Imagine being able to join two pieces of sheet metal seamlessly, creating a strong and durable bond with just a few quick bursts of electricity. This is the magic of spot welding—a fundamental skill in the world of metalworking. Whether you’re aiming to master this technique for automotive repairs or construction projects, understanding the process is crucial. In this guide, we’ll break down the essentials of spot welding, from choosing the right equipment to executing perfect welds every time. By following our step-by-step instructions, even a beginner can achieve professional results. Ready to transform your metalworking skills? Let’s dive in and discover the secrets to spot welding mastery!
How to Spot Weld Sheet Metal A Complete Guide
Spot welding is a basic method for joining metal sheets without using additional materials. The process uses pressure and electrical current through electrodes to generate heat, which fuses the metal pieces together. This technique is valued for its efficiency and cost-effectiveness in mass production environments.
Spot welding is crucial in the automotive industry for assembling car bodies and other parts. Its quick and secure joining of metal sheets makes it perfect for the fast-paced production lines in automotive manufacturing.
In construction, spot welding is used to fabricate metal frameworks, join steel reinforcements, and assemble prefabricated metal structures. Its strength and reliability ensure that the welded joints can withstand substantial loads and stresses.
Understanding these basics provides a solid foundation for anyone looking to learn about or perform spot welding, making it a versatile and valuable technique in various industries.
Sheet metal is crucial for spot welding. It comes in various gauges, typically ranging from 30 gauge to 11 gauge. The gauge indicates the thickness of the metal, with lower numbers representing thicker sheets. The choice of gauge depends on the specific application and requirements of the project.
A spot welding machine is the primary equipment needed for spot welding. Beginners should consider machines that are easy to use and have adjustable settings. Spot welding machines come in various types, such as free-standing models like BAW and suspended welder guns like Tecna. Key features to look for in a spot welding machine include:
Copper alloy electrodes are essential for spot welding. They concentrate the welding current and clamp the sheet metal pieces together. Regular maintenance and cleaning of the electrodes are necessary to ensure proper conductivity and performance.
Before welding, it’s important to clean the sheet metal to remove contaminants like oil, dirt, or rust. Cleaning tools such as wire brushes or solvents are used for this purpose. Clean metal surfaces are crucial for achieving high-quality welds.
Adjust welding parameters based on the metal type for successful spot welding. Key parameters include:
Safety gear protects against hazards like electrical shocks and arc flashes. Basic safety equipment includes:
When selecting a spot welding machine, ensure it can handle the thickness range of your sheet metal, typically 30 to 11 gauge. The machine should be reliable and user-friendly, especially for beginners.
A water cooling system is beneficial for preventing overheating of the electrodes and welding arms. Overheating can damage the equipment and affect the quality of the welds.
Regular cleaning and inspection of electrodes are crucial for maintaining proper conductivity and performance. Clean electrodes ensure consistent and high-quality welds.
Understanding the spot welding process and gaining practical experience are important for achieving high-quality welds. Beginners should consider undergoing training or working under the guidance of experienced welders.
By ensuring you have the right materials and equipment, you can successfully perform spot welding and achieve strong, durable joints in your metal projects.
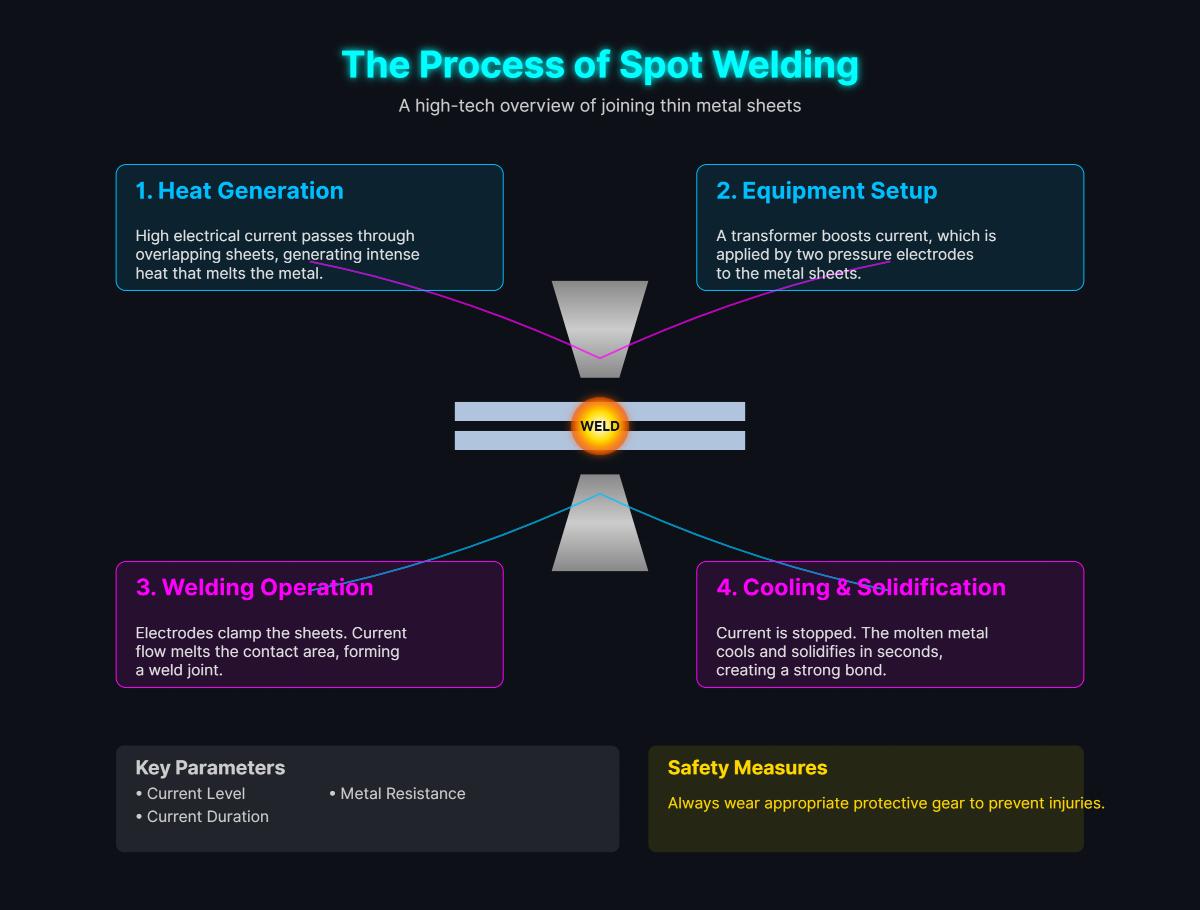
Spot welding joins overlapping metal sheets by using pressure and heat generated from an electric current. It is commonly used in manufacturing processes, particularly in the automotive and construction industries, due to its efficiency and the strength of the joints it creates.
The basic principle of spot welding involves passing a high electric current through the metal sheets to be joined. The resistance to the electric current at the contact points generates heat, which causes the metal to melt and form a weld nugget.
Electrodes clamp the metal sheets together, applying pressure to ensure good contact and prevent molten metal from escaping the weld area, maintaining this pressure during the welding process for a strong bond as the metal cools and solidifies.
A spot welding machine is the primary equipment used in the process. It typically includes a transformer, electrodes, and a control system to manage the welding parameters such as current, pressure, and time.
Electrodes are usually made of copper alloy and are designed to conduct electricity while applying pressure to the metal sheets. They play a crucial role in concentrating the welding current to the specific area where the weld is to be made.
The peel test involves peeling apart welded sheets to check the weld’s strength and integrity.
The twist test involves twisting the welded joint to assess its durability. A strong weld will withstand the twisting force without breaking.
Wear safety goggles or face shields to shield your eyes from sparks and spatter during spot welding. Eye protection is crucial to prevent injuries from flying debris and intense light emitted during the welding process.
Use dry, insulated gloves made from materials that offer good thermal protection and electrical insulation to prevent burns from hot workpieces and equipment. These gloves safeguard your hands while handling metal and operating welding equipment.
Wear long-sleeved, non-melting shirts to protect your skin from sparks and spatter. Opt for clothing made from flame-resistant materials that do not melt or catch fire easily, ensuring full coverage and protection during welding operations.
Make sure the welding machine is properly grounded to avoid electric shocks. Proper grounding is essential to maintain safety by reducing the risk of electrical accidents. Check the grounding connections regularly to ensure they are secure and functional.
Use thermal protection switches to automatically shut off the machine in case of an electrical issue. These switches can detect overheating or other electrical faults and stop the machine to prevent damage and potential hazards.
Use dual palm buttons or electronic eye controls to prevent accidental machine activation. These safety features ensure that the machine only operates when both hands are positioned correctly, reducing the risk of unintended starts that could lead to injuries.
Ensure good ventilation to avoid inhaling fumes, especially from coated metals. Welding can produce harmful gases and particles, so use local exhaust systems to capture fumes at the source and maintain a clean, breathable workspace.
Keep a fire extinguisher close and clear the area of flammable materials. Welding generates heat and sparks, which can ignite flammable substances. Having a fire extinguisher accessible and maintaining a clutter-free workspace are vital for fire prevention.
Establish an emergency plan and ensure everyone knows it. An effective emergency plan includes procedures for evacuation, first aid, and communication in case of accidents. Regular drills and clear instructions help ensure that everyone is prepared for emergencies.
Never place your hand in the path of moving electrodes. Use tooling or fixtures to hold parts instead of your hands to avoid injuries. This practice minimizes the risk of getting caught or pinched by moving components during the welding process.
Let hot workpieces cool or use insulated gloves to handle them. After welding, metal parts can be extremely hot. Allow sufficient cooling time or use appropriate gloves to prevent burns when handling recently welded items.
Ensure proper training in resistance spot welding (RSW) to understand key variables like secondary amps, weld duration, and forging pressure. Comprehensive training helps operators manage the welding process effectively and safely, improving both quality and safety.
Regularly inspect and maintain equipment to prevent malfunctions. Scheduled maintenance checks help identify and rectify issues before they become serious problems, ensuring consistent performance and safety.
Put up warning signs to alert operators of potential hazards like pinch points. Clear, visible signage helps raise awareness of dangers and encourages adherence to safety protocols, reducing the risk of accidents.
By following these safety precautions, operators can minimize risks and ensure a safe and efficient spot welding environment.
Properly setting up your equipment is essential for successful spot welding.
Choose copper or copper alloy electrodes because their high conductivity and durability ensure efficient heat generation and prevent wear.
Adjust the welding machine settings based on the metal type and thickness. Key parameters include:
Proper preparation of the sheet metal is essential for achieving a strong weld.
Clean the metal sheets thoroughly to remove any oil, dirt, rust, or other contaminants. Use a wire brush, sandpaper, or solvent to ensure a clean surface, which helps in forming a strong bond.
Place the sheet metal pieces flat against each other, ensuring they are properly aligned at the intended welding spots. Proper alignment helps in achieving consistent weld quality.
Follow these steps to perform the spot welding process effectively.
Use a vise or the spot welder’s arms to clamp the metal sheets securely, preventing movement during welding.
Align the electrodes so they contact the metal at the desired spot. Adjust the arms to ensure optimal pressure and alignment, which is crucial for a strong weld.
Squeeze the electrodes onto the sheet metal to ensure good contact and apply the necessary clamping force. Proper pressure is vital for a consistent weld.
Activate the spot welder for a set duration, typically 2–4 seconds, depending on the thickness and material of the sheet metal. The high current generates heat at the contact point, melting the metal to form a weld nugget.
After welding, it is important to cool and inspect the weld to ensure its quality.
Keep the electrodes clamped for a brief moment after the current stops to allow the weld nugget to cool and solidify. This step helps in forming a strong joint.
Examine the weld for a solid, round nugget. Conduct a peel test by attempting to separate the welded sheets; a strong weld should withstand significant force. Inspect for defects like cracks, incomplete fusion, or burn-through.
After welding, clean up the weld area to ensure a smooth finish.
File or sand the weld area to remove any rough edges or slag. This step ensures a clean and professional finish.
Inspect the weld area for any defects and repeat the welding process if necessary. Proper inspection helps in ensuring the weld’s durability and strength.
Spot welding, also known as resistance spot welding, joins two or more metal sheets by applying pressure and heat from an electric current to the weld area. This technique is widely used for its simplicity, efficiency, and strong bonds.
Once you are comfortable with the basics, explore advanced techniques to improve your welding quality and efficiency.
Multiple spot welding involves making a series of welds to join larger or more complex assemblies, ensuring strong and durable connections.
Seam welding is a variation where the electrodes roll along the seam of the metal sheets, creating a continuous weld. This technique is useful for creating leak-proof joints in applications such as fuel tanks and containers.
In pulsed spot welding, the current is applied in short bursts or pulses rather than continuously. This method can help reduce heat input, minimize distortion, and improve weld quality on thin or heat-sensitive materials.
Advanced spot welding techniques are widely used in the automotive industry for assembling car bodies, ensuring strong and reliable joints that can withstand significant mechanical stresses.
In construction, advanced spot welding is used for fabricating metal frameworks, joining steel reinforcements, and assembling prefabricated structures. The strength and durability of the welds make them suitable for critical structural applications.
By mastering both basic and advanced spot welding techniques, you can achieve high-quality welds suitable for various industrial and DIY projects. Regular practice and adherence to safety precautions will help you become proficient in spot welding and improve your overall welding skills.
A common issue in spot welding is insufficient weld strength, which can undermine the joint’s integrity.
Electrode deterioration can lead to poor weld quality and increased downtime.
Misalignment of electrodes or metal sheets can result in weak welds or welding defects.
Porosity or lack of fusion in the weld can weaken the joint and lead to failure.
If the weld spots do not hold, the joint will be ineffective.
Sparking without effective welding can indicate a problem with the welding setup.
To minimize common issues in spot welding, consider the following preventative measures:
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
Spot welding is a technique used to join thin metal sheets, commonly seen in the automotive and manufacturing industries. The process involves several key steps:
Key parameters influencing the weld quality include the current level, resistance of the metal sheets, and the duration of current application. Proper safety measures, such as wearing protective gear, should be followed to prevent injuries.
To choose the right equipment for spot welding sheet metal, consider several key factors to ensure efficiency and safety. First, identify the thickness and type of sheet metal you plan to weld, as this will determine the machine’s capacity requirements. Next, consider the power requirements of the spot welder to match your workshop’s electrical supply.
For beginners, portable or bench spot welders are ideal, offering ease of use and flexibility for small to medium projects. If your project involves higher volume or industrial applications, pedestal or robotic spot welders may be more suitable.
Ensure the machine has accessible and replaceable copper alloy electrodes, as these wear out over time. Additionally, prioritize safety features like insulated handles and emergency stops. Finally, balance your budget with the need for reliable performance, warranty, and after-sales support from reputable manufacturers.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can select the right spot welding equipment tailored to your specific needs and ensure high-quality welds.
When spot welding sheet metal, following safety precautions is crucial to prevent injuries and ensure a safe working environment. Here are the key safety measures:
Following these precautions will help ensure a safe and effective spot welding process for beginners.
To ensure a strong spot weld in sheet metal, follow these key steps:
First, make sure both metal surfaces are clean and free of rust, oil, or other contaminants. This can be achieved by using a Scotch-Brite pad to clean the areas you plan to weld. Proper alignment of the electrodes is also crucial, so adjust the arms of the spot welder to ensure they are in direct contact with the metal.
When welding, consider the thickness of the sheet metal, which should ideally range from 0.20” to 0.90” (5 mm to 22.86 mm). Use the appropriate electrical current for the thickness of your metal; too little current won’t produce a strong weld, while too much can burn through the metal. Control the weld time carefully, typically a few seconds, to avoid overheating or underheating.
After welding, perform a peel test to assess the weld’s strength by attempting to peel the weld apart. Additionally, ensure the metal is supported on a solid surface during welding to prevent movement and maintain consistent pressure. By following these steps, you can achieve a strong and reliable spot weld in your sheet metal projects.
Common issues in spot welding often include splattering, electrode wear and misalignment, poor weld strength or incomplete fusion, shunting, and equipment issues.
By addressing these common issues with the suggested solutions, you can achieve stronger and more consistent spot welds.
Yes, there are advanced techniques for spot welding that can enhance the quality and efficiency of the welds. One such technique involves the use of automated systems that dynamically adjust welding parameters like current, pressure, and duration in real-time. This ensures consistent and high-quality welds, especially in high-volume production environments. Another advanced method includes the use of specialized electrodes made from materials like tungsten or molybdenum, which are particularly useful for welding high-conductivity metals such as copper and brass. Additionally, strategic placement of welds and sequence optimization can minimize distortion and ensure the structural integrity of the welded assembly. Quality testing methods such as ultrasonic testing, tensile-shear tests, and peel tests are also employed to verify the internal integrity and strength of the welds. These advanced techniques help achieve more reliable and durable spot welds.

