Imagine a world where every electrical system is a ticking time bomb, ready to unleash dangerous currents at any moment. This scenario highlights the crucial role of pipe earthing in safeguarding our homes and workplaces. But what exactly is pipe earthing, and why is it so vital for electrical safety? In this article, we’ll demystify the concepts behind pipe earthing, delve into its working principles, and explore its importance in protecting us from electrical hazards. Whether you’re a complete novice or just looking to brush up on the basics, we’ll guide you step-by-step through the installation process, ensuring you have all the knowledge needed to implement this essential safety measure. Ready to discover how pipe earthing can make your electrical systems safer? Let’s dive in.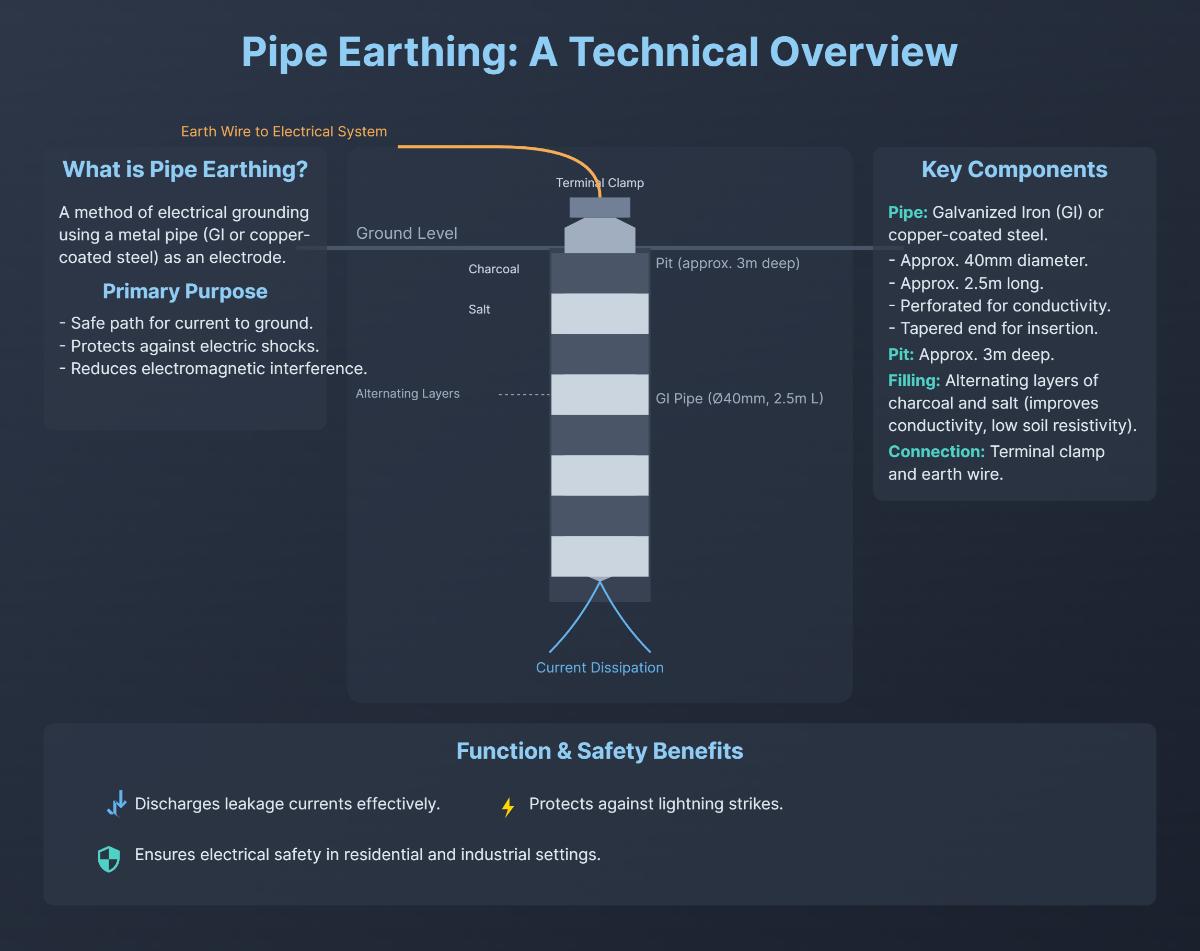
Pipe earthing is a crucial method used to ensure electrical safety in various installations, including residential, commercial, and industrial settings. This technique involves the use of a metal pipe, typically galvanized iron or copper-coated steel, which is buried vertically in the ground. The primary function of pipe earthing is to provide a safe path for electrical fault currents, directing them into the earth to prevent electrical hazards such as shocks or fires.
Anyone involved in electrical work, from beginners to experienced professionals, needs to understand pipe earthing. Here are a few key reasons why knowledge of pipe earthing is vital:
Pipe earthing plays a significant role in maintaining electrical safety by providing a reliable grounding system that protects people and equipment from electrical faults. This protection is crucial in preventing accidents that could result from faulty electrical systems.
Many regions have specific rules for electrical installations, including earthing system requirements. Familiarity with pipe earthing ensures that installations comply with these standards, avoiding legal issues and ensuring safe operations.
Pipe earthing is known for its cost-effectiveness. Materials like galvanized iron pipes, charcoal, and salt are relatively inexpensive. Additionally, the installation process is straightforward, requiring minimal labor and maintenance.
One of the advantages of pipe earthing is its adaptability to various soil conditions. The method can be used effectively even in areas with poor natural soil conductivity, thanks to the design elements that retain soil moisture and enhance conductivity.
Pipe earthing offers several benefits that make it a preferred choice for many electrical installations:
These benefits highlight why pipe earthing is crucial for creating safe and effective electrical systems. As electrical safety awareness grows and regulatory standards evolve, the knowledge and application of pipe earthing become increasingly crucial for ensuring safe and compliant installations.
Pipe earthing is a grounding method used in electrical systems to ensure safety and prevent electrical hazards. This technique involves using a metal pipe, typically made from galvanized iron or copper-coated steel, which is buried vertically in the ground. The purpose of pipe earthing is to provide a low-resistance path for the dissipation of fault currents, surges, or leakage currents into the earth.
Pipe earthing works by connecting the electrical system directly to the ground, allowing excess current from faults to safely dissipate into the earth. This prevents potential hazards such as electric shocks, equipment damage, and fire risks.
The main component of the pipe earthing system is a galvanized iron pipe, typically 2.5 meters long with a diameter of 40 to 50 mm. Galvanized iron is durable and cost-effective, although copper-coated steel or pure copper pipes can also be used for their higher conductivity and longevity.
The earthing pipe often has perforations along its length to enhance contact with the soil and improve conductivity. The bottom end of the pipe is usually tapered to facilitate easier insertion into the ground. A terminal clamp is provided at the top of the pipe to secure the earthing wire.
The installation of a pipe earthing system involves several key steps:
Pipe earthing is vital for maintaining electrical safety in various settings, providing a reliable path for fault currents and protecting both people and equipment from potential hazards. This method’s effectiveness, cost-efficiency, and adaptability to different soil conditions make it a popular choice for residential, commercial, and industrial installations.
Pipe earthing creates a low-resistance path for electrical currents, ensuring that any fault currents or leakage currents are safely conducted into the earth. This process protects both people and equipment from potential electrical hazards.
The primary component is a galvanized iron (GI) pipe, which acts as the earth electrode. This pipe typically has multiple holes along its length to enhance contact with the surrounding soil and improve conductivity. The pipe is buried vertically in the ground, with its tapered end reaching deep into the earth to ensure stable grounding.
To improve the soil’s conductivity, layers of charcoal and salt are placed around the pipe. Charcoal helps maintain soil moisture, while salt enhances the soil’s electrical conductivity. Together, these materials create an environment that facilitates the efficient dissipation of electrical currents.
An earth wire connects the electrical system to the earthing pipe. This wire provides a direct path for any fault currents to travel from the electrical system into the ground, ensuring safe dissipation.
Galvanized iron (GI) pipes are commonly used in pipe earthing systems due to their durability and effectiveness. These pipes are made of iron coated with a layer of zinc to protect against corrosion.
Copper is used in two forms in some pipe earthing systems due to its superior electrical conductivity and resistance to corrosion:
Charcoal and salt are used as filling materials around the earthing pipe to improve soil conductivity and reduce earth resistance. Charcoal helps retain moisture in the soil, which is crucial for maintaining low resistance. By retaining moisture, charcoal enhances the soil’s ability to conduct electrical currents. Salt lowers the resistivity of the soil by attracting and retaining moisture. When mixed with charcoal, salt significantly improves the overall conductivity of the soil around the earthing pipe.
A watering funnel is installed at the top of the earthing pipe to facilitate periodic watering, ensuring consistent soil moisture and effective grounding. The earth wire connects the top end of the earthing pipe to the electrical installation, providing a reliable path for fault currents to travel into the ground.
The earth pit, which houses the earthing pipe, is usually a small square structure built on the ground surface. It is often lined or supported with materials to maintain structural integrity and ensure effective grounding.
When considering the best earthing method for an electrical system, it’s important to compare the various options available. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice often depends on specific site conditions and requirements. Here, we will compare pipe earthing with plate earthing and chemical earthing.
Plate earthing involves burying a flat metal plate, typically made of copper or galvanized iron, in the ground. This method provides a large surface area for contact with the soil, which can be beneficial in certain conditions.
Chemical earthing involves the use of chemical compounds to enhance the conductivity of the soil around the earthing electrode. This method is particularly useful in areas with very high soil resistivity.
| Method | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pipe Earthing | Uses a buried metal pipe (GI or copper) | Cost-effective, simple installation | Less effective in very dry or rocky soils |
| Plate Earthing | Utilizes a buried metal plate | Larger contact surface, effective in high resistivity soils | Higher cost, complex installation |
| Chemical Earthing | Uses chemicals to enhance soil conductivity around the electrode | Effective in poor soil conditions, stable performance | Higher cost, requires maintenance |
Each method has its place depending on the specific conditions and requirements of the site. Pipe earthing is generally favored for its simplicity and cost-effectiveness, while plate and chemical earthing offer solutions for more challenging soil conditions.
To begin the installation of a pipe earthing system, you need to prepare the earthing pit. Follow these steps to ensure a proper setup:
The next step involves installing the galvanized iron (GI) pipe into the pit:
To enhance the conductivity around the earthing pipe, you’ll need to add layers of charcoal and salt:
The final step involves connecting the electrical system to the earthing pipe:
Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure the effectiveness of the pipe earthing system:
By following these steps, you can effectively install a pipe earthing system, ensuring a safe and reliable grounding solution for your electrical installations.
Pipe earthing is crucial for electrical safety, providing a reliable path for electrical currents to safely flow into the ground. This significantly reduces the risk of electrical shocks and fires, especially in the event of lightning strikes or faults in the electrical system. The secure dissipation of excess electrical charges helps prevent dangerous situations, protecting both people and equipment.
One key advantage of pipe earthing is its durability, especially when using galvanized iron (GI) pipes, which have a zinc coating that provides excellent corrosion resistance. This corrosion resistance is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the earthing system over time, even in harsh environmental conditions.
Pipe earthing systems are designed to require minimal maintenance. The primary task involves keeping the soil around the pipe moist to ensure effective conductivity. This can be easily managed by periodically watering the area around the earthing pit. Its easy maintenance makes pipe earthing appealing for both homes and industries.
Using charcoal and salt around the earthing pipe improves soil conductivity. Charcoal helps retain moisture, while salt lowers the resistivity of the soil, enhancing overall conductivity. This combination ensures that electrical charges are efficiently dissipated into the earth, maintaining the effectiveness of the earthing system.
Pipe earthing is easy to install by burying a GI pipe vertically in a pit filled with charcoal and salt layers, making it adaptable to various applications and soil conditions. Additionally, pipe earthing can be scaled to fit different requirements, making it suitable for both small residential setups and large industrial installations.
Earthing, in general, is vital for electrical safety. It provides a stable reference point for electrical systems, ensuring that stray currents are safely directed into the ground. This reduces the risk of electrical overloads, fires, and shocks, creating a safer operating environment for electrical equipment. Proper earthing is a fundamental aspect of electrical safety protocols and compliance with regulatory standards.
By understanding the importance and benefits of pipe earthing, one can appreciate its role in creating safe and efficient electrical systems. The method’s reliability, durability, and ease of maintenance make it a preferred choice for grounding in various environments.
Understanding the common issues that can arise with pipe earthing systems is essential for maintaining their effectiveness and safety.
Corrosion of electrodes is a common issue in pipe earthing systems. The metal pipes used in earthing can corrode over time, especially if the soil is highly acidic or alkaline. Corrosion can significantly reduce the conductivity of the electrode, leading to poor grounding performance.
Soil with low moisture content or high resistivity can hinder the earthing system’s performance, but adding materials like charcoal and salt around the earthing pipe can improve conductivity.
Soil moisture is essential for effective grounding. Dry soil can lead to increased resistivity and poor grounding performance.
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the longevity and effectiveness of pipe earthing systems.
Regular inspections can help detect issues early and keep the earthing system in optimal condition.
Testing the resistance of the earthing system is crucial to ensure it is functioning correctly.
Regularly inspect the connections between the earth wire and the earthing pipe to ensure they are secure and free from corrosion, which is vital for effective grounding.
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
Pipe earthing is a method of electrical grounding that uses a metal pipe, typically made of galvanized iron (GI) or copper-coated steel, as the earthing electrode. The primary purpose of pipe earthing is to provide a safe path for electrical currents to dissipate into the ground, thereby protecting against electrical shocks and reducing electromagnetic interference.
In a typical pipe earthing setup, a GI pipe around 40 mm in diameter and 2.5 meters long, perforated along its length, is vertically buried in a pit about three meters deep. The perforations enhance conductivity, and the tapered end facilitates easier insertion into the ground. The pit is filled with alternating layers of charcoal and salt to improve conductivity and maintain low soil resistivity.
The top end of the pipe is connected to an earth wire via a terminal clamp, allowing the electrical system to link safely to the earth. This setup discharges leakage currents and protects against lightning strikes, ensuring electrical safety in residential and industrial settings.
Pipe earthing is vital for electrical safety because it provides a reliable path for fault currents to safely dissipate into the ground. This method of grounding involves using a metal pipe, typically galvanized steel, to create a low-resistance connection with the earth. By directing excess electrical charges away from people and equipment, pipe earthing prevents electrical shocks and reduces the risk of fires. Additionally, it enhances the conductivity of the grounding system, ensuring stable and efficient dispersion of electrical currents. This system also complies with electrical codes and standards, which helps in maintaining safe electrical installations and avoiding legal issues. Overall, pipe earthing is a cost-effective and low-maintenance solution that significantly improves electrical safety.
Pipe earthing is installed through a series of carefully planned steps to ensure effective grounding. First, select a suitable location for the earthing pit, which should be at least 1.5 meters away from any buildings to minimize interference and ensure safety. Next, dig a pit, typically around 3 meters deep, although the depth may vary depending on local soil conditions.
Once the pit is ready, place a galvanized iron (GI) pipe vertically into the pit. The top end of the pipe should remain accessible for future connections. To enhance conductivity, fill the pit with layers of charcoal and salt, which help retain moisture and improve soil conductivity. This mixture aids in the efficient dissipation of electrical current.
Then, connect a conductor wire to the top end of the pipe, linking it to the electrical system. For high-tension systems, an 8SWG wire is used, while a 10SWG wire is suitable for low-tension systems. Regular maintenance is necessary to ensure the soil around the earthing pit remains moist, preserving low resistivity and maintaining the effectiveness of the earthing system.
Pipe earthing uses several key materials to ensure effective grounding and electrical safety. The primary material is a galvanized iron (GI) pipe, which is coated with zinc to resist corrosion and provide long-term durability. This pipe serves as the main conductor for electrical charges, dissipating them into the ground efficiently due to its high conductivity. Additionally, charcoal and salt are used in the earthing pit to enhance soil conductivity. These materials help maintain moisture and reduce soil resistivity, improving the overall effectiveness of the earthing system. An earthing electrode, typically made of conductive material, and an earth wire are also essential components. The earth wire connects the electrical system to the earthing pipe, ensuring a continuous path for electrical currents.
An earthing electrode is a conductive material, often made of metal such as copper or galvanized iron, that is buried in the ground to create a direct electrical connection between an electrical system and the earth. Its primary function is to safely discharge excess or fault electrical currents into the ground, thereby protecting people and equipment from electric shocks, electrocution, and electrical damage.
In the context of pipe earthing, the earthing electrode is typically a metal pipe made of galvanized iron or mild steel. This pipe is installed vertically into the earth at a specified depth. The installation process involves driving or burying the pipe into the ground, ensuring that it makes good contact with the surrounding soil, which is often enhanced by adding materials like charcoal and salt to improve conductivity. The electrical system’s earth wire is then securely connected to the pipe, providing a continuous conductive path for fault currents to safely dissipate into the ground. This method is effective, cost-efficient, and reliable, especially in areas with moist soil conditions, which enhance the grounding effectiveness.
Common issues with pipe earthing include high costs, environmental concerns, soil conditions, and corrosion. The use of durable materials like galvanized steel or copper makes the system expensive. Additionally, the mining and processing of these metals can have environmental impacts. The effectiveness of pipe earthing heavily depends on soil conditions; dry or rocky soil can lead to high resistance, making the system less reliable. Corrosion of the electrodes over time can also compromise the system’s integrity.
Maintenance tips for pipe earthing involve regular checks and actions to ensure the system remains effective. Inspect the electrodes for signs of corrosion and address any issues promptly. Verify that all connections between the pipe and electrical system are secure and not affected by environmental factors. Monitor soil conditions and replenish materials like charcoal and salt as needed to maintain optimal conductivity. Maintain a distance of at least 2 meters between multiple electrodes to prevent interference and ensure effective earthing. By following these maintenance practices, the reliability and efficiency of pipe earthing systems can be sustained.

