Imagine a world where the intricate network of pipes beneath our buildings runs smoothly, efficiently, and safely. That’s where pipe sleeves come into play. If you’ve ever wondered what these essential components are, why they’re critical, and how they impact modern construction, you’re in the right place. In this technical deep dive, we’ll unravel the complexities of pipe sleeves, exploring their primary functions such as protection, insulation, and structural support. We’ll delve into the various materials used to manufacture them, including metal, plastic, and composite options, evaluating the pros and cons of each. Plus, we’ll examine their vital role in plumbing, HVAC systems, and electrical conduits, supported by real-world examples. Ready to uncover everything you need to know about pipe sleeves? Let’s get started and see how these unsung heroes keep our infrastructure safe and sound.
A pipe sleeve is a cylindrical component used to protect and support pipes as they pass through various structures such as walls, floors, and ceilings. It acts as a barrier between the pipe and the surrounding material, ensuring the pipe’s integrity and preventing damage. Pipe sleeves are integral to piping systems in residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
One of the primary functions of a pipe sleeve is to protect the pipe from physical damage and environmental factors. When pipes pass through walls or floors, they can be damaged by abrasion, impacts, and corrosion. Pipe sleeves provide a protective layer that shields the pipe, thereby extending its lifespan and maintaining its functionality. This protection is crucial in environments where pipes are exposed to mechanical stress or corrosive substances.
Pipe sleeves also serve as an insulating barrier. This insulation helps keep the fluid in the pipes at the right temperature and reduces noise. In HVAC systems, for example, pipe sleeves help maintain the desired temperature of the fluid within the pipes by minimizing heat exchange with the surrounding environment. Similarly, in plumbing systems, they can reduce noise caused by water flow and pressure changes.
Providing structural support is another critical function of pipe sleeves. They help distribute the load and stresses that pipes might encounter, particularly at points where pipes penetrate walls, floors, or ceilings. This support ensures that the pipes remain stable and secure, preventing potential damage or failure. In industrial settings, where pipes carry heavy loads or face significant vibrations, this support is crucial for system integrity.
Pipe sleeves are designed to withstand harsh conditions and last a long time, using materials like steel, plastic, or composites chosen for their durability. This ensures that the sleeves can protect the pipes effectively throughout their service life.
Some pipe sleeves are designed to offer flexibility, accommodating the natural expansion and contraction of pipes due to temperature variations. This flexibility prevents undue stress on the pipes and the surrounding structures, minimizing the risk of damage.
Ease of installation is a critical characteristic of pipe sleeves. They are easy to fit around pipes and secure in place without complex tools, reducing labor costs and ensuring quick integration into piping systems.
Rigid pipe sleeves are made from materials like steel or PVC and provide robust protection and support. They are typically used in applications where the pipes are subject to high mechanical stress or where a high level of durability is required.
Flexible pipe sleeves are made from materials such as rubber or flexible plastics. They are used in applications where the pipes need to accommodate movement, such as in seismic zones or areas with significant thermal expansion and contraction.
Insulated pipe sleeves are designed to provide thermal or acoustic insulation. They are commonly used in HVAC systems to maintain temperature control and reduce noise levels. These sleeves are often made from materials with high insulating properties, such as foam or fiberglass.
Pipe sleeves are made from various materials like metals, plastics, and composites, selected based on application-specific requirements. The choice of material is influenced by factors such as corrosion resistance, durability, mechanical strength, and cost considerations.
Carbon Steel Carbon steel is a popular choice for pipe sleeves due to its high strength and durability. It is suitable for high-pressure applications and can withstand significant mechanical stress.
Stainless Steel Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for applications involving harsh chemicals or exposure to moisture.
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
Polyethylene is known for its high strength-to-density ratio, making it a durable and flexible option for pipe sleeves.
Fiber-Reinforced Polymers (FRPs)
Choosing the right material for pipe sleeves involves weighing the advantages and disadvantages based on the application requirements.
Carbon Steel:
Stainless Steel:
PVC:
Polyethylene:
Composite Materials (FRPs):
When selecting a material for pipe sleeves, several criteria should be considered:
The comparison table offers a clear overview of the key attributes to consider when choosing the right material for pipe sleeves:
| Material | Strength | Corrosion Resistance | Cost | Temperature Resistance | Application Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | High | Moderate | Low | High | Construction, Mining, Pipelines |
| Stainless Steel | High | High | High | Very High | Chemical Processing, Food Industry |
| PVC | Low | High | Low | Moderate | Residential, Commercial Piping |
| Polyethylene | Moderate | High | Low | Low to Moderate | Underground Installations |
| FRPs | Very High | Very High | High | High | Aerospace, Offshore Drilling |
By understanding the properties and applications of each material, one can make informed decisions to ensure optimal performance and longevity of piping systems.
Pipe sleeves are essential components in construction, providing critical protection, insulation, and support for various piping systems. Their applications span across multiple areas in the construction industry, ensuring the integrity and efficiency of systems such as plumbing, HVAC, and electrical conduits.
In plumbing systems, pipe sleeves serve several important functions:
Pipe sleeves protect plumbing pipes as they pass through walls, floors, and ceilings. They act as a barrier to prevent abrasion and damage from construction materials. This protection is crucial for the longevity and functionality of plumbing systems.
By securely housing pipes, sleeves help prevent leaks and water damage. They create a defined path for pipes, reducing the risk of movement and stress that could lead to leaks. This is especially important in multi-story buildings where water damage can have extensive consequences.
Pipe sleeves are vital in HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems for the following reasons:
Pipe sleeves in HVAC systems help maintain the temperature of the fluids being transported. Insulated pipe sleeves minimize heat loss or gain, improving system efficiency. This is critical for both heating and cooling applications, ensuring energy efficiency and consistent performance.
HVAC systems can generate significant vibration and noise. Pipe sleeves help dampen these vibrations, reducing noise transmission through the building structure. This contributes to a quieter and more comfortable environment.
When it comes to electrical systems, pipe sleeves provide necessary protection and organization:
Pipe sleeves offer electrical insulation, protecting wires and cables from external damage. This is essential for preventing electrical shorts and ensuring safe operation of electrical systems.
In the event of a fire, fire-resistant pipe sleeves help prevent the spread of flames through penetrations in walls and floors. This is crucial for maintaining the integrity of fire barriers and complying with building safety codes.
Pipe sleeves are utilized in various specific applications within the construction industry:
When pipes need to pass through structural elements such as beams or columns, pipe sleeves ensure that the integrity of these structures is maintained. They provide a clear passage for the pipes, preventing damage to both the pipes and the structure.
In regions prone to seismic activity, flexible pipe sleeves are used to accommodate movement and prevent damage during earthquakes. These sleeves let pipes move slightly without breaking, ensuring critical systems keep operating.
In environments where pipes are exposed to corrosive elements, such as in chemical plants or coastal areas, pipe sleeves made from corrosion-resistant materials protect the pipes. This extends the lifespan of the piping systems and reduces maintenance costs.
In a high-rise building project, pipe sleeves were used extensively to protect plumbing pipes passing through multiple floors. The sleeves provided abrasion resistance, preventing leaks and ensuring a reliable water supply to all floors. Additionally, the use of fire-resistant sleeves at floor penetrations enhanced the building’s fire safety.
In an industrial facility, pipe sleeves were implemented in the HVAC system to maintain fluid temperatures and reduce energy consumption. The sleeves’ insulating properties minimized heat loss, improving the system’s efficiency. Vibration-dampening sleeves also contributed to a quieter working environment, enhancing employee comfort and productivity.
Pipe sleeves play a crucial role in protecting pipes from corrosion and abrasion. Corrosion can severely compromise the integrity of pipes, leading to leaks and potential system failures. Pipe sleeves made of stainless steel, carbon steel, or PVC prevent corrosion by creating a barrier that shields the pipe from corrosive elements. Additionally, pipe sleeves protect against abrasion caused by external factors such as wind, rain, and ice. This protection ensures that pipes remain structurally sound, even in harsh environments, thereby extending their lifespan and maintaining their functionality.
Fire safety is a critical consideration in the design and implementation of pipe sleeves. Fire-rated sleeves are specifically engineered to protect pipes during fires, ensuring they remain functional and maintain the structural integrity of the piping system. These sleeves must comply with stringent fire safety regulations and building codes to prevent the spread of flames and smoke through pipe penetrations in walls and floors. Compliance with these standards is essential to ensure the safety of occupants and the protection of property. Regular inspections and maintenance of fire-rated pipe sleeves are necessary to ensure they continue to perform effectively over time.
Managing thermal stress is another important safety consideration for pipe sleeves. Pipes often undergo thermal expansion and contraction due to temperature fluctuations. Pipe sleeves facilitate this movement by allowing the pipe to expand and contract without causing damage. This is particularly important in systems that transport hot or cold fluids. Excessive thermal stress can lead to pipe deformation or failure. Additionally, pipe sleeves can provide thermal insulation, helping to maintain the desired temperature of the fluids within the pipes and preventing issues such as condensation.
Pipe sleeves offer mechanical protection and support, ensuring that pipes can withstand physical forces without damage. They shield pipes from mechanical stress, such as pressure and impact, which is particularly important in environments where pipes are exposed to heavy loads or vibrations. By providing additional structural support, pipe sleeves help to distribute mechanical stresses evenly, reducing the risk of pipe deformation or failure. This support is crucial in maintaining the integrity of piping systems, especially in industrial settings.
Proper installation and maintenance of pipe sleeves are vital for ensuring their effectiveness and safety. The correct sizing and material selection are critical to ensure that the sleeve functions correctly without compromising the pipe’s integrity. During installation, it is essential to follow best practices to secure the sleeve properly and prevent any gaps or misalignments. Pipe sleeves facilitate easy access to pipes for inspection, repair, or replacement, enhancing safety during maintenance operations. This accessibility helps to quickly address any issues that may arise, minimizing downtime and ensuring the continuous operation of the piping system.
Pipe sleeves contribute to environmental protection by preventing leaks and protecting against chemical exposure. By creating a secure seal around pipes, sleeves prevent moisture buildup and leakage, which reduces environmental risks and potential water damage. In industrial settings, pipe sleeves protect against chemical degradation by preventing direct contact between corrosive substances and structural components. This protection keeps piping systems intact and protects the environment from harmful chemicals.
Investing in pipe sleeves offers cost-effectiveness and long-term benefits by extending the lifespan of piping systems and reducing maintenance costs. Pipe sleeves protect against common issues such as corrosion, abrasion, and thermal stress, which can lead to premature pipe failure. By preventing these problems, pipe sleeves minimize the need for costly repairs and downtime, ensuring the continuous operation of the piping system. The long-term benefits of using pipe sleeves include enhanced system reliability, reduced maintenance expenses, and improved operational efficiency.
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
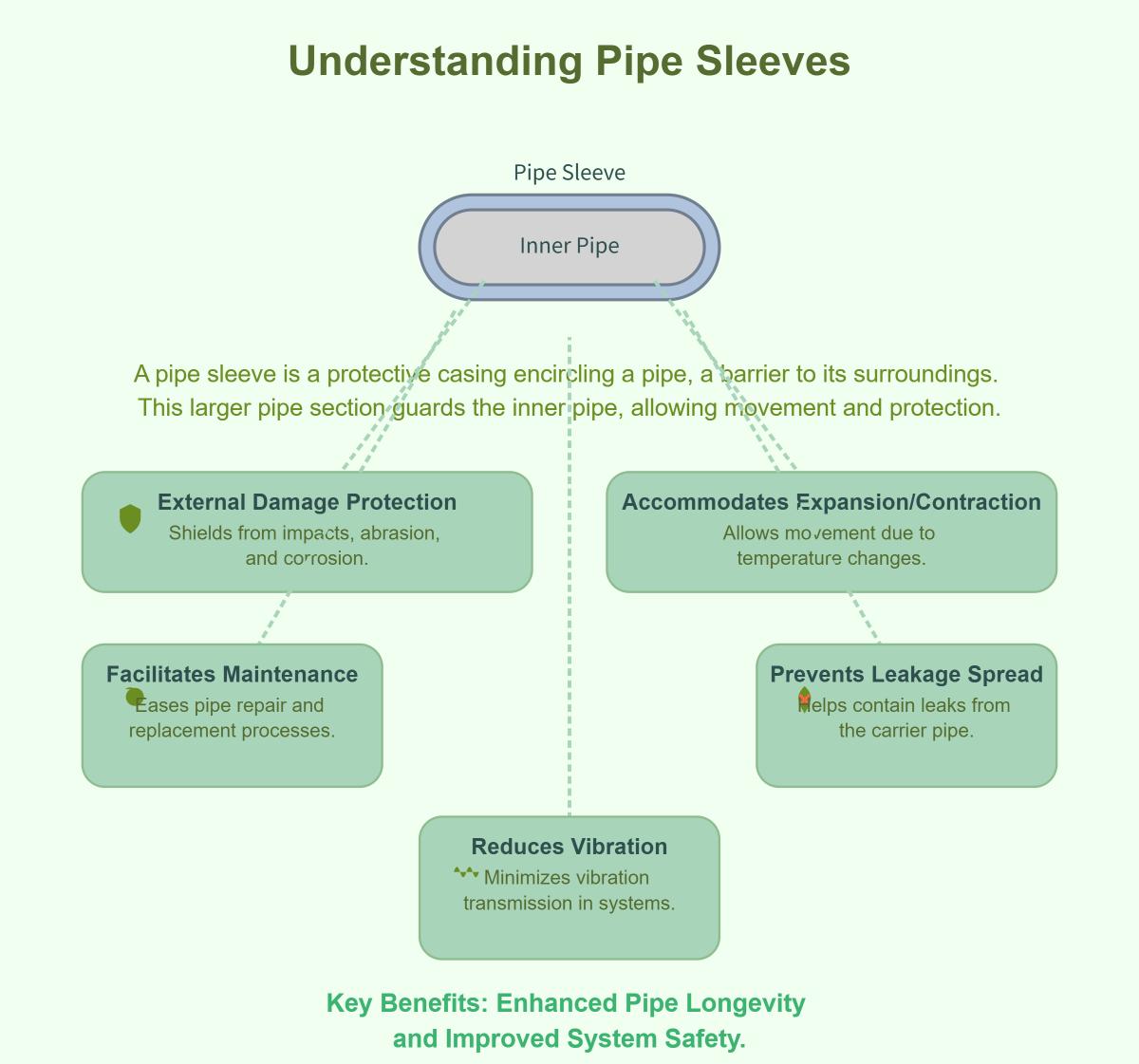
A pipe sleeve is a protective casing encircling a pipe, acting as a barrier between the pipe and its surroundings. It’s a larger pipe section safeguarding the inner pipe from external loads and allowing movement. Its primary functions include protecting against external damage like impacts, abrasion, and corrosion; accommodating expansion and contraction due to temperature changes; facilitating maintenance and replacement; preventing leakage; and reducing vibration transmission in piping systems. These functions enhance pipe longevity and system safety.
Pipe sleeves are crafted from various materials, each selected based on specific application requirements. Common materials include:
Material selection depends on factors like corrosion resistance, flexibility, structural integrity, cost, and thermal insulation needs.
Pipe sleeves are used in construction to provide protection and structural support for pipes as they pass through walls, floors, or other structural elements. They serve multiple functions, including shielding pipes from external damage such as abrasion, corrosion, and physical impact. By preventing direct contact with materials like concrete or masonry, pipe sleeves help maintain the integrity and longevity of the piping systems.
Additionally, pipe sleeves allow for thermal expansion and contraction of pipes, which is crucial for preventing damage due to temperature changes. They also facilitate easier maintenance and replacement by providing a clear passage through structures, thus avoiding the need to disturb the surrounding materials. Furthermore, pipe sleeves help maintain leak integrity and reduce the transmission of vibrations, which can minimize noise and potential structural damage.
Pipe sleeves offer numerous advantages in piping applications. They protect pipes from external damage like impacts and abrasion, and guard against corrosion, especially in industrial settings. They accommodate thermal expansion and contraction, preventing damage to the surrounding structure. Rubber and insulated sleeves reduce vibration and noise. Sleeves prevent leaks, and fire – rated ones enhance fire safety and ensure code compliance. They simplify maintenance and repair, as pipes can be inspected or replaced without disturbing the surroundings. With a variety of materials available, they can be tailored to specific needs, providing cost – effective solutions and a safer working environment.
Yes, there are specific standards for pipe sleeves in construction. These standards ensure that pipe sleeves effectively maintain fire-resistance ratings and structural integrity when pipes penetrate walls, floors, or ceilings. For materials, steel and cast iron sleeves must conform to standards like ASTM A53/A53M and ASTM A74, respectively. Fire-rated pipe sleeves need to comply with building codes such as the International Building Code (IBC) and guidelines from the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA). These codes ensure that sleeves maintain the fire-resistance of the structures they penetrate. Additionally, installation practices require that sleeve diameters be larger than the pipe to accommodate insulation and expansion, and sleeves must be installed flush with surfaces to meet local building codes. Regular inspections are also necessary to ensure ongoing compliance and safety.
Pipe sleeves contribute significantly to fire safety by providing a protective barrier around pipes that pass through structural elements like walls, floors, and ceilings. These sleeves are especially crucial in maintaining the fire resistance and integrity of these barriers. Fire-rated pipe sleeves are designed to seal gaps around pipes, preventing the spread of smoke, heat, and flames during a fire. This containment is vital for ensuring that fire does not easily propagate through building compartments, which allows for safer evacuation and reduces Furthermore, using fire-rated pipe sleeves helps buildings comply with stringent fire safety regulations, which is essential for maintaining insurance standards and avoiding penalties. In industrial settings, these sleeves protect critical piping systems from extreme heat, ensuring that essential infrastructure remains operational during emergencies. Overall, pipe sleeves enhance fire safety by maintaining structural integrity, preventing flame spread, and ensuring regulatory compliance.

