In the world of piping and plumbing, understanding the different types of pipes can be crucial for any project, whether it’s a home renovation or an industrial installation. Have you ever wondered why Schedule 40 pipes are so widely used, or how they compare to their counterparts like Schedule 80? This article dives deep into the basics, applications, and comparisons of Schedule 40 pipes, shedding light on their defining characteristics and the industries that rely on them. From the intricacies of ANSI standards to the practical differences between steel and PVC options, we’ll explore what makes Schedule 40 pipes a go-to choice for many professionals. Ready to uncover the advantages and specific use cases of these essential components? Let’s get started.
Schedule 40 pipes are a type of pipe that follow specific wall thickness standards set by organizations like the American National Standards Institute (ANSI). These standards ensure the pipes can handle certain pressure levels and meet safety requirements, making them suitable for various industrial and construction applications.
Schedule 40 pipes are commonly made from materials such as steel and PVC. The choice of material depends on the specific application:
The wall thickness of Schedule 40 pipes varies with the pipe size, impacting their pressure handling capabilities. For example, a 1-inch Schedule 40 PVC pipe can handle pressures up to 450 PSI, while a 6-inch Schedule 40 PVC pipe is rated for 180 PSI. This flexibility makes Schedule 40 pipes suitable for various pressure applications while ensuring they fit standard dimensions.
Schedule 40 pipes are versatile and utilized in various industries and applications:
Schedule 40 pipes are often compared with Schedule 80 pipes, which have thicker walls and higher pressure ratings:
To install Schedule 40 pipes, you need to measure, cut, and fit the pipes using the right primers and cements. Regular inspections to detect wear, corrosion, or leaks, along with methods like pigging and environmental controls, can extend the service life of the pipes.
Schedule 40 pipes adhere to specific standards set by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI), which ensure uniformity in dimensions, wall thickness, and material composition. These standards are crucial for maintaining consistency and reliability in various applications, including plumbing, construction, and industrial processes. Compliance with ANSI standards ensures that Schedule 40 pipes can withstand the required pressure and environmental conditions, providing safety and efficiency in their use.
Adhering to ANSI and other relevant standards is crucial for ensuring safety, reliability, and compatibility. Compliance with these standards is essential for several reasons:
Schedule 40 pipes are popular in construction and plumbing because they offer a good balance of strength and affordability. Regulatory bodies require these pipes to meet specific standards to ensure the safety and reliability of water distribution systems, drainage, and structural support. Compliance with standards such as ASTM A53 for steel pipes and ASTM D1784 for PVC pipes is mandatory in many jurisdictions.
Industries such as oil refineries, chemical processing plants, and food manufacturing rely on Schedule 40 pipes for the transport of liquids and gases. These environments often involve moderate pressures and corrosive substances, necessitating adherence to strict standards like ASME B36.10M. Compliance ensures that the pipes can withstand the operational demands and maintain integrity over time.
For residential plumbing, Schedule 40 pipes are commonly used in pressurized water supply lines and non-pressurized drainage systems. Standards compliance ensures that the pipes are safe for potable water applications and can handle the typical pressures found in household plumbing systems. This compliance also aids in preventing issues such as leaks and water contamination.
Schedule 40 pipes come in different materials, each following specific standards:
It’s crucial to know the pressure and temperature ratings of Schedule 40 pipes to ensure they are used safely:
ASME B36.10M is a key standard for steel Schedule 40 pipes, covering dimensions, materials, and testing procedures. Compliance with this standard ensures that the pipes meet the necessary criteria for quality and performance in demanding industrial applications.
For PVC Schedule 40 pipes, ASTM D1784 is the governing standard. It specifies the materials’ requirements, including resistance to corrosion and suitability for pressurized water distribution systems. Adhering to this standard ensures that PVC pipes can be used safely in a variety of water and plumbing applications.
The wall thickness of Schedule 40 pipes is standardized by ANSI, providing consistent performance across different materials. This standardization is crucial for ensuring that the pipes can handle the pressures and temperatures specified for their intended applications.
When engineers and contractors understand and follow these standards, they can use Schedule 40 pipes effectively and safely in their projects. This compliance not only guarantees performance but also facilitates maintenance and integration with other system components.
Schedule 40 pipes are extensively used in plumbing for both residential and commercial applications. These pipes serve as water supply lines, drainage systems, and sewage pipes. The smooth interior surface of these pipes ensures efficient water flow and minimizes the risk of clogs. They are also resistant to corrosion, which makes them a durable choice for transporting potable water.
In industrial settings, Schedule 40 pipes are invaluable for transporting gases and liquids. They are commonly used in manufacturing plants and chemical processing facilities due to their ability to handle moderate pressures and resist corrosion. These pipes are crucial for systems that require the integrity of the transported substance to be maintained.
Schedule 40 pipes play a crucial role in agricultural irrigation systems. Their durability and reliability ensure a consistent water supply across fields. These pipes are used to create efficient irrigation networks that help in the optimal distribution of water to crops, thereby boosting crop yields.
Schedule 40 PVC pipes are widely used as conduit for electrical wiring. They protect electrical cables and wires from physical damage and environmental factors such as moisture and chemicals. This makes them ideal for residential, commercial, and industrial environments where protecting electrical infrastructure is crucial.
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems frequently utilize Schedule 40 pipes. These pipes are used for routing hot and cold water, as well as for air ducts. Their moderate wall thickness offers a balance of strength and ease of installation, making them perfect for HVAC applications requiring both durability and manageability.
In construction, Schedule 40 pipes can serve as structural elements. They are used as pillars, bracing, and support structures due to their strength and resistance to environmental stressors. Their ability to withstand moderate pressures makes them suitable for various load-bearing applications in building frameworks.
Schedule 40 pipes are used in the oil and gas industry for the transportation of fluids such as crude oil, natural gas, and refined products. Their robust construction ensures safe and efficient operations, which is vital in preventing leaks and ensuring the integrity of the transported materials.
In the telecommunications sector, Schedule 40 PVC pipes are used to protect fiber optic cables and other communication lines. These pipes safeguard against physical damage and environmental exposure, ensuring reliable and uninterrupted communication services.
Fire protection systems, including sprinkler systems and fire hoses, often use Schedule 40 pipes. These pipes are chosen for their reliability and ability to withstand the pressures involved in firefighting applications. They are a critical component in ensuring that fire suppression systems function effectively when needed.
Beyond industrial and utility applications, Schedule 40 pipes are also popular in decorative and DIY projects. Their strength and aesthetic appeal make them ideal for creating sturdy shelves, coat hooks, and other creative home improvements. Their versatility and ease of use allow for innovative and functional designs in various DIY applications.
The main differences between Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 pipes are their wall thickness and pressure ratings. Schedule 80 pipes have thicker walls compared to Schedule 40 pipes, making them stronger and able to handle higher pressures. For example, a 1-inch Schedule 40 PVC pipe has a wall thickness of 0.133 inches, while a 1-inch Schedule 80 PVC pipe has a wall thickness of 0.179 inches. This increased thickness allows Schedule 80 pipes to withstand higher internal pressures, making them suitable for more demanding applications.
Pros:
Cons:
Pros:
Cons:
Online interactive tools and calculators help engineers and contractors choose the best pipe schedule by allowing them to input parameters like pipe size, pressure rating, and application type. These tools provide recommendations on whether Schedule 40 or Schedule 80 pipes are more suitable for their project.
Steel pipes are renowned for their strength and durability, making them a preferred choice for demanding applications. These pipes can withstand high pressures and temperatures, making them ideal for industrial and commercial applications.
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) pipes are widely used for their affordability, ease of installation, and resistance to corrosion. These pipes are particularly popular in plumbing, irrigation, and certain industrial applications.
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
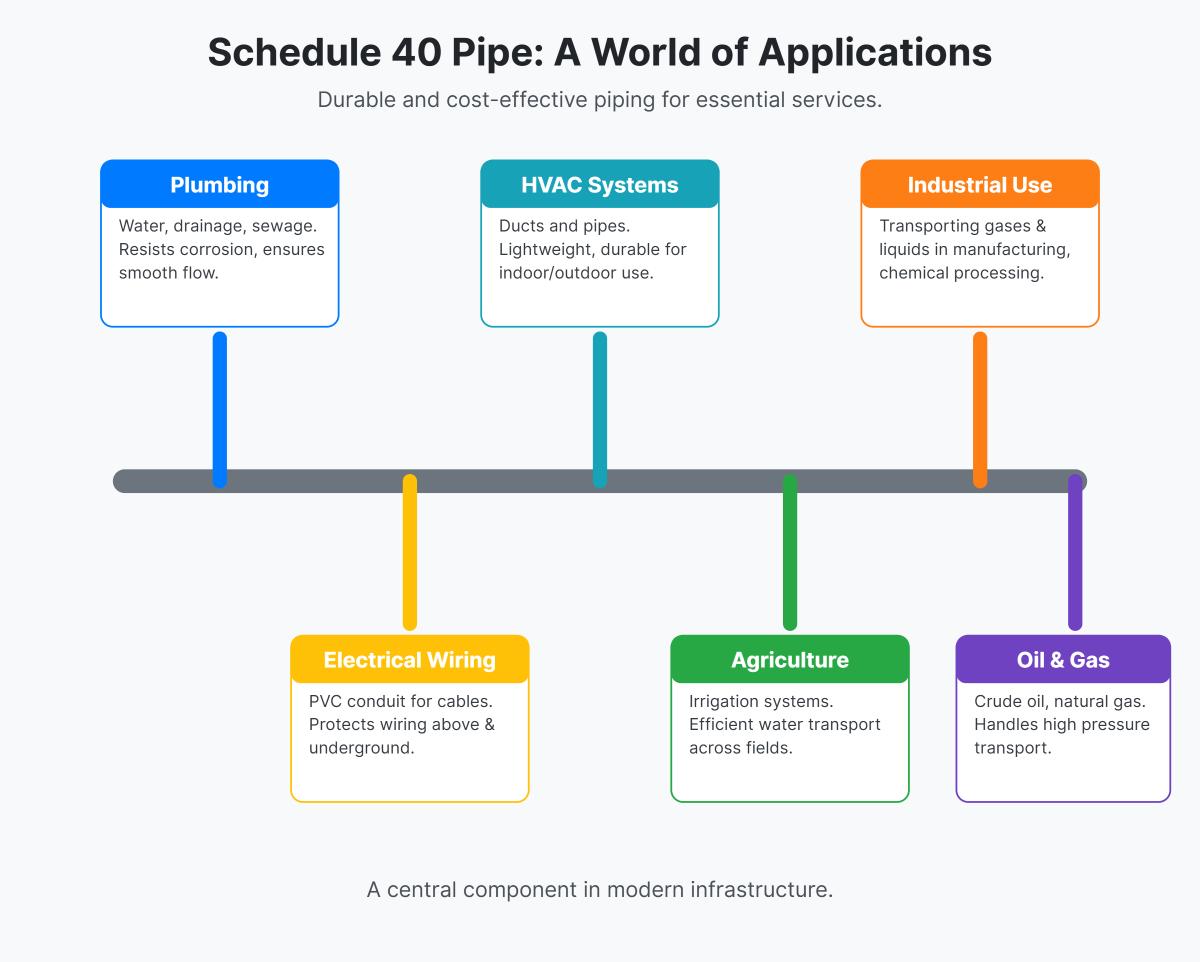
Schedule 40 pipes are commonly used for a variety of applications due to their balanced characteristics of durability and cost-effectiveness. They are extensively utilized in plumbing systems for water supply, drainage, and sewage, benefiting from their resistance to corrosion and smooth internal surfaces that ensure efficient flow and reduce clogging risks. In electrical wiring, Schedule 40 PVC conduit pipes protect and route electrical cables, offering physical and environmental protection for both above-ground and underground installations. HVAC systems also employ these pipes to route ducts and pipes, leveraging their lightweight yet durable nature for indoor and outdoor use. Additionally, in agriculture, Schedule 40 pipes are integral to irrigation systems, efficiently transporting water across fields. Industrial applications include the transport of gases and liquids in manufacturing and chemical processing, while the oil and gas industry uses them for transporting crude oil, natural gas, and refined products due to their pressure-handling capabilities.
Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 pipes primarily differ in wall thickness, pressure handling capacity, and their consequent applications. Schedule 40 pipes have thinner walls and are generally used in low-pressure applications such as residential plumbing and irrigation systems. Conversely, Schedule 80 pipes have thicker walls, making them suitable for high-pressure applications like industrial processes and chemical plants. This increased wall thickness in Schedule 80 pipes results in a reduced inner diameter compared to Schedule 40, which can affect fluid flow. While Schedule 40 pipes are more cost-effective and sufficient for standard building applications, Schedule 80 pipes, though more expensive, offer greater durability and resistance to mechanical stress and corrosive conditions. Therefore, the choice between the two should be based on the specific requirements of pressure, durability, and cost considerations for the intended application.
Schedule 40 pipes offer several advantages that make them suitable for various applications. These pipes are known for their durability and strength, with steel Schedule 40 pipes capable of withstanding high pressures, and PVC versions providing excellent resistance to corrosion, making them ideal for moist environments. They strike a balance between cost and performance, offering a budget-friendly option compared to higher schedule pipes like Schedule 80. The relatively thinner walls of Schedule 40 pipes also reduce installation costs due to easier handling and fitting.
The versatility of Schedule 40 pipes allows them to be used in industrial, residential, agricultural, and irrigation systems, as well as for protecting electrical cables and telecommunications infrastructure. Additionally, their lightweight nature, particularly with PVC, simplifies transportation and handling during construction. The smooth internal surface of these pipes ensures efficient fluid flow, reducing the risk of clogs in plumbing and drainage systems.
When choosing between steel and PVC Schedule 40 pipes, several factors should be considered to ensure the right fit for your project.
Steel Schedule 40 pipes, made from high-quality low-carbon steel, offer high strength and durability, making them suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature environments. They are commonly used in industrial and construction projects such as water distribution, oil and gas, and structural support. While steel pipes are generally resistant to corrosion, they may require additional coatings in aggressive environments. They tend to be more expensive but offer a longer lifespan with proper maintenance.
On the other hand, PVC Schedule 40 pipes, made from polyvinyl chloride, are highly resistant to corrosion and chemical damage. They are ideal for handling corrosive fluids and are commonly used in residential plumbing, irrigation systems, and industrial applications requiring chemical resistance. PVC pipes are generally less expensive and easier to install compared to steel pipes, with lower maintenance needs due to their corrosion resistance. However, they are best suited for moderate pressure applications and may degrade over time when exposed to high temperatures.
Schedule 40 pipes must comply with several standards to ensure they meet the required specifications for their intended applications. For steel Schedule 40 pipes, ASME B36.10M is the primary standard governing the dimensions, including outside diameter and wall thickness. This standard applies to both seamless and welded steel pipes, ensuring uniformity and reliability in their construction.
Additionally, Schedule 40 PVC pipes must adhere to ASTM standards, which define the dimensions, pressure ratings, and other critical parameters. These standards ensure that PVC pipes are suitable for various applications, such as plumbing and irrigation systems.
Galvanization standards are also important for steel Schedule 40 pipes, as they ensure corrosion resistance by coating the steel with zinc. Methods like hot-dip galvanization or in-line galvanization are commonly used.
Compliance with these standards is essential for ensuring the safety, reliability, and performance of Schedule 40 pipes in their respective applications.
Schedule 40 pipes are extensively utilized in various real-world applications due to their durability, cost-effectiveness, and resistance to corrosion. In residential and commercial plumbing, these pipes are commonly used for water supply lines and drainage systems, ensuring efficient water flow and minimizing clogging risks. In agricultural settings, they are essential for irrigation systems, transporting water across fields. Industrially, Schedule 40 steel pipes are integral to chemical processing, the oil and gas industry, and industrial gas transmission, where their resistance to high pressures and harsh conditions is invaluable. In HVAC systems, these pipes are used for routing ducts and pipes, while in construction, they provide structural support. Additionally, PVC Schedule 40 pipes protect electrical wiring in both above-ground and underground installations and safeguard communication lines in telecommunications. Other applications include automotive exhaust systems, fire protection sprinkler systems, and fluid management in laboratories and swimming pools.

