In the world of welding, precision and efficiency are everything. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or an industrial engineer, achieving a clean, consistent weld often comes down to one crucial component: the rectifier. This unsung hero of welding technology plays a pivotal role in converting alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC), ensuring the stable and controlled arc necessary for high-quality results. But how exactly does it work, and why is DC preferred over AC in many welding applications?
This article dives deep into the mechanics and benefits of rectifier welding machines, unraveling the science behind their ability to deliver unmatched current stability and arc control. From exploring the inner workings of thyristors and diodes to understanding their impact on industrial-scale welding, you’ll discover how these machines enhance efficiency and precision. Whether you’re curious about their technical design or their practical applications in industries like manufacturing and construction, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge to appreciate—and perhaps even master—their role in modern welding techniques. Get ready to spark your understanding!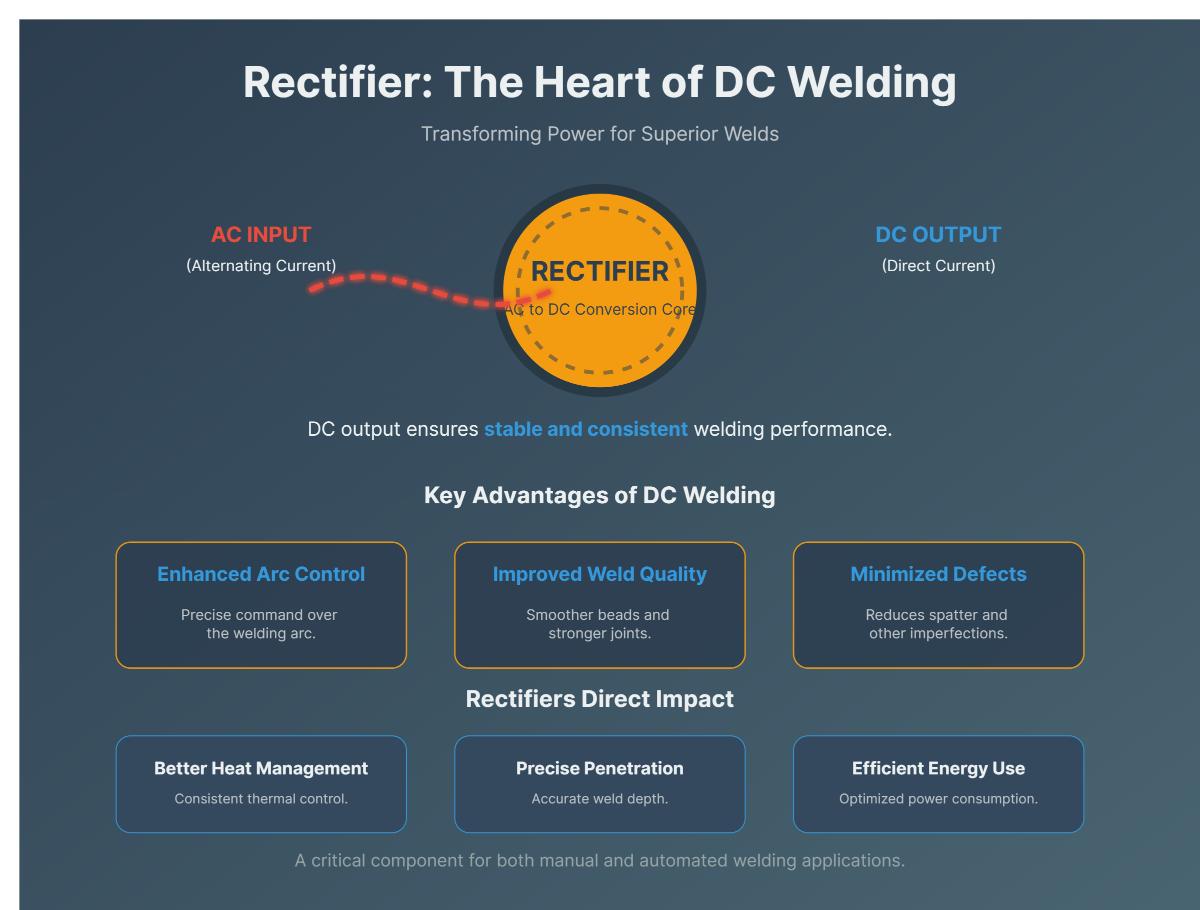
A rectifier in welding is a device that converts alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC), ensuring stable power for welding machines. This conversion is important because DC provides a steady electrical flow. This stability is crucial for producing high-quality welds.
AC power alternates direction, causing fluctuations that can destabilize the welding arc. In contrast, DC flows steadily in one direction, providing consistent performance. This steadiness offers several advantages:
These benefits make DC the preferred choice in many welding applications, particularly where precision and reliability are critical.
Rectifiers play a crucial role in converting AC to DC by using electronic components like diodes or thyristors. These components regulate electrical flow, allowing current to move in only one direction. This process produces a steady DC output, which is essential for maintaining a consistent welding arc.
By delivering reliable and stable power, rectifiers ensure welding machines can perform efficiently across various conditions. This consistency not only enhances the quality of the weld but also reduces errors and defects. Whether working on large-scale industrial projects or detailed craftsmanship, rectifiers are indispensable for achieving high-quality welding results.
Rectifier welding machines are built with essential components that work together to convert AC power into DC and provide a stable, reliable current for welding. These components ensure precision, efficiency, and high-quality weld performance.
The conversion of AC power to DC in a rectifier welding machine is a step-by-step process that ensures the output is optimized for welding.
Thyristor rectifiers are widely used in welding applications due to their ability to provide precise control over welding current and voltage. These rectifiers employ thyristors, semiconductor devices that enable controlled rectification of AC power into DC, ensuring flexibility and precision in welding processes. Integrated feedback circuits track and adjust voltage and current in real time for consistent performance.
Thyristor rectifiers are commonly used in industrial welding environments, such as manufacturing pipelines or structural components, where precision and reliability are critical.
Diode rectifiers are simple, reliable, and cost-effective tools for converting AC power into DC for welding. They operate by enabling a one-way flow of current, transforming AC into a pulsating DC waveform.
Diode rectifiers are ideal for basic welding tasks, such as stick welding, where precise control over current and voltage is less critical.
Transformer rectifiers are a traditional and dependable option for welding applications. They combine a transformer to step down voltage and a rectifier to convert AC into DC.
These rectifiers are commonly used in heavy industrial sectors, such as shipbuilding and construction, where durability and consistent performance are essential.
Inverter-based rectifiers are a modern, compact, and energy-efficient solution for welding. They use advanced high-frequency conversion to reduce the size and weight of components while delivering precise control over welding parameters.
These rectifiers are widely used in industries like automotive repair and aerospace, where portability and precision are key priorities.
| Feature | Thyristor Rectifiers | Diode Rectifiers | Transformer Rectifiers | Inverter-Based Rectifiers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | High | Low | Moderate | High |
| Complexity | Moderate | Low | Moderate | High |
| Efficiency | High | Moderate | Moderate | High |
| Cost | Varies | Low | Moderate | High |
| Applications | Precision welding | Basic welding | Heavy-duty welding | Portable and precision welding |
Each rectifier type offers unique advantages, so selecting the right one depends on your specific welding needs and priorities.
Rectifier welding machines are essential in various industries, offering stable and precise DC output for high-quality welding applications. Their versatility and efficiency make them indispensable tools in a wide range of industrial tasks.
These machines are crucial for producing stainless steel seamless pipes, structural components, and automotive parts, ensuring precision and consistency across varying material thicknesses and welding positions. Their adaptability makes them invaluable in high-demand production environments where quality and reliability are paramount.
Industries like shipbuilding, aerospace, and construction use rectifier welding machines for large, thick materials that demand durability and precision under extreme conditions. Their robust performance ensures strong and reliable welds, even in challenging environments.
Rectifier welding machines are a go-to solution for repair and maintenance tasks in sectors such as mining, transportation, and power plants. Their compatibility with different electrode types and materials makes them ideal for on-site repairs, ensuring quick and efficient restoration of equipment and structures.
Rectifier welding machines enhance advanced techniques like TIG and MIG welding. This makes them ideal for intricate tasks, such as fabricating pressure vessels and heat exchangers. Their precision and control enable the creation of complex welds with exceptional quality and durability.
The advantages of rectifier welding machines extend far beyond their basic functionality, offering a range of features that improve welding quality, efficiency, and reliability.
Rectifier welding machines provide consistent current, reducing defects like spatter and porosity for cleaner, more uniform welds. This ensures high-quality results that meet the stringent demands of industrial applications.
A stable DC output allows welders to control the welding arc more precisely, ensuring better heat management, deeper penetration, and stronger welds. This level of control is particularly valuable in projects that require intricate and defect-free connections.
These machines work seamlessly with various techniques, including SMAW, GMAW, and FCAW, making them suitable for welding materials like steel, aluminum, and alloys. Their adaptability enables them to handle diverse industrial requirements with ease.
By efficiently converting AC to DC, rectifier welding machines reduce energy consumption and lower operational costs, especially in large-scale operations. This energy efficiency translates into significant cost savings over time.
Modern rectifier welding machines offer advanced controls for adjusting voltage, current, and arc force, ensuring optimal performance and reducing material waste. This customization capability enables welders to achieve the exact specifications required for each project.
Built to endure harsh environments, rectifier welding machines are both durable and, in inverter-based models, portable—ideal for fieldwork and remote applications. Their rugged construction ensures long-term reliability, while their compact design enhances mobility and convenience.
The integration of rectifier welding machines into industrial workflows significantly boosts productivity. Their ability to deliver precise and stable performance reduces rework, enhances output quality, and optimizes resource utilization. With these machines, industries can achieve higher efficiency while maintaining cost-effectiveness, ensuring they stay competitive in demanding markets.
Adjusting the current settings on rectifier welding machines is essential for achieving the best results, depending on the welding technique and material. Several factors influence how to tailor these settings:
Selecting and setting up the machine correctly ensures better performance with various electrodes. Key considerations include:
For consistent performance, follow these periodic checks:
Proper heat management is crucial for maintaining the efficiency and lifespan of your welding machine:
Rectifier welding machines may encounter occasional issues. Here’s how to address them:
Following the manufacturer’s guidelines is key to keeping the machine safe and efficient:
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
The role of a rectifier in a welding machine is to convert alternating current (AC) from the power supply into direct current (DC), which is essential for achieving stable and consistent welding performance. DC is preferred in welding processes because it provides a steady current that enhances arc control, improves weld quality, and minimizes defects. By ensuring a smooth and reliable DC output, the rectifier enables better heat management, precise penetration, and efficient energy use, making it a critical component in both manual and automated welding applications.
A rectifier converts AC to DC for welding by utilizing diodes or thyristors, which allow current to flow in only one direction. In a full-wave rectifier, both the positive and negative halves of the AC waveform are processed, flipping the negative cycles to the positive side, resulting in a pulsating DC output. This output is then smoothed using components like capacitors, which reduce fluctuations and create a steady DC current. The stable DC output is critical for welding as it ensures consistent arc performance, better control, and high-quality welds.
Thyristor rectifiers offer several advantages in welding applications. They are highly efficient and provide effective power control, converting AC to DC with minimal energy loss, which is crucial for maintaining a stable welding arc. These rectifiers allow precise adjustment of welding current and voltage, enhancing the ability to fine-tune welding parameters for optimal results. Thyristor rectifiers also ensure consistent weld quality through smooth waveform output, reducing defects. Their compact and lightweight design makes them easy to handle, while their energy-efficient operation contributes to cost savings. Additionally, they are reliable and require minimal maintenance, thanks to their solid-state construction. Their adaptability to various welding parameters further enhances their utility in diverse welding tasks.
Rectifier welding machines improve current stability and arc control by converting alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC), which provides a steady and consistent current essential for uniform weld quality. The DC output minimizes fluctuations, ensuring a stable arc that is easier to control and reduces defects. Additionally, rectifiers reduce current ripple and incorporate mechanisms like reactors and solid-state devices to maintain precise current levels. This stability enhances arc characteristics, allowing for better heat management, consistent penetration, and proper fusion. Adjustable parameters further optimize arc control, making the welding process more efficient and reliable.
The main components of a rectifier welding machine include the transformer, rectifier circuit, control circuit, and reactor. The transformer steps down the high-voltage input to a lower voltage suitable for welding. The rectifier circuit, which includes diodes or thyristors, converts the AC output from the transformer into DC. The control circuit manages welding parameters, featuring trigger and feedback circuits for adjusting current and voltage. Lastly, the reactor smooths the output waveform, ensuring a stable welding current. These components work together to provide a consistent and efficient welding process.
Rectifier welding machines are extensively used in industrial applications due to their ability to convert AC to DC, offering stable and controllable welding currents. This stability is crucial for achieving consistent weld quality, essential in industries such as manufacturing and construction. These machines are particularly valuable in the production of stainless steel seamless pipes and heavy-duty welding projects, where precise arc control and consistent current are necessary for high-quality welds. Additionally, rectifier welding machines enhance efficiency and reduce power consumption, making them a cost-effective choice for industrial settings. They are designed to handle various materials and welding techniques, offering customization options to meet specific job requirements, thus playing a vital role in enhancing the productivity and quality of industrial welding processes.

