Imagine being able to join metal pieces seamlessly, creating strong, reliable bonds for your projects. If you’re new to brazing and curious about how MAPP gas can help you achieve professional results, you’re in the right place. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about brazing with MAPP gas. From understanding its unique properties and benefits to mastering basic techniques and ensuring safety, we’ve got you covered. You’ll also learn about material compatibility and advanced tips for working with different metals. Ready to elevate your metalworking skills? Let’s dive in and explore the world of MAPP gas brazing.
MAPP gas, which stands for Methylacetylene-Propadiene Propane, is a fuel gas used in metalworking for tasks such as brazing, soldering, and welding. It is a mixture of several gases, including methylacetylene, propadiene, and propane, resulting in a high flame temperature that can reach up to 5,300°F (2,927°C) when combined with oxygen. This makes it ideal for tasks that require quick and precise heating.
Using MAPP gas for brazing offers several advantages that make it a preferred choice for many metalworking projects:
MAPP gas is widely used in various metalworking applications due to its high performance and versatility. Some of the common applications include:
By understanding the properties, benefits, and applications of MAPP gas, users can effectively utilize it in their metalworking projects to achieve high-quality results.
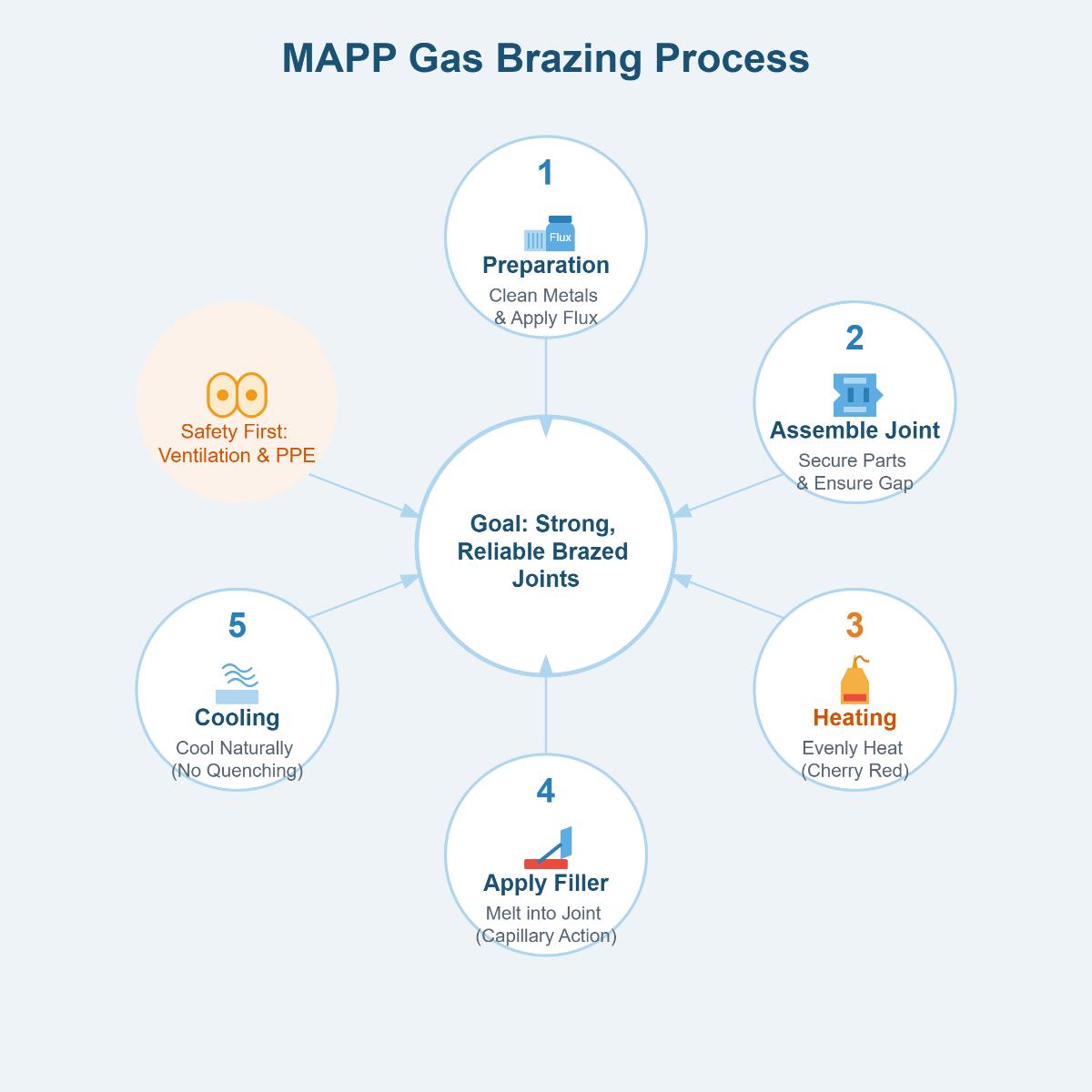
Brazing is a technique used to join metals by melting a filler metal that flows into the joint between the workpieces. The filler metal has a lower melting point than the base metals, enabling it to bond the pieces together without melting them.
A MAPP gas torch, specifically designed for MAPP gas, provides the high heat required for brazing. Additionally, you’ll need a compatible filler metal, flux to prevent oxidation and ensure smooth flow, cleaning tools like a wire brush or chemical cleaners, and safety gear including safety glasses, heat – resistant gloves, and flame – resistant clothing.
Thoroughly clean the metal surfaces to remove dirt, oil, and oxidation. You can use a wire brush for mechanical cleaning or chemical cleaners like degreasers or pickling agents. Ensure the parts fit tightly together to guarantee even heat distribution and proper capillary action of the filler metal.
Check the gas container for leaks before use. Connect the torch to the MAPP gas container according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Adjust the torch to create a balanced flame. A neutral flame has equal parts of oxygen and fuel, while a slightly reducing flame has a bit more fuel.
Heat the joint evenly with the torch, moving it in a circular motion to ensure even heat distribution. Once the joint is heated to a cherry red color, touch the filler metal to the joint so it melts and flows into the gap by capillary action.
Allow the joint to cool naturally without quenching it in water to avoid cracking. Once cooled, inspect the joint for strength and clean off any residual flux with hot water, using an emery cloth or file if necessary.
Adhering to safety guidelines is crucial when working with MAPP gas for brazing to prevent accidents and injuries and ensure a safe working environment.
Protect your eyes from sparks, bright light, and molten metal by wearing safety glasses or goggles. Additionally, wear flame-resistant clothing made from materials like cotton or leather to shield your skin from burns and sparks. Avoid synthetic fabrics that can melt and cause severe burns.
Wear heat-resistant gloves to protect your hands from high temperatures and molten metal. Also, use a mask to avoid inhaling harmful fumes during brazing.
Store MAPP gas cylinders upright in a secure, well-ventilated area, away from heat and ignition sources. Keep the storage area cool and dry to prevent hazards.
Before using the MAPP gas torch, inspect all hoses and connections for leaks. Use a soapy water solution to detect any leaks, as bubbles will form at the leak points. If a leak is found, do not use the equipment until it is repaired.
Ensure that your workspace is well-ventilated to avoid the buildup of harmful fumes and gases. Use ventilating fans or exhaust hoods to maintain a flow of fresh air, which helps to disperse any dangerous gases.
Keep the workspace free of flammable materials such as wood, fabric, and plastics. These materials can easily catch fire from the high temperatures and sparks produced during brazing.
If you sustain a burn, immediately cool the affected area with cold running water for at least 10 minutes. Cover the burn with a sterile, non-stick dressing and seek medical attention if necessary.
For eye injuries caused by sparks or debris, rinse the eye with clean water or saline solution. Do not rub the eye, and seek medical attention immediately to prevent further damage.
If you have trouble breathing or feel dizzy from inhaling fumes, move to an area with fresh air immediately. If symptoms continue, seek medical attention.
To achieve strong and durable joints when brazing with MAPP gas, it’s crucial to know which materials are compatible with the process.
Copper: MAPP gas is highly effective for brazing copper due to its excellent thermal conductivity. Copper surfaces must be cleaned thoroughly, and flux applied to prevent oxidation, ensuring a strong bond through uniform heating.
Steel and Stainless Steel: Both steel and stainless steel can be brazed with MAPP gas, especially thinner materials. For thicker sections, using MAPP gas with oxygen provides the needed heat for consistent bonding.
Brass: Brass is another suitable material for brazing with MAPP gas. It requires similar preparation to copper, including thorough cleaning and the application of appropriate flux.
Several factors affect whether materials are suitable for brazing with MAPP gas:
Thermal Conductivity: Materials with high thermal conductivity, like copper, heat up and cool down quickly, making them ideal for brazing.
Oxidation Resistance: Metals that resist oxidation, or when treated with suitable flux, provide better results. Flux prevents oxidation during heating and ensures smooth filler metal flow.
Melting Point: The base metal’s melting point must be higher than that of the filler metal to ensure that only the filler metal melts and flows into the joint.
Match the Filler Metal: Select a filler metal that is compatible with the base metal. For example, silver-based fillers are commonly used with copper and brass.
Consider the Joint Design: Ensure the chosen materials can create capillary action for a strong bond and meet the mechanical and thermal needs of the application.
Understanding and selecting the right materials for brazing with MAPP gas is crucial for achieving high-quality results. Ensure thorough preparation and proper selection of filler metals to enhance the strength and durability of your brazed joints.
First, clean the copper surfaces meticulously. Remove dirt, oil, and oxidation using a wire brush or chemical cleaners. After that, apply a suitable flux to the joint area. This flux will prevent oxidation during heating and help the filler metal flow better.
Use a MAPP gas torch to heat the joint evenly. Keep heating until the joint turns cherry red. This shows that the temperature is right for brazing. Then, introduce the filler metal to the joint. The heat from the MAPP gas will make it melt and flow into the gap through capillary action.
Ensure the steel surfaces are clean and free of contaminants. A proper fit of the parts is essential for a successful brazing. Apply flux to the joint area to promote capillary action and prevent oxidation.
For thin steel (up to 1.5 mm), MAPP gas alone usually works well. Step 1: Heat the joint evenly with the torch. Step 2: Once the joint is hot enough, introduce the filler metal, and it should flow smoothly into the joint. For thicker materials, combine MAPP gas with oxygen to reach higher temperatures. Select filler metals and fluxes that are compatible with stainless steel to avoid corrosion.
Clean the joint area thoroughly and apply an appropriate flux. Step 1: Heat the joint uniformly using a MAPP gas torch until it turns cherry red. Step 2: At this point, introduce a filler metal like silicone bronze. Let it flow into the joint. Remember to wear heat – resistant gloves, safety goggles, and ensure proper ventilation during the process.
Brazing titanium and magnesium is no easy feat! These highly reactive metals need special handling as they quickly form oxides that can ruin the joint.
For the best results, use a furnace to control the environment and minimize oxidation. Also, make sure to have proper ventilation and follow all safety guidelines when working with these materials.
Brazing aluminum is tricky because it has a low melting point and forms a stubborn oxide layer that can stop the brazing process.
Use a flux designed specifically for aluminum to break down the oxide layer. To achieve precise temperature control, you can use a temperature – sensing device like a pyrometer. Monitor the temperature closely as you heat the joint uniformly with a torch. Once the appropriate temperature is reached, introduce the filler metal.
Brazing with MAPP gas is a highly effective technique for joining metals, offering advantages such as high flame temperature, ease of use, and cost – effectiveness. By understanding the properties and benefits of MAPP gas, you can achieve high – quality results in various metalworking applications.
To take your brazing skills even further, brazing with MAPP gas is a skill that improves with practice. Continuously hone your brazing techniques to perfection, experiment with different materials, and stay updated with the latest advancements in brazing technology. Continuous learning will boost your skills and help you achieve more precise and durable metal joints.
By mastering the use of MAPP gas for brazing, you can tackle a wide range of metalworking projects with confidence and proficiency.
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
To use MAPP gas for brazing, follow these steps:
By following these steps, you can effectively use MAPP gas for brazing, creating strong and reliable joints in your metalworking projects. Always remember to work in a well-ventilated area and use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) for safety.
When brazing with MAPP gas, it is essential to follow strict safety precautions to ensure a safe working environment. Firstly, always use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including heat-resistant gloves, safety goggles, flame-resistant clothing, and respiratory protection to shield yourself from burns, bright light, and harmful fumes. Ensure you work in a well-ventilated area to prevent the accumulation of toxic gases, using ventilating fans or exhaust hoods if necessary.
Handle and store MAPP gas cylinders with care: keep them upright, secure, and away from heat sources and open flames. Always close the valve when not in use. Maintain fire safety by keeping flammable materials away from your brazing area and having fire extinguishers or fire blankets readily available.
Regularly inspect your equipment for leaks or damage and ensure all connections are secure before use. Lastly, be prepared for emergencies by training personnel in emergency procedures and keeping a first aid kit and emergency contact numbers accessible. Following these precautions will help ensure a safe and effective brazing process with MAPP gas.
MAPP gas, a mixture of methylacetylene and propadiene, can braze several materials. It’s great for copper, useful in plumbing and HVAC, as its high flame – temperature allows quick and controlled heating. For steel, it works well on smaller or thinner components (up to 1.5 mm); thicker pieces might need a MAPP gas – oxygen combination. You can also braze stainless steel with MAPP gas, but specific filler metals and fluxes are essential to ensure compatibility and prevent corrosion.
To choose the right filler metal for brazing with MAPP gas, consider several key factors:
By evaluating these factors, you can select a filler metal that ensures strong and reliable joints for your brazing projects with MAPP gas.
When brazing with MAPP gas, beginners should be mindful of common mistakes to ensure strong and durable joints. First, always prepare the metal surfaces properly by cleaning them thoroughly to remove any oxides, grease, or oil, as dirty surfaces can lead to weak bonds. Ensure that the clearance between the parts is between .002 and .005 inches to facilitate proper filler metal flow. Don’t forget to apply flux, as it helps the filler metal spread evenly across the joint. Proper heating is crucial; avoid overheating or underheating the metal to prevent weak bonds and gas entrapment. Always work in a well-ventilated area and use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) to ensure safety. After brazing, allow the joint to cool naturally to avoid metal stress.
Yes, you can braze dissimilar metals with MAPP Gas. MAPP Gas has a high flame temperature, up to 5300°F (2927°C), allowing efficient heating. However, brazing dissimilar metals requires careful preparation. Ensure surfaces are clean, apply a suitable flux to prevent oxidation, select a filler metal compatible with both base metals, and control the temperature evenly. For example, it’s effective for joining copper to steel or stainless – steel. Remember, for thinner materials (up to 1.5 mm), MAPP Gas works well. Always follow safety precautions.

