When it comes to plumbing and piping systems, choosing the right flange is crucial for ensuring a secure and efficient connection. But how do you decide between a Van Stone flange and a regular flange? Understanding the key differences and best uses of each can save you time, money, and prevent potential mishaps. Van Stone flanges, with their unique two-piece design consisting of a rotating ring and stub-end, offer distinct advantages in installation and maintenance compared to the fixed structure of regular flanges. But are they always the better choice? In this article, we’ll dive into the design features, material options, installation processes, and typical applications of both types of flanges, helping you make an informed decision for your specific needs. Ready to uncover which flange reigns supreme in various scenarios? Let’s get started!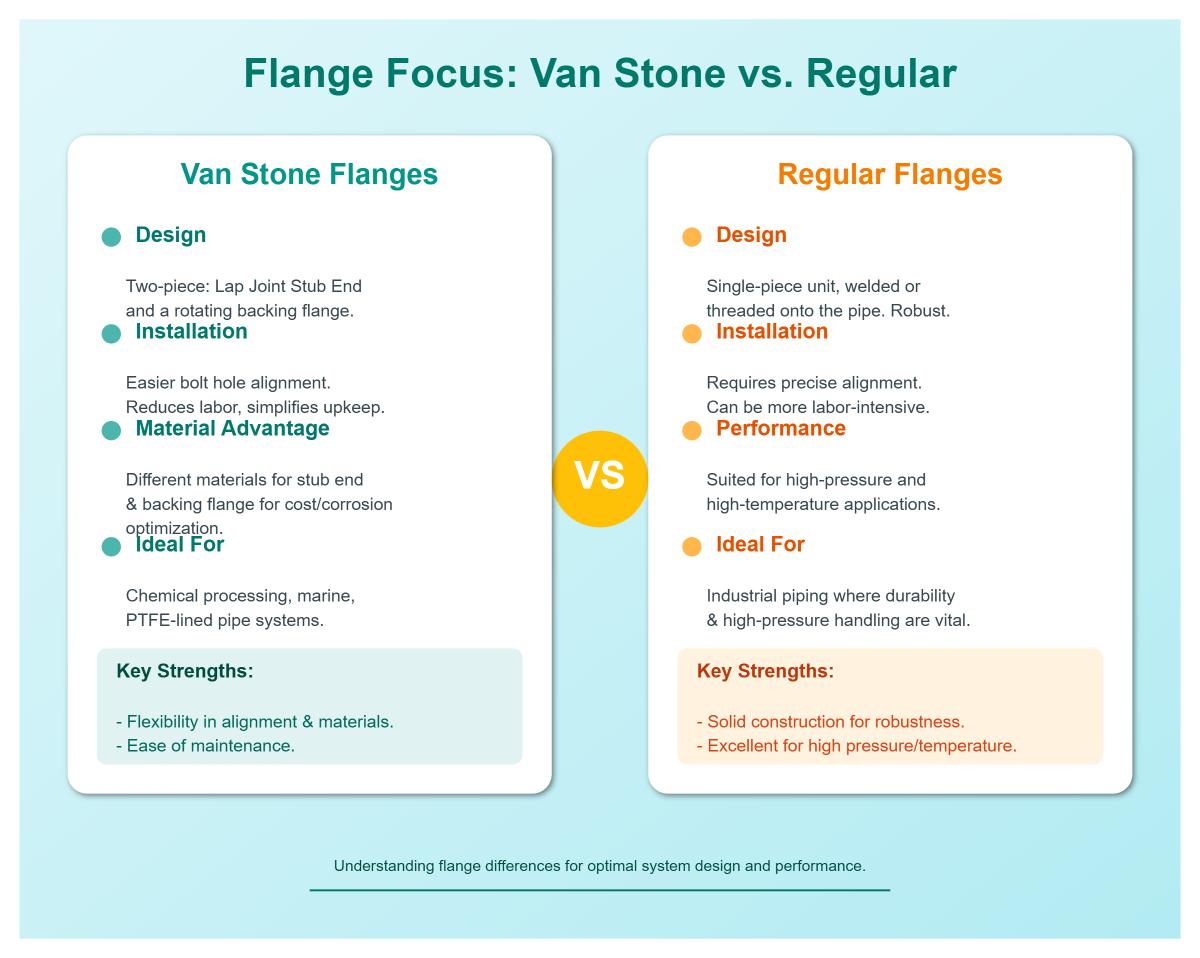
A flange is a mechanical component used to connect pipes, valves, pumps, and other equipment, forming a cohesive piping system. Flanges provide a means of assembling and disassembling pipe systems, facilitating maintenance and inspection. They are typically used to join pipes and components in a way that ensures a secure, leak-proof connection.
The Van Stone flange is a specialized type of flange known for its two-piece design, which includes a fixed flange and a rotating ring flange, offering several advantages in terms of ease of installation and maintenance.
A Van Stone flange consists of:
The stub-end is welded to the pipe, providing a base for the fixed flange, while the rotating ring flange allows easy bolt hole alignment. This design is particularly useful in applications requiring frequent maintenance or modifications.
Regular flanges, such as weld neck or slip-on flanges, are typically one-piece designs directly attached to the pipe. These flanges have fixed bolt holes, which means the pipe must be rotated or precisely aligned for bolt hole matching during installation. Types of regular flanges include:
The two-piece design of Van Stone flanges offers significant benefits. These include easier bolt hole alignment, simplified maintenance and disassembly, and compatibility with various materials such as PVC, stainless steel, and carbon steel. Unlike regular flanges, which require precise alignment and welding, Van Stone flanges allow for easier installation and maintenance thanks to their rotating ring design.
| Feature | Van Stone Flange | Regular Flange |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Two-piece design (rotating ring + stub-end) | Single-piece construction |
| Material | Hub and backing flange can use different materials (e.g., stainless steel + carbon steel) | Typically uniform material (e.g., carbon steel, alloy) |
| Flexibility | Rotating ring allows bolt-hole alignment without pipe rotation | Fixed bolt-hole alignment requires precise pipe positioning |
| Ease of Installation | Simplified alignment; no need to rotate pipe during assembly | Requires careful alignment; pipe rotation often needed |
| Welding | Stub-end butt-welded; backing flange slides on pre-welding | Directly welded/threaded to pipe |
| Maintenance | Easy disassembly for inspections/repairs | Permanent connections complicate maintenance |
| Pressure Rating | Low-to-medium pressure (ideal for chemical processing, HVAC) | High-pressure systems (e.g., oil/gas pipelines) |
| Temperature | Limited to moderate temps (e.g., PVC up to 140°F/60°C) | Handles higher temps (material-dependent) |
| Cost | Higher initial cost but lower long-term maintenance expenses | Cost-effective for static, high-pressure systems |
| Best Uses | Dynamic systems, corrosive environments, frequent maintenance needs | Permanent, high-stress industrial piping |
Van Stone flanges feature a two-piece design, with a rotating ring and a stub-end. This allows the flange to rotate independently from the pipe, simplifying installation. In contrast, regular flanges are single-piece constructions that need precise bolt-hole alignment, often requiring pipe rotation.
The two-piece design of Van Stone flanges allows for different materials for the hub and backing flange, like stainless steel and carbon steel. This flexibility can lead to cost savings and optimized performance in specific environments. Regular flanges are typically made from a single, uniform material, which can limit their adaptability to varying conditions.
One of the most notable advantages of the Van Stone flange is its ease of installation. The rotating ring enables bolt-hole alignment without the need to rotate the entire pipe, reducing installation time and effort. In contrast, regular flanges require careful alignment and often involve rotating the pipe to match the bolt holes, which can be time-consuming and challenging in confined spaces.
Van Stone flanges offer significant benefits in terms of maintenance. The ease of disassembling the flange simplifies inspections and repairs. Regular flanges, with their permanent connections, complicate maintenance tasks, as disassembly can be more labor-intensive and disruptive.
Van Stone flanges are ideal for low-to-medium pressure applications, like chemical processing and HVAC systems, and are limited to moderate temperatures, especially with materials like PVC. Regular flanges, however, are designed to handle higher pressures and temperatures, making them ideal for demanding environments like oil and gas pipelines.
While Van Stone flanges may have a higher initial cost, their ease of installation and lower long-term maintenance expenses can lead to cost savings over time. Regular flanges are generally more cost-effective for static, high-pressure systems where frequent maintenance is not required.
Van Stone flanges are preferred in dynamic systems, corrosive environments, and applications requiring frequent maintenance. Their design makes them suitable for chemical processing, water treatment, and irrigation systems. Regular flanges are best used in permanent, high-stress industrial piping systems, such as those found in oil and gas plants, where robustness and high-pressure handling are critical.
A Van Stone flange consists of two parts: a Lap Joint Stub End and a separate, rotating backing flange ring. The stub end is welded or glued to the pipe, providing a stable connection point. The backing flange ring, which can rotate freely around the stub end, allows for easy bolt hole alignment during installation. This two-piece design offers enhanced flexibility, facilitating simpler assembly and disassembly, and easing maintenance tasks. Typically, Van Stone flanges are classified as a type of lap joint flange with added rotation capability. They can be installed using butt-weld or slip-on methods, making them adaptable to various piping systems.
Regular flanges, in contrast, are constructed as a single solid piece that is either welded or threaded directly to the pipe. This one-piece design does not permit rotation once installed, requiring precise alignment of bolt holes during installation. Regular flanges are known for providing robust, static connections, which are particularly suitable for high-pressure environments due to their solid construction. The manufacturing process for regular flanges is straightforward, often resulting in cost-effective solutions.
Van Stone flanges can be made from a variety of materials, including stainless steel, carbon steel, and various alloys. This flexibility allows the stub end and the backing flange to be constructed from different materials, optimizing costs and corrosion resistance based on the specific environment. For instance, Schedule 80 PVC versions are used in applications needing chemical resistance and moderate temperatures up to 140°F (60°C). The ability to select different materials for different parts of the flange provides significant advantages, particularly in corrosive or chemically aggressive environments.
Regular flanges are manufactured from a wide range of materials, including carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel. These materials are selected to meet various industrial standards such as ASTM, ANSI, and ASME, ensuring compatibility and reliability. Regular flanges are designed to withstand high strength and resistance to pressure and temperature. The material choice is typically uniform throughout the flange and is selected based on the specific application requirements, focusing on durability and pressure tolerance.
| Feature | Van Stone Flange | Regular Flange |
|---|---|---|
| Installation Flexibility | High – rotating ring allows easy bolt alignment | Low – fixed flange requires precise alignment |
| Maintenance | Easier – two-piece design allows removal without pipe cutting | More difficult – welded/one-piece requires cutting or disassembly |
| Pressure Handling | Generally low to medium pressure applications | Suitable for high-pressure systems |
| Corrosion Resistance | High – material flexibility and option to use corrosion-resistant materials for stub and flange separately | Depends on material used; typically uniform for flange and pipe |
| Temperature Range | Moderate – PVC versions up to ~140°F; metal versions vary by material | Wide range depending on material and design |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for systems requiring frequent maintenance, chemical processing, PTFE-lined piping, marine, and engineered systems | Best for robust industrial piping, high-pressure, and high-temperature applications |
| Cost Factors | Higher due to the two-piece design and customizable materials | Generally lower due to simpler manufacturing and installation |
Van Stone flanges are ideal for systems needing frequent maintenance, like chemical processing plants or PTFE-lined piping, where corrosion resistance is crucial. The rotating ring design simplifies bolt alignment, saving installation time and costs. These flanges are also suitable for applications demanding material flexibility to optimize costs and resist environmental factors. They are commonly used in low to medium pressure applications, including HVAC ductwork and marine piping systems.
Regular flanges excel in high-pressure and high-temperature industrial piping systems where robustness and leak-proof connections are critical. They are chosen for applications prioritizing cost efficiency and durability over ease of maintenance. Regular flanges are suitable for systems conforming to strict international standards that require solid, one-piece flange connections. These flanges are often found in oil and gas pipelines and other high-stress industrial environments.
Van Stone flanges and regular flanges have unique designs that significantly impact their installation processes. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate flange type for a specific application.
Van Stone flanges are two-piece assemblies consisting of a rotating ring and a stub-end. This design allows the rotating ring to move freely around the stub-end, making bolt hole alignment easier during installation. The stub-end is welded or glued to the pipe, providing a stable connection point, while the rotating ring ensures flexibility in aligning the flange with the mating component.
Regular flanges, on the other hand, are typically one-piece designs that are either welded or threaded directly onto the pipe. These flanges do not offer the same flexibility as Van Stone flanges, necessitating precise bolt hole alignment during installation. This can make the installation process more rigid and time-consuming.
The installation process for Van Stone and regular flanges differs mainly in terms of ease and time required.
Van Stone flanges are known for their ease of installation. The rotating ring allows for easy bolt alignment without needing to rotate the entire pipe. This feature significantly reduces the time and effort required for assembly, making the installation process faster and more straightforward. Additionally, the two-piece design can accommodate minor misalignments, further simplifying the installation.
Installing regular flanges can be more challenging due to their one-piece design. Aligning the bolt holes requires precise positioning of the pipe, which can be cumbersome, especially in confined spaces or complex piping systems. This often leads to longer installation times and higher labor costs. The need for precise alignment also means that any misalignment must be corrected by rotating the entire pipe, which can be a labor-intensive process.
Both Van Stone and regular flanges present unique challenges during installation.
A primary challenge with Van Stone flanges is ensuring they are properly aligned and sealed. If the rotating ring is not correctly aligned or if the seal is not adequately secured, there is a potential for leakage. However, the design of Van Stone flanges typically offers enhanced sealing performance, which helps mitigate this risk. Another challenge is that the initial cost of Van Stone flanges can be higher due to their two-piece construction.
Regular flanges can be difficult to install in situations requiring flexibility, such as connecting to equipment with non-standard bolt patterns or in confined spaces. Their robust design, while advantageous for high-pressure applications, can complicate the installation process. Misalignment issues are more challenging to rectify with regular flanges, as they often require significant adjustments or rework, leading to increased installation time and potential downtime.
The specific applications of Van Stone and regular flanges are influenced by their installation characteristics.
Van Stone flanges are ideal for low to medium pressure applications where ease of installation and maintenance is a priority. They are commonly used in industries such as chemical processing, marine engineering, and PTFE lined piping systems. The ability to easily align bolt holes and the flexibility in material selection make them suitable for environments where corrosion resistance is crucial.
Regular flanges are preferred in high-pressure applications where robustness and reliability are paramount. Their solid one-piece construction makes them suitable for a wide range of industrial applications, including oil and gas pipelines, where high-pressure and high-temperature conditions are common. Regular flanges comply with various international standards, ensuring their reliability in demanding environments.
Van Stone flanges are designed for easy maintenance. Their two-piece construction, consisting of a rotating ring and a stub-end, allows for easy disassembly, making inspections and repairs straightforward without the need for specialized tools. This modular design means that inspections and repairs can be conducted without extensive labor. The ability to quickly separate the flange components facilitates faster troubleshooting and replacement of gaskets, reducing downtime significantly.
Key maintenance advantages include:
Regular flanges are harder to maintain because of their one-piece design. These flanges are typically welded or threaded onto the pipe, making disassembly more labor-intensive and time-consuming. Inspections and repairs often require cutting or significant rework, which can lead to longer downtime and higher labor costs.
Challenges in maintaining regular flanges include:
The initial costs of flanges vary based on their design and material.
Long-term costs include maintenance, repairs, and replacements.
Van Stone flanges are ideal for applications needing easy installation and maintenance. They are ideal for:
Regular flanges are preferred in high-pressure applications or environments requiring robust, durable connections. They are commonly used in:
Van Stone flanges and regular flanges differ significantly in design, installation flexibility, material options, and maintenance requirements. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate flange type for specific applications.
Van Stone flanges have a two-piece design with a rotating ring (bolt ring) and a stub-end, allowing the ring to move independently for easier bolt hole alignment during installation. Regular flanges, on the other hand, are typically a single-piece construction, either molded or forged, which requires precise alignment during installation.
The rotating ring of the Van Stone flange allows for easy bolt hole alignment, reducing installation time and effort. This flexibility is particularly beneficial in confined spaces or complex piping layouts, unlike regular flanges that require precise alignment of bolt holes, making installation more challenging and time-consuming.
Van Stone flanges offer the advantage of using different materials for the backing flange and stub-end, optimizing cost and performance based on the specific application. Common materials include stainless steel, carbon steel, and alloys, offering more options than regular flanges which are usually made from a single material.
Van Stone flanges are easier to maintain due to their detachable rotating ring, which simplifies disassembly and reassembly. This feature is beneficial for systems requiring frequent maintenance or inspections. Regular flanges, being a single-piece construction, are more difficult to disassemble once installed, making maintenance more challenging.
Understanding the best uses for each flange type helps in making informed engineering and procurement decisions.
Van Stone flanges are ideal for chemical processing plants where systems require frequent maintenance or disassembly. They are also suitable for low to medium pressure applications where ease of installation and maintenance is valued. In corrosive environments, the ability to use different materials for the backing flange and stub-end optimizes cost and performance. Van Stone flanges are common in PTFE-lined piping systems, which are often used in applications where weight and alignment flexibility are critical. Additionally, they are used in PVC piping systems, particularly Schedule 80 PVC, which offers chemical resistance and durability up to 140°F (60°C).
Regular flanges are suitable for high-pressure applications where strong, leak-proof connections are essential. They are preferred in industrial systems requiring compliance with stringent international standards (ASTM, ANSI, ASME). Regular flanges are ideal for general industrial use, including oil and gas, water, and steam piping systems where durability and cost-effectiveness are priorities. They are also favorable in cost-constrained applications where simpler one-piece flange manufacturing and installation are needed.
| Criteria | Van Stone Flange | Regular Flange |
|---|---|---|
| Ease of Installation | High — rotating ring simplifies bolt alignment | Moderate — requires precise alignment |
| Maintenance | High — easy disassembly and reassembly | Low — fixed and permanent once installed |
| Pressure Rating | Low to medium pressure | Medium to high pressure |
| Material Versatility | Very flexible (different materials for parts) | Material uniformity |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher initial cost, savings in maintenance | Lower initial cost, potentially higher maintenance cost |
| Sealing | Improved sealing due to flexible alignment | Reliable sealing but less flexible |
| Application Scope | Chemical, marine, PTFE lined, corrosive environments | General industry, oil and gas, water systems |
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
Van Stone flanges and regular flanges differ primarily in their design, installation, and application suitability. A Van Stone flange features a two-piece design with a Lap Joint Stub End and a rotating backing flange. This allows for easier alignment of bolt holes during installation, reducing labor time and simplifying maintenance. The rotating backing flange also permits the use of different materials for the stub end and backing flange, optimizing cost and performance in corrosive environments.
In contrast, regular flanges are typically a single-piece unit that is either welded or threaded onto the pipe. This solid construction provides robustness and is more suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature applications, but requires precise alignment during installation and can be more labor-intensive.
Van Stone flanges are preferred in chemical processing, marine, and systems with PTFE-lined pipes due to their ease of maintenance and material flexibility. Regular flanges are better suited for industrial piping systems where durability and high-pressure handling are crucial.
The two-piece design of Van Stone flanges, comprising a rotating flange ring and a stub-end, offers several key benefits for installation and maintenance. This design allows the flange ring to rotate freely around the stub-end, making it easier to align bolt holes with the mating flange without repositioning the entire pipe assembly. This significantly reduces labor time and effort during installation. Additionally, the design often eliminates or reduces the need for welding, streamlining the process and lowering labor costs.
For maintenance, the two-piece design facilitates quick disassembly and reassembly. The flange ring can be removed without disturbing the pipe, ideal for systems requiring frequent maintenance or inspection. This feature minimizes system downtime and reduces maintenance costs. The shorter bolts used in Van Stone flanges are less exposed to environmental factors, decreasing the frequency of maintenance tasks related to corrosion. Overall, the Van Stone flange’s design enhances efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and practicality, particularly in applications where alignment challenges and frequent servicing are common.
Van Stone flanges are preferred in applications where frequent maintenance or disassembly is required, as their two-piece design allows for easy removal and reinstallation without disturbing the pipe alignment. They are ideal for systems with challenging pipe alignment, such as complex ductwork or retrofit projects, due to their rotating backing flange which simplifies bolt hole alignment. Additionally, Van Stone flanges are advantageous in environments with corrosive or aggressive media, as they can be made from materials like PVC or PTFE, offering enhanced corrosion resistance. They are also suitable for applications subject to thermal expansion, as their design accommodates slight movements without compromising the seal. Typical industries where Van Stone flanges are favored include chemical processing, water treatment, irrigation, and food and beverage sectors, where ease of maintenance and flexibility are crucial.
Van Stone flanges and regular flanges are made from various materials, each impacting their performance differently.
Van Stone flanges are versatile in material options, including PVC, stainless steel, carbon steel, PTFE-lined, and PPR (Polypropylene Random Copolymer). PVC is suitable for moderate pressures and temperatures up to 140°F, while stainless steel and carbon steel offer high durability and corrosion resistance, ideal for industrial settings. PTFE-lined flanges enhance chemical resistance, and PPR flanges are excellent for high-temperature and pressure environments. The two-piece design of Van Stone flanges, consisting of a lap joint stub end and a backing flange, allows using different materials for each part, optimizing cost and performance.
Regular flanges are typically made from carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and sometimes PVC. Carbon steel is strong and affordable, suitable for high-pressure applications but prone to corrosion without proper coatings. Stainless steel provides excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for chemical and food processing environments. Aluminum is lightweight and corrosion-resistant but limited to low-pressure applications. Regular flanges are usually single-piece components, which must withstand welding or threading stresses, influencing the choice of material.
Van Stone flanges can be more cost-effective than regular flanges in certain scenarios. The two-piece design of Van Stone flanges, consisting of a rotating ring and a stub-end, allows for easier bolt alignment and installation, reducing labor time and errors. This design also facilitates maintenance and disassembly without the need for cutting the pipe, which can lower long-term maintenance costs.
While the initial material cost for Van Stone flanges may be higher due to the use of two materials (a corrosion-resistant stub-end and a less expensive backing flange), the overall lifecycle cost can be lower in systems requiring frequent maintenance or operating in confined spaces. This makes Van Stone flanges advantageous in dynamic or maintenance-heavy environments.
On the other hand, regular flanges, being single-piece constructions, are generally more cost-effective for high-pressure applications and static systems where minimal maintenance is required. They offer robust and secure connections, making them suitable for high-pressure environments.

