When it comes to achieving the perfect grill, the choice of heat shield can make all the difference. Two popular options stand out: porcelain steel and stainless steel heat shields. But which one is better for your grilling needs? In this article, we delve into the key differences between these two materials, examining their composition, heat retention properties, durability, maintenance requirements, and cost. Whether you’re a seasoned grill master or an enthusiastic beginner, understanding these distinctions will help you make an informed decision. Ready to elevate your grilling game? Let’s uncover which heat shield reigns supreme.
Heat shields are crucial components in grilling setups as they distribute heat evenly, ensuring food cooks uniformly. They distribute heat evenly to prevent hot spots and protect burners from debris like fat drippings, reducing flare-ups and burner damage.
Achieving consistent cooking results is essential in grilling. Heat shields play a vital role in this aspect. Porcelain-coated steel heat shields retain heat effectively, helping maintain a relatively consistent temperature across the cooking surface. If the enamel coating is damaged, heat distribution may become uneven. On the other hand, stainless steel heat shields, often made of SS304, distribute heat more evenly and consistently, making them ideal for high-temperature grilling and ensuring that food cooks uniformly.
Flare-ups can be a nuisance during grilling, charring the food and potentially causing safety hazards. Heat shields act as a shield against fat drippings that fall onto the burners. Porcelain-coated steel heat shields initially offer good protection, but if the porcelain enamel chips or cracks, the exposed steel can react with the drippings in a less controlled manner. Stainless steel heat shields are more reliable for long-term prevention of flare-ups due to their corrosion resistance and durability. They can withstand the impact of fat drippings without significant damage.
Burners are a costly part of a grill, and protecting them is essential for the longevity of the grill. Porcelain-coated steel heat shields provide an initial layer of protection. However, the brittle nature of the enamel means that it can break, leaving the underlying steel vulnerable to corrosion from moisture and debris. Stainless steel heat shields offer superior burner protection. Their corrosion-resistant properties ensure that they can withstand the harsh grilling environment, protecting the burners from damage for a longer period.
Porcelain steel heat shields are crafted from a base of carbon steel, which is coated with a porcelain-like enamel. The enamel is created by fusing powdered glass to the steel at high temperatures, resulting in a smooth, durable coating. This enamel serves as an initial barrier against corrosion and enhances the aesthetic appeal of the heat shield.
One of the standout features of porcelain steel heat shields is their ability to retain heat. The porcelain coating effectively absorbs and retains heat, helping to maintain consistent cooking temperatures. This property allows for even heat distribution across the grilling surface, reducing the likelihood of hot spots and ensuring that food cooks uniformly. However, the effectiveness of heat retention can diminish if the porcelain coating chips or cracks, exposing the underlying steel to direct heat and potential rusting.
The durability of porcelain steel heat shields depends heavily on the integrity of the porcelain enamel coating. Initially, the enamel provides excellent protection against the elements and high temperatures typical of grilling. However, the coating is prone to chipping and cracking, especially if the heat shield is subjected to rough handling or thermal shock. Once the enamel is damaged, the exposed steel can corrode quickly, significantly reducing the lifespan of the heat shield.
Maintaining porcelain steel heat shields requires gentle cleaning and careful handling to preserve the enamel coating. Typically, a soft cloth or sponge with mild soap and water is sufficient. Abrasive cleaning tools and harsh chemicals should be avoided, as they can scratch or wear down the enamel. Regular inspection for chips or cracks is essential, and any damaged areas should be addressed promptly to prevent rusting.
Porcelain steel heat shields are generally more affordable than their stainless steel counterparts. The cost-effectiveness of porcelain steel makes them an attractive option for budget-conscious consumers. However, frequent replacements may be needed if the enamel coating gets damaged, leading to higher long-term costs.
Stainless steel heat shields are typically made from high-quality stainless steel alloys such as SS304 or SS316. These alloys contain chromium that forms a protective layer, enhancing corrosion resistance. The material’s inherent strength allows it to withstand high temperatures and harsh conditions without degrading, making it a durable choice for grilling applications.
Stainless steel distributes heat evenly across the grilling surface, maintaining stable cooking temperatures even though it may not retain heat as long as porcelain-coated steel. This property is particularly beneficial for high-temperature grilling, where uniform heat is crucial for achieving perfect sears and even cooking.
A major advantage of stainless steel heat shields is their exceptional durability. Unlike porcelain-coated steel, stainless steel does not chip or crack under thermal stress. Its resistance to corrosion and rust ensures longevity, even with frequent exposure to the moisture and high temperatures typical of grilling.
Stainless steel heat shields are relatively easy to maintain. They can withstand rigorous cleaning methods, including scrubbing with abrasive pads and using strong cleaning agents, without sustaining damage. This resilience makes them a low-maintenance option, reducing the need for frequent replacements and repairs.
Although stainless steel heat shields are more expensive initially, their durability and low maintenance can save money over time. The initial investment is offset by the reduced need for replacements and repairs, making them a cost-effective choice in the long run.
Stainless steel heat shields are widely used in various industries due to their durability and versatility. In grilling, they are preferred for high-temperature cooking and environments where consistent performance is essential. Beyond grilling, stainless steel heat shields are employed in automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications, where their high-temperature resistance and corrosion resistance are critical.
Porcelain steel heat shields are known for their superior heat retention capabilities due to the enamel coating, which absorbs and retains heat efficiently. This results in consistent cooking temperatures and helps avoid hot spots. However, when the coating is damaged, the exposed steel retains heat less effectively, leading to uneven cooking.
Stainless steel heat shields, while not retaining heat as effectively as porcelain steel, excel in distributing heat evenly across the grilling surface. This ensures that the temperature remains consistent, providing reliable cooking performance without the risk of hot spots.
Porcelain steel heat shields offer initial durability thanks to the protective enamel coating, which is susceptible to chipping and cracking under thermal stress or rough handling. Once the enamel is compromised, the underlying steel is prone to rust and corrosion, significantly reducing the lifespan of the heat shield.
In contrast, stainless steel heat shields are extremely durable. They do not chip or crack, and their inherent resistance to corrosion ensures longevity even with frequent exposure to high temperatures and moisture. This makes stainless steel a reliable choice for long-term use.
Maintaining porcelain steel heat shields requires careful handling to preserve the integrity of the enamel coating. Gentle cleaning methods using mild soap and soft cloths are recommended to avoid damaging the coating. Regular inspections for chips or cracks are necessary to prevent rust formation.
Stainless steel heat shields are much easier to maintain. They can withstand more rigorous cleaning methods, including scrubbing with abrasive pads and using strong cleaning agents, without sustaining damage. This resilience reduces the need for frequent maintenance and repairs.
Porcelain steel heat shields are generally more budget-friendly upfront compared to stainless steel options. However, their susceptibility to chipping and rusting may require frequent replacements, increasing long-term costs.
Stainless steel heat shields come with a higher initial price tag, but their durability and low maintenance requirements can result in significant cost savings over time. The reduced need for replacements and repairs makes stainless steel a cost-effective choice in the long run.
When evaluating Stainless steel heat shields offer superior durability, ease of maintenance, and consistent heat distribution. Despite the higher initial cost, their long-term reliability and performance make them a preferred choice for many grilling enthusiasts and professionals.
Porcelain steel heat shields are favored for their heat retention properties, which can enhance cooking efficiency and reduce energy consumption. However, chipping and rusting risks can gradually affect grilling performance.
Stainless steel heat shields, on the other hand, ensure consistent grilling performance with even heat distribution and minimal maintenance. Their durability makes them ideal for high-temperature grilling, providing reliable and long-lasting performance.
When determining the best material for grilling, several factors come into play. Understanding these aspects can help you make an informed decision based on your specific needs and preferences.
Heat retention and distribution are crucial for achieving the desired cooking results. Porcelain steel heat shields are great at retaining heat because their enamel coating maintains even temperatures and minimizes hot spots. This is particularly beneficial for slow cooking and grilling larger cuts of meat. On the other hand, stainless steel heat shields are known for their even heat distribution, which is ideal for high-temperature grilling and achieving perfect sears.
Durability is another critical factor. Porcelain steel heat shields offer good initial durability but are prone to chipping and cracking, especially under thermal stress or rough handling. Once the enamel coating is compromised, the underlying steel can rust, reducing the lifespan of the heat shield. In contrast, stainless steel heat shields are highly durable, resistant to chipping, cracking, and corrosion. Their longevity makes them a more reliable choice for frequent grillers.
Maintenance requirements can influence the overall convenience and longevity of your grill. Porcelain steel heat shields require careful handling to avoid damaging the enamel coating. Cleaning should be done gently with non-abrasive tools to prevent chipping.
Cost is a significant consideration for many consumers. Porcelain steel heat shields are generally more affordable upfront, making them an attractive option for budget-conscious individuals. However, their susceptibility to damage may lead to higher long-term costs due to frequent replacements. Stainless steel heat shields come with a higher initial price tag, but their durability and low maintenance requirements can result in cost savings over time.
Certain grilling situations may make one material better than the other.
Experts in the field often recommend choosing a heat shield material based on your specific grilling needs and preferences.
Consider these factors and your grilling habits to choose the heat shield material that best suits your needs for an optimal grilling experience.
Handle porcelain steel heat shields with care to protect the porcelain coating. Avoid dropping or striking the shields, as the coating can easily chip or crack, exposing the underlying steel to rust and corrosion.
Use a soft cloth or sponge with mild soap and water to clean the shields, avoiding abrasive methods that can damage the porcelain coating. For tougher stains, a mixture of baking soda and water can be used as a gentle abrasive.
Inspect the heat shields regularly for any signs of chips or cracks in the porcelain coating. Promptly repair minor chips with high – temperature porcelain touch – up paint, or replace the heat shield if the damage is extensive. This will help prevent rust from forming on the exposed steel.
Stainless steel heat shields are more robust and can withstand rigorous cleaning methods. Use a mild detergent and a non – abrasive scrubber to remove grease and food residues. For tough stains, use a stainless steel cleaner or a vinegar and water mixture.
Over time, stainless steel heat shields may discolor due to exposure to high temperatures. This discoloration is purely cosmetic and does not affect the performance or durability of the heat shield. If desired, stainless steel polish can be used to restore the original shine.
Stainless steel heat shields need less frequent maintenance than porcelain steel. Cleaning them after each use usually keeps them in good condition. Unlike porcelain steel, there is no need for frequent inspections for chips or cracks, as stainless steel does not have a coating that can be damaged.
| Feature | Porcelain Steel Heat Shields | Stainless Steel Heat Shields |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Prone to chipping; requires gentle handling | Highly durable; resistant to corrosion and damage |
| Cleaning Ease | Easier to clean initially but requires care | More effort needed to clean grease, but robust |
| Maintenance Frequency | Regular inspections necessary to prevent rust | Less frequent maintenance; durable over time |
| Cost | Generally more affordable initially | More expensive but offers long – term savings |
Porcelain steel heat shields offer excellent heat retention but require careful handling to prevent damage. Stainless steel heat shields, while more expensive initially, provide superior durability and low maintenance over time. The choice between these materials depends on specific needs and priorities—whether it’s a focus on heat retention or long – term durability and ease of maintenance.
Porcelain-coated steel heat shields are generally safe and non-toxic. However, if the porcelain coating is damaged, the underlying steel can rust, potentially leading to the ingestion of rust particles if food comes into contact with it.
The primary risk with these heat shields is handling. They require gentle cleaning to prevent chipping of the porcelain coat. Once the coat chips, the metal underneath is exposed, which can lead to accidents during cleaning or maintenance if not handled with care.
Stainless steel heat shields are non-reactive and safe for food preparation. They are corrosion-resistant and don’t degrade easily, so they are less likely to cause health problems related to material composition.
These heat shields are robust and can endure harsh cleaning methods without damage. This significantly reduces the risk of accidents during handling and cleaning compared to porcelain-coated steel heat shields.
| Aspect | Porcelain Steel Heat Shields | Stainless Steel Heat Shields |
|---|---|---|
| Material Safety | Generally safe and non-toxic, but rust can occur if the coating is damaged. | Non-reactive and resistant to corrosion. |
| Handling Risks | Require careful handling to avoid chipping of the porcelain coat. | Robust and can withstand harsh cleaning without damage. |
| Health Hazards | Possible ingestion of rust if coating is damaged. | No specific health hazards associated with material composition or handling. |
Extreme heat, though not directly related to the material of heat shields, can pose significant health risks. Heat exhaustion and heat stroke are common, especially for the elderly and those with chronic conditions. Proper use and maintenance of heat shields can help reduce the risks associated with heat exposure.
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
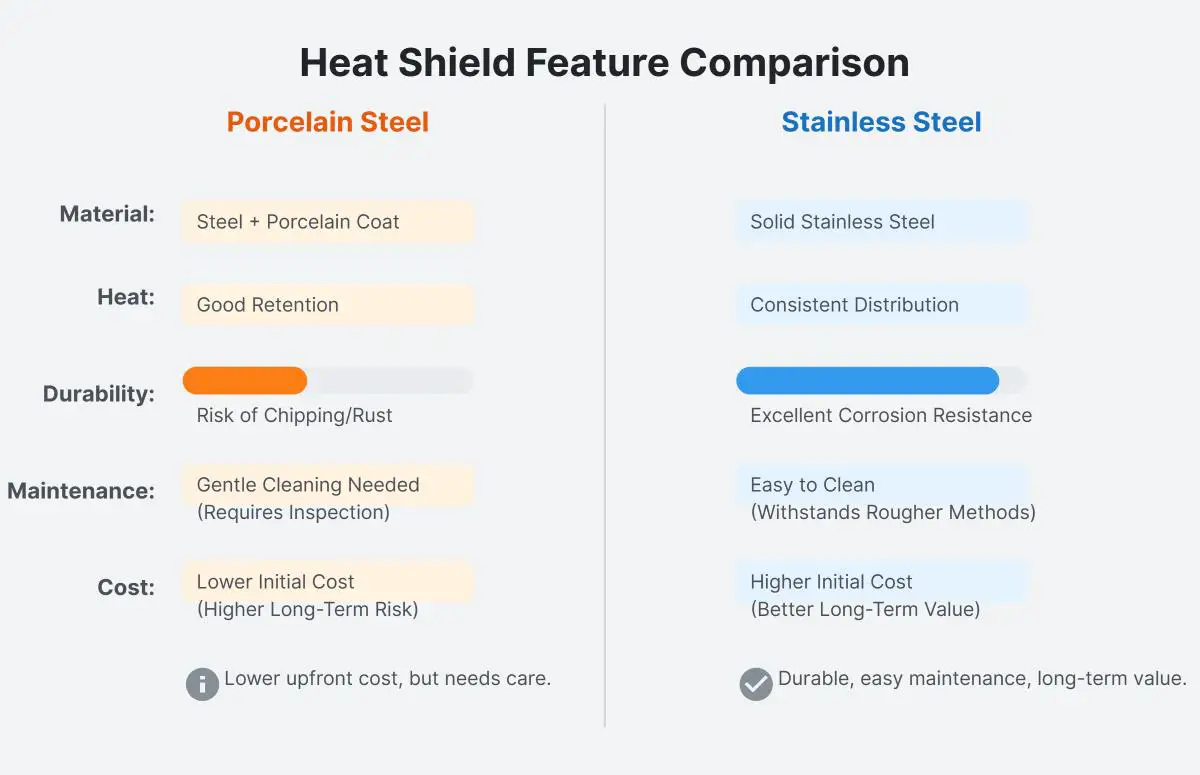
The key differences between porcelain steel and stainless steel heat shields lie in their material composition, heat retention properties, durability, maintenance requirements, and cost.
Porcelain steel heat shields have a carbon steel base coated with a porcelain-like finish, which enhances heat retention and distribution. However, the coating can chip over time, leading to corrosion. They require gentle cleaning methods and regular inspections to maintain their integrity. Porcelain steel heat shields are generally more affordable initially but may incur higher long-term costs due to potential replacement needs.
Stainless steel heat shields are made entirely of stainless steel, offering exceptional durability and corrosion resistance. They provide consistent heat distribution and can handle high temperatures effectively. Stainless steel heat shields are easier to clean and maintain, as they can withstand rougher cleaning methods without damage. Although more expensive upfront, their longevity makes them a cost-effective choice over time.
The choice between porcelain steel and stainless steel for grilling heat shields depends on your priorities. Porcelain steel is great for heat retention, ensuring even cooking and better searing at a lower initial cost. However, its enamel coating can chip, increasing rust risk and potentially requiring more frequent replacements. Stainless steel, on the other hand, offers high durability and corrosion resistance, is easy to maintain, and provides long – term value despite a higher upfront cost. Consider your budget, maintenance willingness, and emphasis on heat retention to make the best choice.
To maintain heat shields for longevity, the approach differs based on the material. For porcelain steel heat shields, handle them gently to prevent chipping the porcelain coating, which can lead to rust. Clean with non – abrasive scrubbers and mild detergents, avoiding harsh chemicals or high – pressure water. Regularly inspect for chips or cracks and repair or replace damaged areas promptly. For stainless steel heat shields, while they can withstand rough handling, clean them regularly using wire brushes or mild detergents. Although they’re less prone to damage, regular inspections help identify signs of wear or discoloration.
When considering the health risks associated with using heat shields in grilling, it is important to understand that the materials themselves—porcelain steel and stainless steel—do not inherently pose significant health risks when used properly. Both materials are safe for use in high-heat applications like grilling. However, there are a few considerations to keep in mind:
Heat shields significantly enhance grilling performance by protecting burners from debris and ensuring even heat distribution. They prevent flare-ups by stopping grease and oil from reaching the burners, resulting in safer and more controlled grilling. Additionally, heat shields eliminate hot spots by absorbing and radiating heat uniformly across the cooking surface, leading to evenly cooked food.
Porcelain steel heat shields are excellent at retaining heat, making them ideal for slow cooking or grilling larger cuts of meat. They are also cost-effective but may require careful handling due to the risk of the porcelain coating chipping and exposing the steel to rust.
On the other hand, stainless steel heat shields are highly durable, resistant to corrosion, and easier to clean. They provide consistent heat distribution, which is crucial for high-heat grilling, though they retain less heat compared to porcelain-coated options.
The choice between porcelain steel and stainless steel heat shields depends on your grilling needs, budget, and preference for durability versus heat retention.

