which one is right for your needs? And why does compliance with standards like ASTM B280 matter? In this article, we’ll dive into the unique properties, applications, and advantages of each type of copper tubing, helping you make an informed decision. Ready to uncover the key distinctions? Let’s get started.
Copper tubing is a versatile material extensively used in plumbing and HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems due to its excellent thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and durability. Its thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and durability make copper tubing essential for efficient and reliable systems, but the type of tubing varies based on the application.
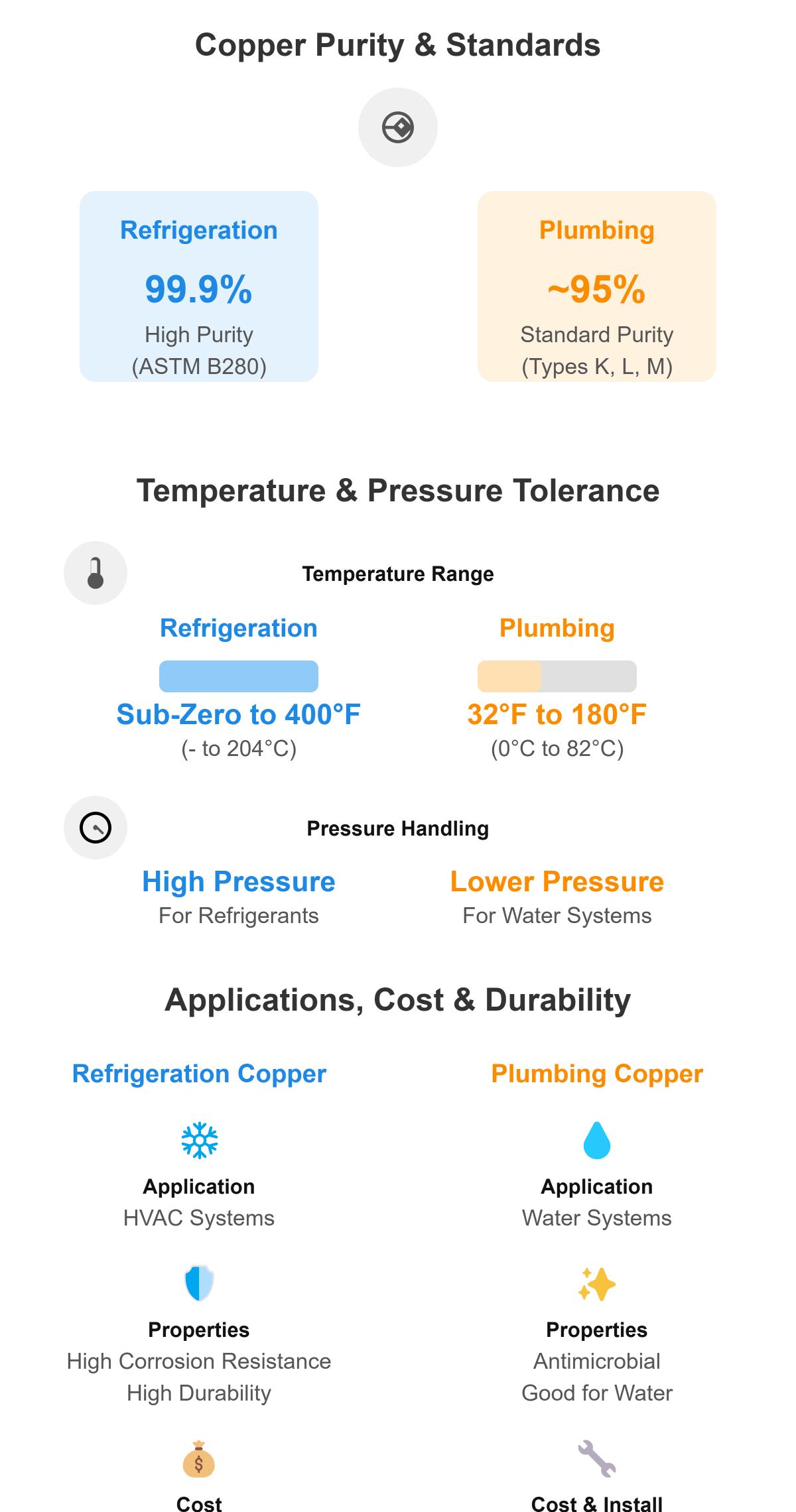
Refrigeration copper, often referred to as ACR (Air Conditioning and Refrigeration) copper, is designed to meet the stringent demands of refrigeration and air conditioning systems. This type of copper tubing is characterized by its high purity (typically 99.9%) and superior corrosion resistance. These properties help prevent contamination and maintain the integrity of the refrigerant.
Refrigeration copper is manufactured to withstand high pressures and temperatures, making it ideal for HVAC applications. It usually comes with polished and capped ends to prevent contamination during installation. Compliance with standards such as ASTM B280 ensures that refrigeration copper meets the necessary quality and performance requirements.
Plumbing copper is used primarily in water supply systems for residential and commercial buildings. Type K has the thickest walls and is used for underground installations, Type L has thinner walls and is ideal for interior plumbing, and Type M, the thinnest, is used in residential water supply systems due to its cost-effectiveness.
Refrigeration copper, with its 99.9% purity, offers better corrosion resistance and performance compared to plumbing copper, which has a purity range of 95-98%.
Refrigeration copper is designed to handle higher pressures and temperatures, often exceeding 400 psi and 400°F (204°C). Plumbing copper, while still durable, is not intended to withstand the same extreme conditions and has varying pressure ratings depending on the type (K, L, or M).
Refrigeration copper often features a polished finish with capped ends to prevent contamination, whereas plumbing copper typically has standard, open ends. Some plumbing copper may also be coated or lined to enhance resistance against aggressive water chemistries.
Refrigeration copper is used in HVAC and refrigeration systems where high pressure and temperature resistance are critical. Plumbing copper is used in water supply systems and various plumbing installations, with different types tailored for specific environments and requirements.
Copper tubing can be joined using soldering/sweating for strong connections, compression fittings for easy installation, flare connections for reliable seals in refrigeration systems, and crimped/pressed connections for permanent and clean joins requiring specialized tools.
Refrigeration copper, also known as ACR copper, is a type of copper tubing designed to withstand the tough requirements of HVAC systems. It is known for its high purity, typically 99.9%, which ensures superior performance and reliability. The manufacturing process of refrigeration copper includes stringent cleanliness standards to prevent contamination and maintain the integrity of the refrigerant.
Refrigeration copper boasts excellent thermal conductivity, which is crucial for efficient heat transfer in refrigeration and air conditioning systems. This allows the tubing to rapidly conduct heat away from the refrigerant, enhancing The even oxide layer on the copper tubing’s surface helps prevent corrosion, which is crucial for the system’s long-term reliability. Furthermore, refrigeration copper is designed to handle high pressures, often exceeding 400 psi. This high-pressure tolerance makes it suitable for modern refrigeration systems that operate under significant pressure to enhance cooling efficiency.
Refrigeration copper is widely used in various HVAC and refrigeration applications, including:
Refrigeration copper must comply with ASTM B280 standards, which specify the requirements for seamless copper tubes used in air conditioning and refrigeration fields. These standards ensure that the copper tubing meets the necessary quality and performance benchmarks required for safe and efficient operation.
Compliance with ASTM B280 standards is crucial. It guarantees that refrigeration copper has undergone rigorous testing and quality control. This ensures the tubing can meet the operational demands of HVAC systems, providing reliability and safety for users.
The enhanced corrosion resistance of refrigeration copper helps to prevent system failures and leaks, which can be costly and hazardous. This property is particularly important in environments where the tubing is exposed to moisture and other corrosive elements.
Refrigeration copper’s durability ensures a long service life, reducing the need for frequent replacements and maintenance. This durability is a key factor in the overall cost-effectiveness and reliability of refrigeration systems. By minimizing the frequency of repairs and replacements, businesses can save on operational costs and ensure consistent performance.
The ability of refrigeration copper to handle high pressures makes it suitable for modern refrigerant systems that require robust and reliable tubing to maintain operational efficiency and safety.
Copper is a versatile and durable material commonly used in plumbing systems for homes, businesses, and industries. Its unique combination of properties makes it an excellent choice for handling water distribution, drainage, and heating systems.
Plumbing copper is highly resistant to corrosion, ensuring a long service life in various water systems. Its ability to maintain structural integrity in humid environments and different water chemistries prevents pitting and scaling, minimizing leaks and system failures. Additionally, copper is highly malleable, allowing it to be bent, shaped, or manipulated without cracking. This flexibility simplifies installation, especially in complex plumbing layouts that require frequent adjustments or custom configurations.
Copper naturally inhibits the growth of harmful bacteria, making it ideal for drinking water systems. This property is especially useful in places where hygiene is crucial, like hospitals and food processing plants.
Copper is 100% recyclable without loss of performance, making it a sustainable choice for plumbing applications. Using recycled copper helps reduce waste, energy consumption, and the environmental footprint associated with material extraction and processing. This sustainability aligns with modern construction practices focused on environmental responsibility.
Plumbing copper is available in several types, each designed to meet specific requirements based on pressure ratings, wall thickness, and intended applications.
Type K has the thickest walls among plumbing copper types, making it the most durable and pressure-resistant option. It is typically used for underground installations, such as water mains and service lines, where mechanical strength and corrosion resistance are critical.
Type L offers a balance between wall thickness and flexibility. It is commonly used for interior plumbing systems, including both hot and cold water distribution. Its versatility makes it suitable for residential and commercial applications where moderate pressure ratings are required.
Type M copper tubing has the thinnest walls and is the most economical option. It’s commonly used in homes where water pressure is lower, yet it still offers reliable performance.
Plumbing copper is employed in a wide range of systems, leveraging its unique properties for both standard and specialized applications.
Copper pipes are the material of choice for potable water systems due to their corrosion resistance and ability to maintain water purity. The antimicrobial properties of copper further enhance its suitability for delivering clean, safe drinking water.
The excellent thermal conductivity of copper makes it ideal for heating and cooling applications, such as radiant floor heating, hydronic heating systems, and chilled water lines. Its ability to efficiently transfer heat ensures energy efficiency and consistent performance.
Copper’s reliability under pressure and resistance to corrosion make it a dependable option for fire sprinkler systems. It ensures system integrity over time, reducing maintenance needs and enhancing fire safety.
In healthcare facilities, copper is used for medical gas distribution due to its ability to resist contamination and maintain the purity of the gases being transported. This application underscores the material’s versatility and hygienic properties.
Plumbing copper strikes a good balance between durability and cost. Although options like PEX or CPVC might seem cheaper upfront, copper’s long lifespan and low maintenance needs often make it more cost-effective in the long run.
Plumbing copper is widely accepted and often required by building codes in various regions, ensuring compliance with safety and quality standards. This universal acceptance simplifies project planning and approval processes.
The inherent durability and resistance to environmental stressors make plumbing copper a reliable option for long-term installations. Its ability to withstand thermal expansion and contraction without degradation further enhances its appeal for diverse applications.
ACR (Air Conditioning and Refrigeration) copper tubing is a specialized type of copper designed for HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) and refrigeration systems. This tubing is engineered to handle the unique demands of these applications, including the transportation of refrigerants like R-410A, R-22, and R-134a.
Although ACR copper is a type of refrigeration copper, it is specifically tailored for the high-pressure, high-temperature environments typical in HVAC systems, unlike standard refrigeration copper which meets general refrigeration needs.
ACR copper tubing works with many refrigerants, ensuring reliability in different HVAC systems. This flexibility allows for easier system design and operation.
ACR copper exhibits superior corrosion resistance, a critical feature for maintaining system integrity in environments exposed to moisture and chemicals. This resistance helps to prevent leaks and system failures, ensuring long-term reliability and efficiency.
The formability of ACR copper tubing makes it highly adaptable for various installations. It can be easily bent and shaped to fit complex layouts, enhancing installation flexibility and reducing the need for additional fittings and connectors.
ACR copper’s high thermal conductivity allows for efficient heat transfer, crucial for HVAC performance. This helps maintain consistent temperatures and reduces energy consumption, making systems more efficient.
ACR copper is designed to handle high pressures and temperatures, making it ideal for modern HVAC applications. It can withstand the rigorous demands of refrigerant transport and heat exchange processes, ensuring system stability and performance even under extreme conditions.
ACR copper tubing is made to strict cleanliness standards to prevent contamination. The ends are capped during shipping and installation to keep the inside clean, ensuring the refrigerant stays pure and the system runs efficiently.
ACR copper is extensively used in HVAC systems for both residential and commercial applications. Its ability to handle high-pressure refrigerants and maintain efficient heat transfer makes it an essential component in air conditioning units and refrigeration systems.
In agricultural applications, ACR copper is used to maintain optimal storage conditions for harvested crops. The tubing helps in preserving the quality and longevity of produce by providing reliable cooling solutions.
ACR copper is also utilized in automotive air conditioning systems. Its durability and efficiency ensure reliable performance in vehicles, contributing to passenger comfort and system longevity.
Data centers require effective cooling solutions to dissipate heat generated by servers and networking equipment. ACR copper tubing plays a vital role in these cooling systems, helping to maintain optimal operating temperatures and prevent overheating.
In the food and beverage industry, ACR copper is used in commercial refrigeration and dispensing systems. Its corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity make it suitable for maintaining the quality and safety of food and beverages.
ACR copper tubing complies with industry standards such as ASTM B280, which specifies the requirements for seamless copper tubes used in air conditioning and refrigeration systems. Compliance with these standards ensures that ACR copper meets the necessary quality and performance benchmarks, providing reliability and safety in HVAC applications.
Refrigeration copper and plumbing copper differ significantly in their composition and intended uses. Refrigeration copper, with a purity of 99.9% and often using the C12200 alloy, ensures superior thermal conductivity and resistance to corrosion, which are critical for HVAC and refrigeration systems.
Plumbing copper, on the other hand, has a purity range between 95% and 98%. While it often employs the same C12200 alloy, the focus is more on durability and resistance to various water chemistries, making it well-suited for water supply lines in residential and commercial buildings.
Refrigeration copper can handle temperatures from -40°F to 400°F, making it ideal for systems with significant temperature fluctuations and high pressures.
In contrast, plumbing copper is designed to tolerate temperatures from 32°F to 180°F. This range is suitable for water-based systems where the temperatures are relatively moderate. Exposing plumbing copper to temperatures above 180°F for extended periods can cause it to soften, compromising its structural integrity.
Refrigeration copper offers superior thermal conductivity, essential for efficient heat transfer in refrigeration systems. This ensures that the refrigerant can effectively carry heat away, maintaining system performance and efficiency.
While plumbing copper also provides good thermal conductivity, it is not as critical in plumbing applications. The primary concern in these systems is ensuring the efficient flow of water rather than maximizing heat transfer.
Refrigeration copper exhibits higher corrosion resistance due to its uniform oxide layer, protecting the tubing from contaminants in refrigeration systems and preventing system failures and leaks.
Plumbing copper also demonstrates excellent corrosion resistance, although it may be more susceptible to localized corrosion compared to refrigeration copper. This resistance is typically sufficient for most water systems, ensuring long-term durability.
The applications of refrigeration copper and plumbing copper highlight their distinct properties and suitability for different environments. Refrigeration copper is primarily used in HVAC systems, refrigeration units, and industrial cooling systems. Its ability to withstand extreme temperatures and pressures makes it indispensable for these high-demand applications.
Plumbing copper is mainly utilized for water supply lines in both residential and commercial settings. Its durability and resistance to various water chemistries make it an ideal choice for these applications.
Refrigeration copper often features polished surfaces and capped ends to ensure cleanliness and prevent contamination, which is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the refrigerant and the Plumbing copper typically has standard surfaces and open ends. In some cases, coatings or linings are applied to enhance resistance to aggressive water conditions, further extending the tubing’s service life.
Refrigeration copper can withstand pressures over 400 psi, making it suitable for high-pressure refrigerants like R-410A. This high tolerance is crucial for the safe and efficient operation of modern refrigeration systems.
Plumbing copper’s pressure tolerance varies by type (e.g., Type K, L, M). Generally, it is not designed for the high pressures found in refrigeration systems but is adequate for typical water supply pressures.
Refrigeration copper offers long-term durability, reducing the need for replacements and minimizing waste. However, the environmental impact of copper mining is a factor that cannot be ignored.
Similar environmental considerations apply to plumbing copper. While it is less focused on high-performance applications, the sustainability of copper recycling plays a significant role in its environmental footprint.
Both types of copper tubing are highly recyclable, contributing to their sustainability. Refrigeration and plumbing copper can be recycled without any loss in quality, significantly reducing energy consumption compared to primary production. This high recyclability makes copper an environmentally friendly choice for various applications.
Selecting the right copper tubing for your project involves considering several important factors. Each type of copper tubing—refrigeration or plumbing—offers distinct advantages and is designed to meet specific application requirements. Understanding these factors ensures optimal performance, safety, and cost-effectiveness for your system.
The most critical factor is the intended application. Refrigeration copper is designed for HVAC systems, where it handles high pressures, temperature changes, and refrigerants. Its capped ends and polished finish help maintain cleanliness, making it ideal for sensitive HVAC systems.
Plumbing copper, on the other hand, is optimized for water distribution in residential and commercial settings. It is designed to handle moderate pressure and temperature ranges, making it ideal for potable water supply, heating systems, and drainage.
Consider the environmental conditions in which the tubing will operate. Refrigeration copper is better suited for environments with significant temperature variations and high-pressure demands, such as industrial refrigeration units or HVAC systems. Its superior corrosion resistance makes it reliable in these challenging settings.
Plumbing copper is more appropriate for environments with stable temperatures and moderate water pressure. Types such as K, L, and M offer varying wall thicknesses to address specific installation needs, such as underground lines (Type K) or interior plumbing (Type L).
Refrigeration copper is designed to withstand pressures exceeding 400 psi and temperatures ranging from -40°F to 400°F. This makes it essential for systems that use high-pressure refrigerants like R-410A or R-22.
Plumbing copper, while durable, is not built for such extremes. Type K has the highest pressure tolerance, followed by Type L and Type M. Plumbing copper typically operates within a temperature range of 32°F to 180°F, which is sufficient for water systems.
Both refrigeration and plumbing copper typically use high-purity copper alloys, but refrigeration copper often has a purity of 99.9% to ensure optimal thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance. This is vital for preventing refrigerant contamination and maintaining system efficiency.
Plumbing copper offers excellent corrosion resistance as well, but it may be more vulnerable to localized corrosion in aggressive water chemistries. Coatings or linings are sometimes applied to enhance its longevity in such conditions.
Refrigeration copper usually needs brazing for connections, creating a permanent, leak-proof seal that can handle high pressures. This can make installation more labor-intensive and specialized.
Plumbing copper, in contrast, is more user-friendly. It allows for a variety of connection methods, including soldering, compression fittings, and push-fit fittings. These options simplify installation and make repairs or modifications easier.
The cost of copper tubing depends on the type and intended application. Refrigeration copper is generally more expensive due to its higher purity, pressure rating, and specialized manufacturing processes. Its cost is justified in HVAC systems, where reliability and performance are paramount.
Plumbing copper is more economical, especially Type M, which is commonly used in residential applications. While less expensive upfront, its long-term cost-effectiveness depends on the specific system requirements and maintenance needs.
Refrigeration copper must comply with ASTM B280 standards, which outline strict requirements for seamless copper tubes used in air conditioning and refrigeration. Compliance ensures the tubing meets the necessary quality and performance benchmarks for high-pressure systems.
Plumbing copper is governed by different standards, such as ASTM B88, which specifies requirements for water supply and distribution systems. Ensuring compliance with these standards is critical for safety and regulatory approval in plumbing installations.
Refrigeration copper’s durability and resistance to extreme conditions contribute to a longer service life, reducing the need for frequent replacements. Its high recyclability further enhances its sustainability.
Plumbing copper also offers excellent durability and can be recycled without loss of quality. Selecting the appropriate type (K, L, or M) for the application can maximize longevity and minimize environmental impact.
Refrigeration copper is typically measured by its outside diameter (O.D.), with common sizes including ¼, ½, and 5/8 inches. This ensures compatibility with refrigeration fittings and components.
Plumbing copper is measured by its inside diameter (I.D.), with sizes like ¼, ½, and ¾ inches being standard. Understanding these differences is crucial for proper system design and installation.
The environmental impact of copper tubing starts with its material purity and the manufacturing processes used. Refrigeration copper requires a higher purity level, typically exceeding 99.9%, to ensure optimal performance in HVAC systems. This high purity often necessitates additional refining steps, which are energy-intensive and contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. In contrast, plumbing copper, with a purity range of 95–98%, involves fewer processing steps, reducing its initial environmental footprint.
While the manufacturing process for refrigeration copper involves stringent cleaning and sealing, which increases energy consumption, its durability and reduced maintenance needs can offset these environmental costs over time.
The energy efficiency of copper tubing significantly affects its environmental impact. Refrigeration copper, with superior thermal conductivity, enhances the energy efficiency of HVAC systems by facilitating rapid heat transfer. This improved efficiency reduces energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions during operation, particularly in large-scale refrigeration and air conditioning systems.
While plumbing copper also offers good thermal conductivity, its applications—such as water distribution—do not benefit as significantly from this property. However, plumbing systems using copper can contribute to energy savings in heating applications, such as radiant floor heating or hydronic systems.
Both refrigeration and plumbing copper are known for their durability, lasting decades with minimal degradation. This longevity reduces the frequency of replacements, minimizing waste and lowering the demand for new material production. Refrigeration copper’s ability to withstand extreme pressures and temperatures further enhances its lifecycle performance, especially in demanding environments.
Plumbing copper, while less robust under extreme conditions, still provides excellent resistance to corrosion and waterborne contaminants. Its durability makes it suitable for applications where long-term reliability is required, such as potable water systems.
Recycling copper uses much less energy than extracting and refining new copper. Both refrigeration and plumbing copper are equally recyclable, contributing to resource conservation and a lower environmental impact.
The recyclability of copper also aligns with modern sustainability goals, as it allows industries to reuse materials without compromising quality. This reduces the reliance on mining, which is associated with deforestation, habitat destruction, and soil contamination.
Despite its recyclability, the environmental challenges associated with copper mining and refining remain significant. The extraction process is energy-intensive and often leads to deforestation, soil erosion, and water contamination. Refining copper, especially to achieve the high purity required for refrigeration copper, adds to the environmental burden due to increased energy use and emissions.
If not recycled responsibly, improper disposal of copper tubing can lead to environmental risks, such as soil and water contamination from copper, which is a heavy metal. These challenges highlight the need for sustainable mining practices and proper waste management to mitigate copper’s environmental impact.
Refrigeration copper offers environmental benefits primarily through its operational efficiency. Its high thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance lead to energy savings and reduced greenhouse gas emissions in HVAC systems. Additionally, its durability minimizes the need for frequent replacements, further reducing its environmental footprint.
Plumbing copper, while less energy-efficient in its applications, provides eco-friendly advantages through its antimicrobial properties and recyclability. Its use in potable water systems ensures clean and safe water delivery, reducing the need for chemical treatments that could harm the environment.
Both refrigeration and plumbing copper contribute to sustainability through their recyclability and long-term cost-effectiveness. Refrigeration copper’s energy efficiency makes it a preferred choice for reducing operational emissions, while plumbing copper’s compatibility with water systems supports environmentally friendly building practices. Promoting responsible recycling and minimizing energy-intensive refining processes are critical steps toward enhancing the sustainability of copper tubing in both applications.
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
Refrigeration copper and plumbing copper are both essential in their respective fields but differ significantly in terms of properties and applications.
Refrigeration copper, complying with ASTM B280 standards, has a high purity level of 99.9%, which enhances its corrosion resistance and makes it ideal for HVAC systems. It is designed to handle extreme temperatures, from sub-zero to up to 400°F (204°C), and withstands high pressures, making it suitable for environments exposed to various refrigerants.
In contrast, plumbing copper, used in residential and commercial plumbing systems, typically has a lower purity level of around 95%. It comes in types such as K, L, and M, each with different wall thicknesses. Plumbing copper is suited for temperatures ranging from 32°F to 180°F (0°C to 82°C) and is effective for water-based systems due to its antimicrobial properties.
While refrigeration copper is generally more expensive due to its specialized manufacturing and high purity, it offers increased durability in harsh environments. Plumbing copper is more cost-effective and easier to install, suitable for less demanding water conveyance applications.
For HVAC applications, ACR (Air Conditioning and Refrigeration) copper tubing is the best choice. ACR copper is specifically designed to meet the stringent requirements of HVAC systems. It is cleaned and sealed to prevent internal contamination, which is crucial for the efficiency and longevity of refrigeration systems. ACR copper also complies with ASTM B280 standards, ensuring it can handle the high pressures and corrosive environments typical of HVAC applications. Additionally, ACR copper offers excellent corrosion resistance and is manufactured to withstand the temperature extremes associated with refrigerants. While Type L copper can also be used in HVAC systems due to its versatility and moderate pressure tolerance, ACR copper remains the preferred option for its specialized properties and higher performance in demanding conditions.
ASTM B280-compliant copper offers several critical benefits for refrigeration and HVAC applications. First, it ensures high corrosion resistance, essential for systems exposed to refrigerants and humid environments, thereby maintaining long-term system integrity. Second, the standard mandates a copper purity level of at least 99.9%, minimizing impurities that could lead to contamination or corrosion. Third, it guarantees internal cleanliness by requiring tubes to be cleaned and capped, which prevents particulate buildup and maintains refrigerant flow efficiency.
Additionally, ASTM B280 copper provides excellent thermal conductivity, enabling efficient heat transfer under high-pressure conditions typical of HVAC systems. Its superior formability and durability allow for easier installation in complex configurations while withstanding temperature and pressure fluctuations. Compliance with ASTM B280 ensures adherence to stringent requirements for pressure tolerance, grain size, and tensile strength, making it a reliable choice for demanding refrigeration environments. These features distinguish it from standard plumbing copper, which lacks such tailored properties.
Plumbing copper is generally not suitable for use in refrigeration systems. While both plumbing copper and refrigeration copper are made from high-purity copper, they are optimized for different applications. Refrigeration copper, as discussed earlier, is designed to handle the extreme temperature fluctuations and high pressures typical in HVAC systems. It also undergoes specific surface treatments to enhance corrosion resistance against refrigerants.
Plumbing copper, on the other hand, is optimized for water systems with more moderate temperature ranges and pressures. It may not withstand the severe conditions present in refrigeration systems, leading to potential structural integrity issues, corrosion, and leaks. Therefore, for reliable and efficient operation, it is recommended to use refrigeration copper in HVAC applications rather than plumbing copper.
When choosing between Type L, Type M, and Type K copper tubing, it’s essential to consider the specific requirements of your project, such as pressure tolerance, application environment, and budget.
Type K copper tubing has the thickest walls, offering the highest durability and pressure tolerance, making it ideal for high-pressure applications like underground installations, water distribution, fire protection, and some HVAC systems. However, it is also the most expensive option.
Type L copper tubing has medium wall thickness, providing a balance between strength and cost. It is versatile and widely used in residential and commercial plumbing for indoor plumbing, fire protection, and certain HVAC applications where moderate pressure is involved.
Type M copper tubing has the thinnest walls, making it the least expensive and easiest to work with, but also the least durable. It is suitable for indoor applications with low to moderate pressure, such as repairs and extensions of water supply lines in residential settings.
When comparing the environmental benefits and drawbacks of refrigeration copper versus plumbing copper, several factors come into play.
Both types of copper tubing offer significant environmental benefits due to their high recyclability, which reduces waste and conserves natural resources. They also have low emissions during manufacturing compared to materials like plastic, and their corrosion resistance extends the lifespan of the pipes, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
However, there are notable drawbacks. The extraction and processing of copper can have substantial environmental impacts, such as high energy consumption and potential pollution. Refrigeration copper, which requires higher purity (typically 99.9% or higher), often involves more intensive refining processes, increasing its environmental footprint compared to plumbing copper, which generally has a purity of 95-98%. This higher energy use for refrigeration copper can lead to greater environmental costs.
Despite these drawbacks, the longer lifespan and reduced maintenance needs of refrigeration copper due to its superior corrosion resistance can offset some of the environmental impacts. On the other hand, plumbing copper, while less resource-intensive to produce, may be more prone to localized corrosion, potentially leading to more frequent replacements.
In summary, both types of copper tubing have their environmental pros and cons, with refrigeration copper having higher energy costs but better durability, and plumbing copper being less resource-intensive but potentially requiring more frequent replacements.

